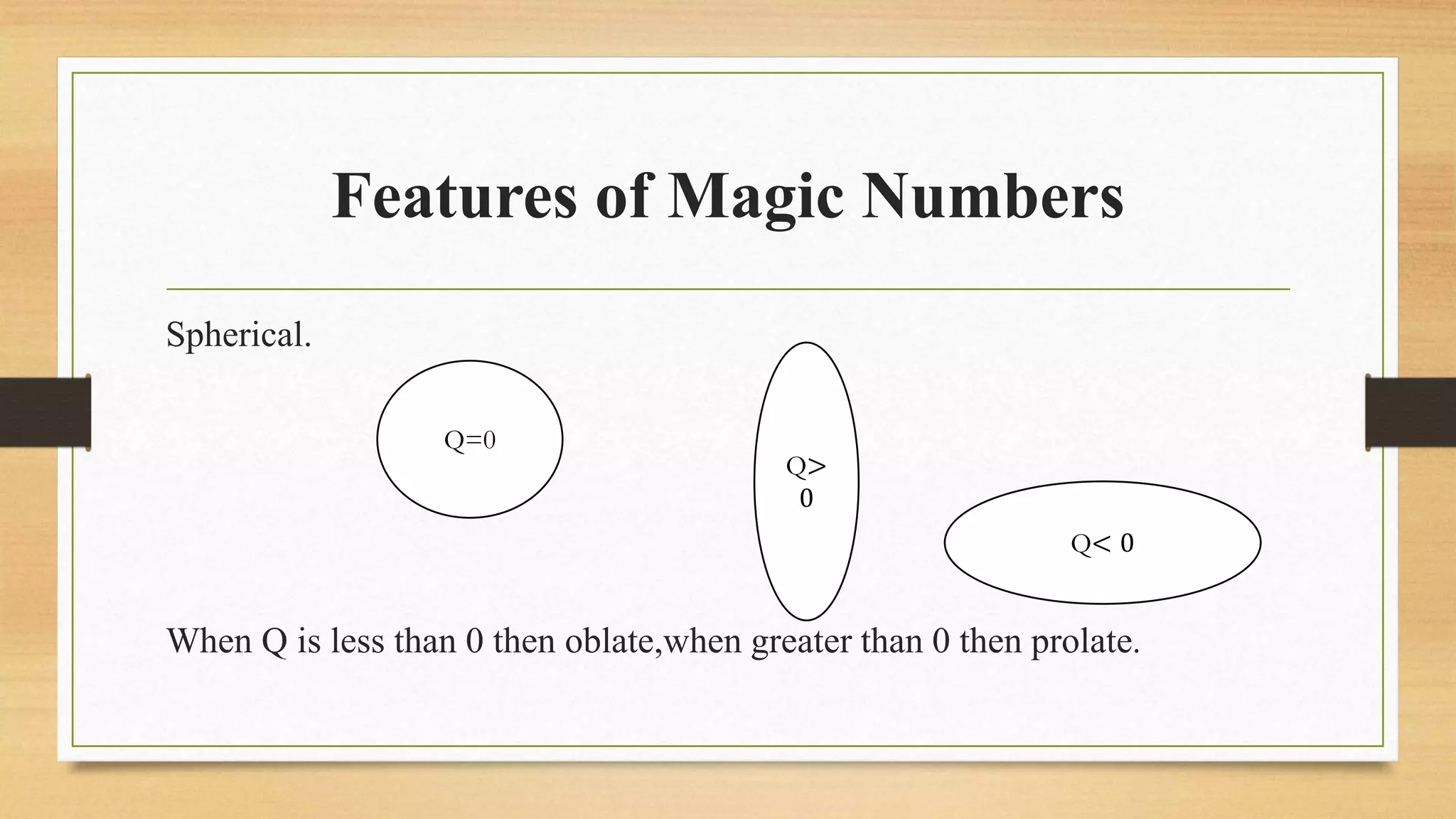
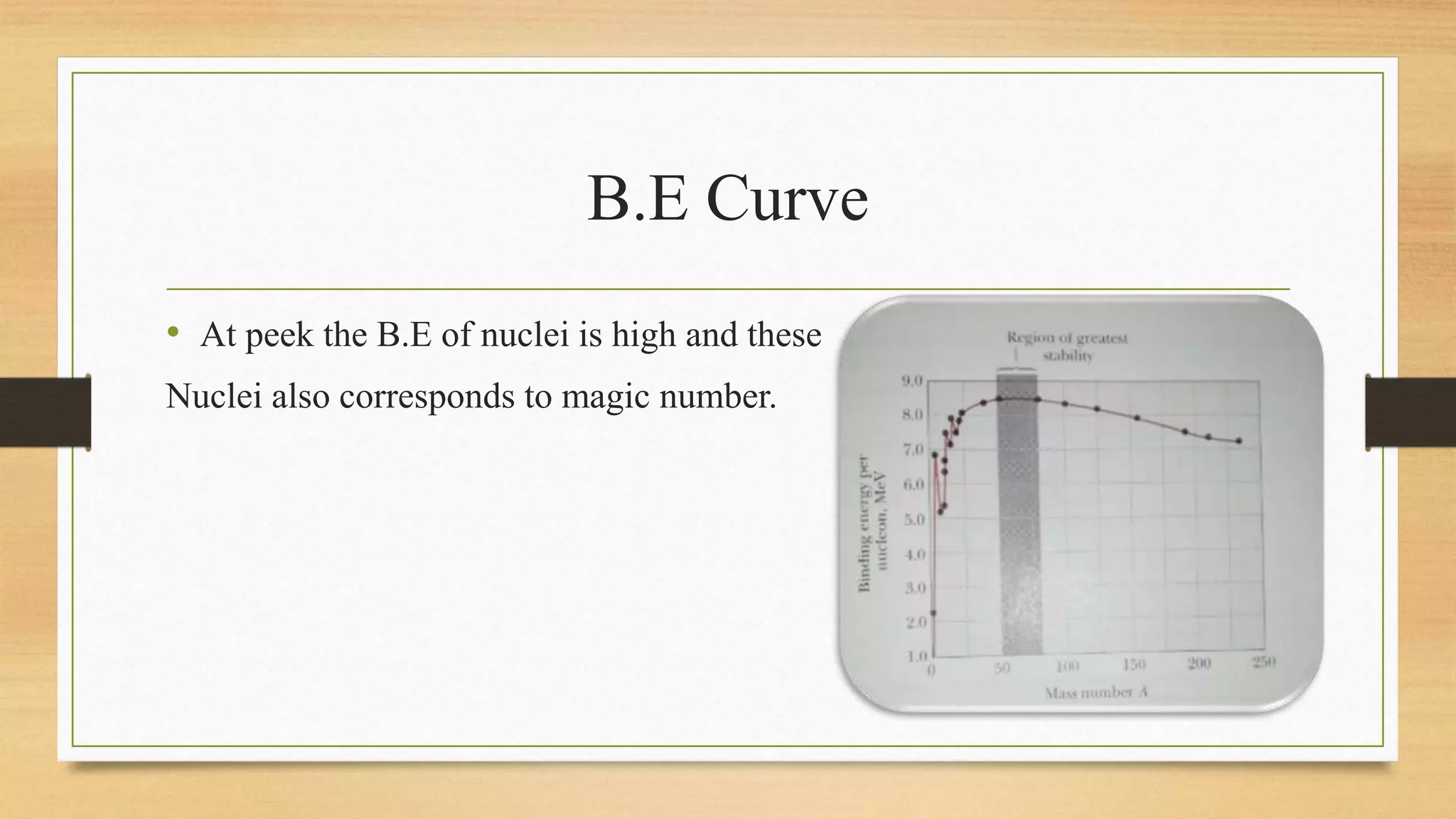
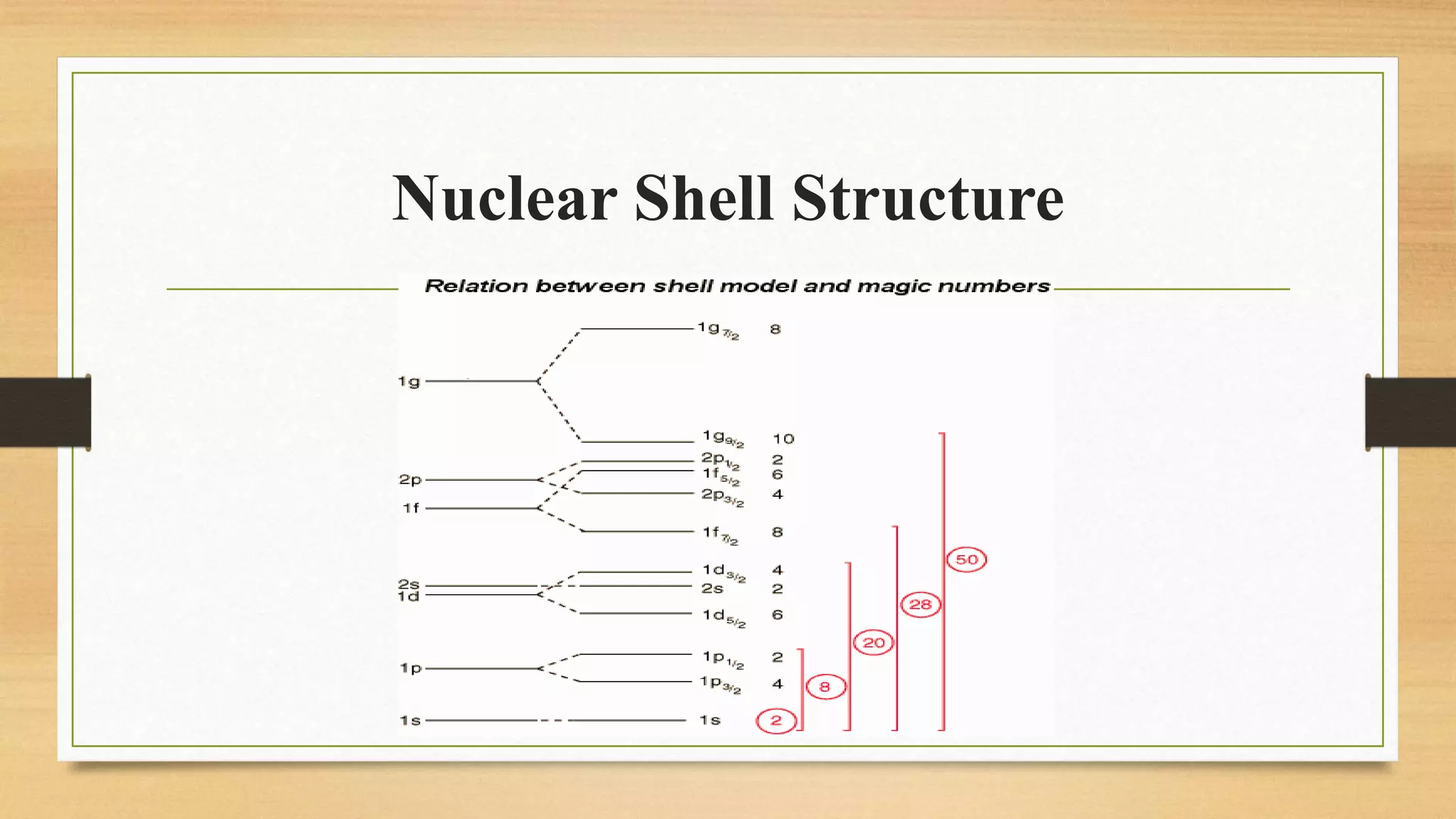
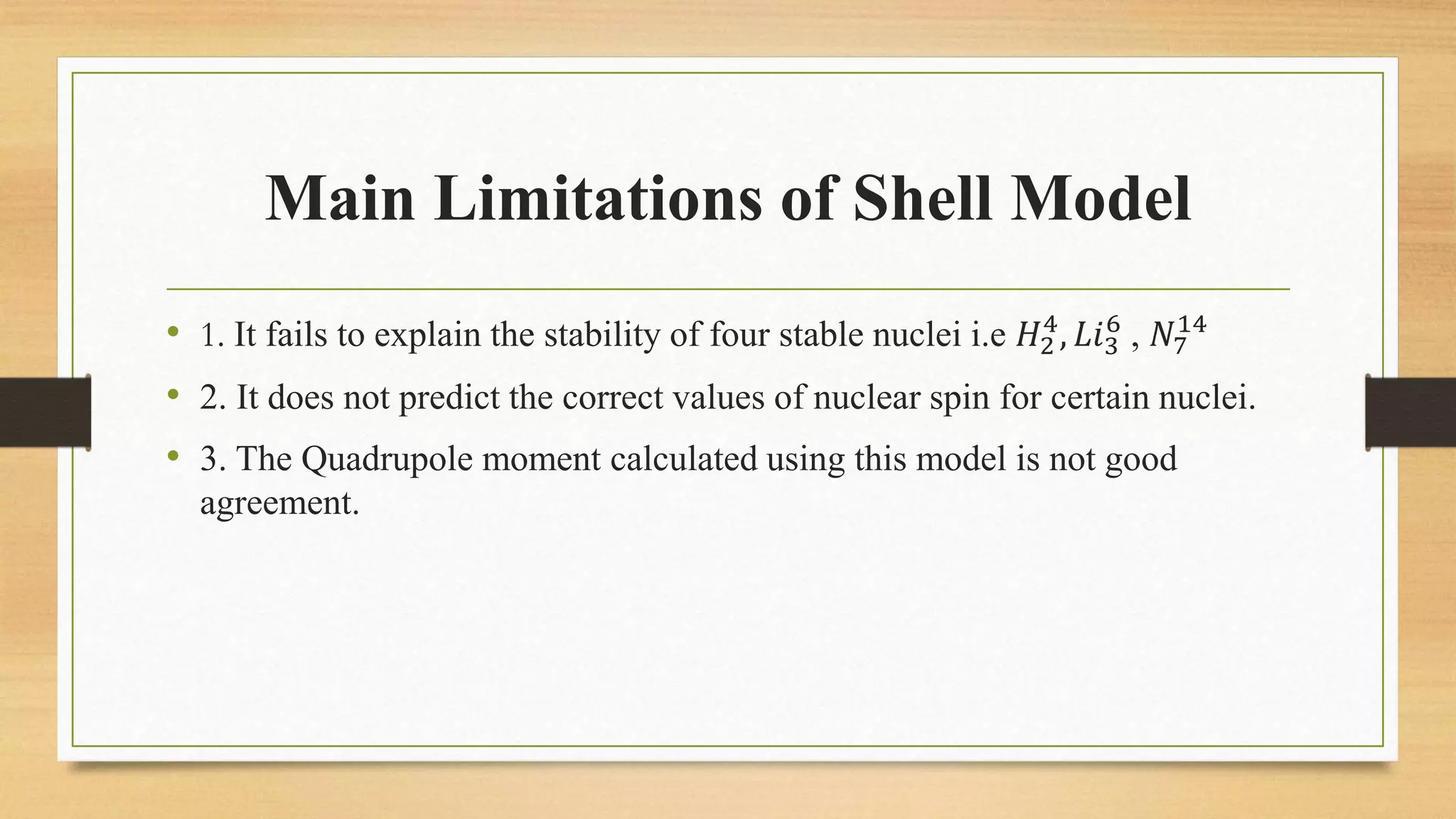
The nuclear shell model is a theoretical framework in nuclear physics developed to describe the atomic nucleus's structure based on energy levels, initially proposed by Dmitry Ivanenko in 1932. It explains key concepts such as magic numbers, the stability of certain nuclei, and provides insights into the magnetic moments and ground state spins, while also acknowledging its limitations in predicting the stability and spin values of some nuclei. Notably, stable nuclei correspond to magic numbers which indicate increased stability and a higher likelihood of existing isotopes.