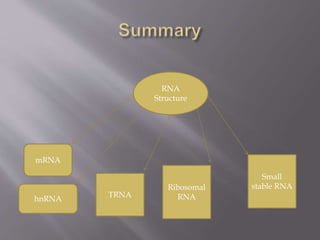
This document summarizes different types of RNA:
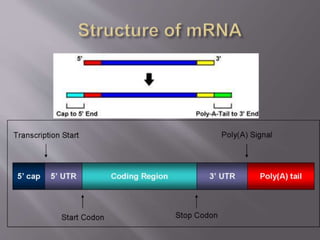
- Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries genetic information from DNA to the protein synthesis machinery. It has a 5' cap and 3' poly-A tail that protect it from degradation.
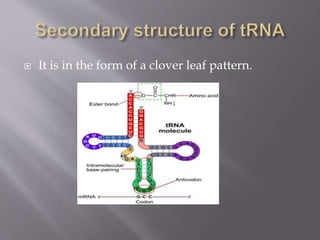
- Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain during protein synthesis according to the mRNA codon sequence. It has a cloverleaf secondary structure.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a component of ribosomes and helps in protein translation. The eukaryotic ribosomal subunit contains 5S, 5.8S and 28S rRNAs.