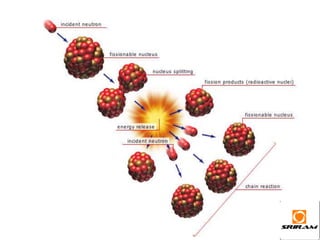
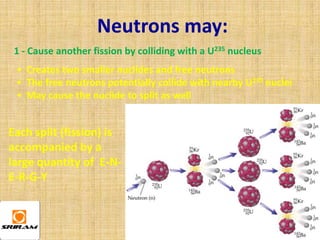
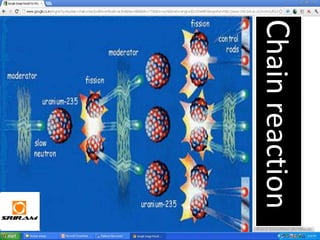
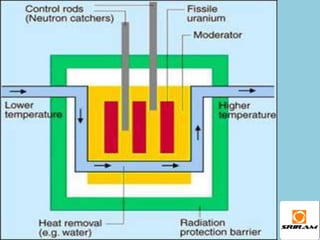
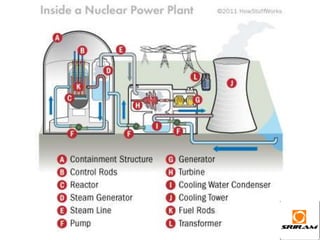
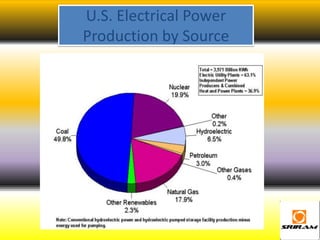
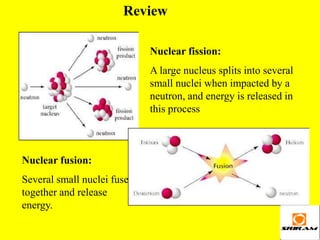
The document provides an overview of nuclear reactions, specifically focusing on nuclear fission and fusion. It explains the processes involved in fission, including the splitting of heavy atomic nuclei like uranium-235 when bombarded by neutrons, leading to a release of energy. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and disadvantages of nuclear power, highlighting its energy production potential and challenges related to radioactive waste and plant safety.