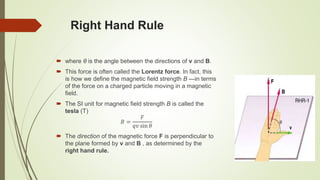
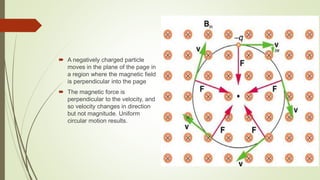
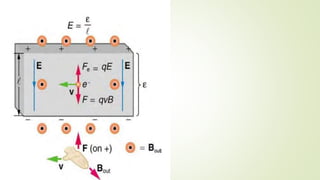
This document discusses magnetic fields and their properties. It explains that magnets have two poles, north and south, and that like poles repel while unlike poles attract. It defines magnetic fields as representing magnetic forces that act at a distance without physical contact. It describes magnetic field lines and their properties, including that their direction shows the field orientation and strength increases with closer spacing. It discusses the force on moving charges in magnetic fields, including how this causes circular or spiral motion, and explains the Hall effect where a magnetic field perpendicular to current flow in a conductor creates a voltage across it.