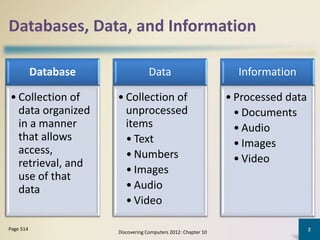
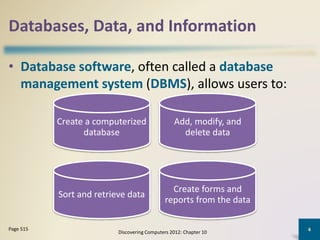
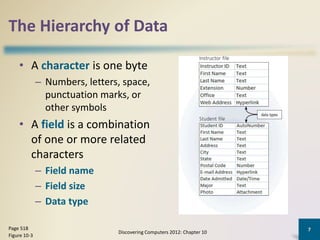
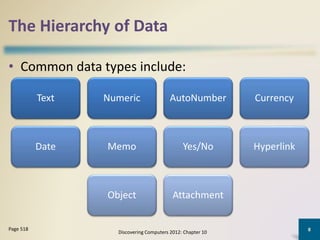
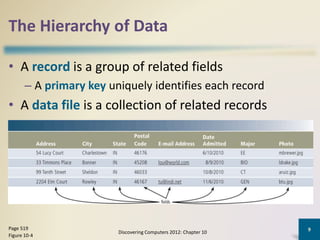
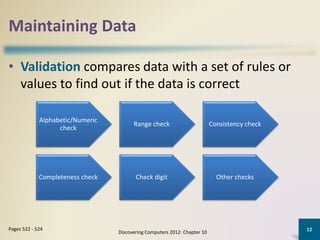
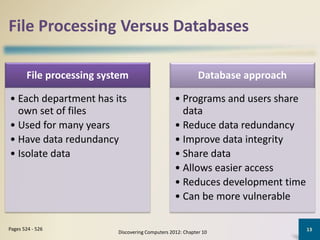
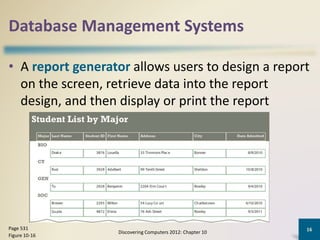
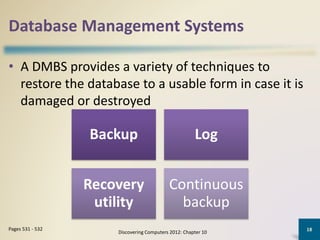
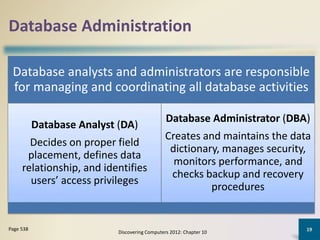
Databases organize data into collections that can be easily accessed, managed, and shared. A database management system allows users to create, modify, and retrieve data from a database. It also provides tools like query languages and report generators. Database administrators ensure the security and integrity of the database through techniques such as backups, access controls, and change management.