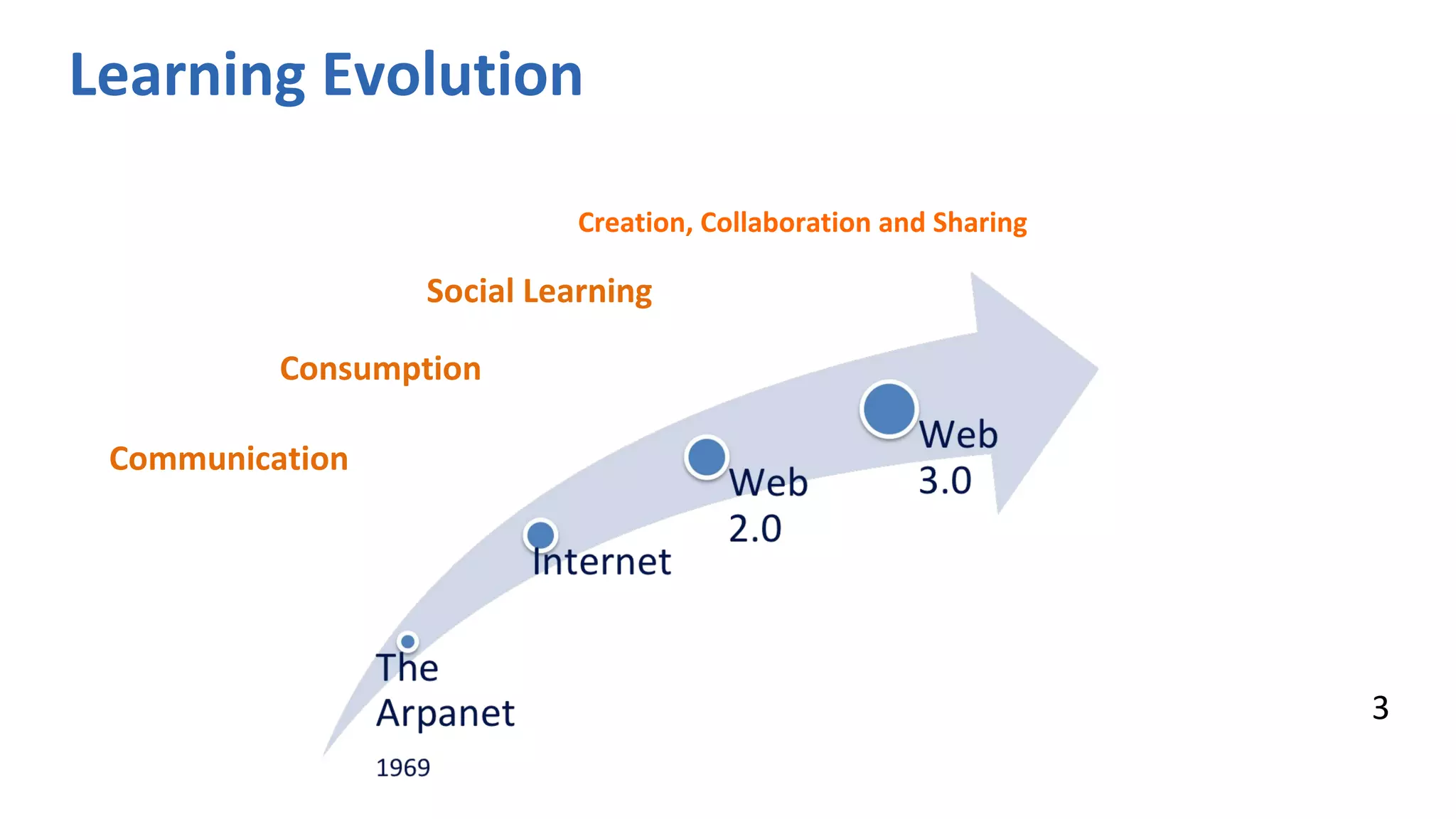
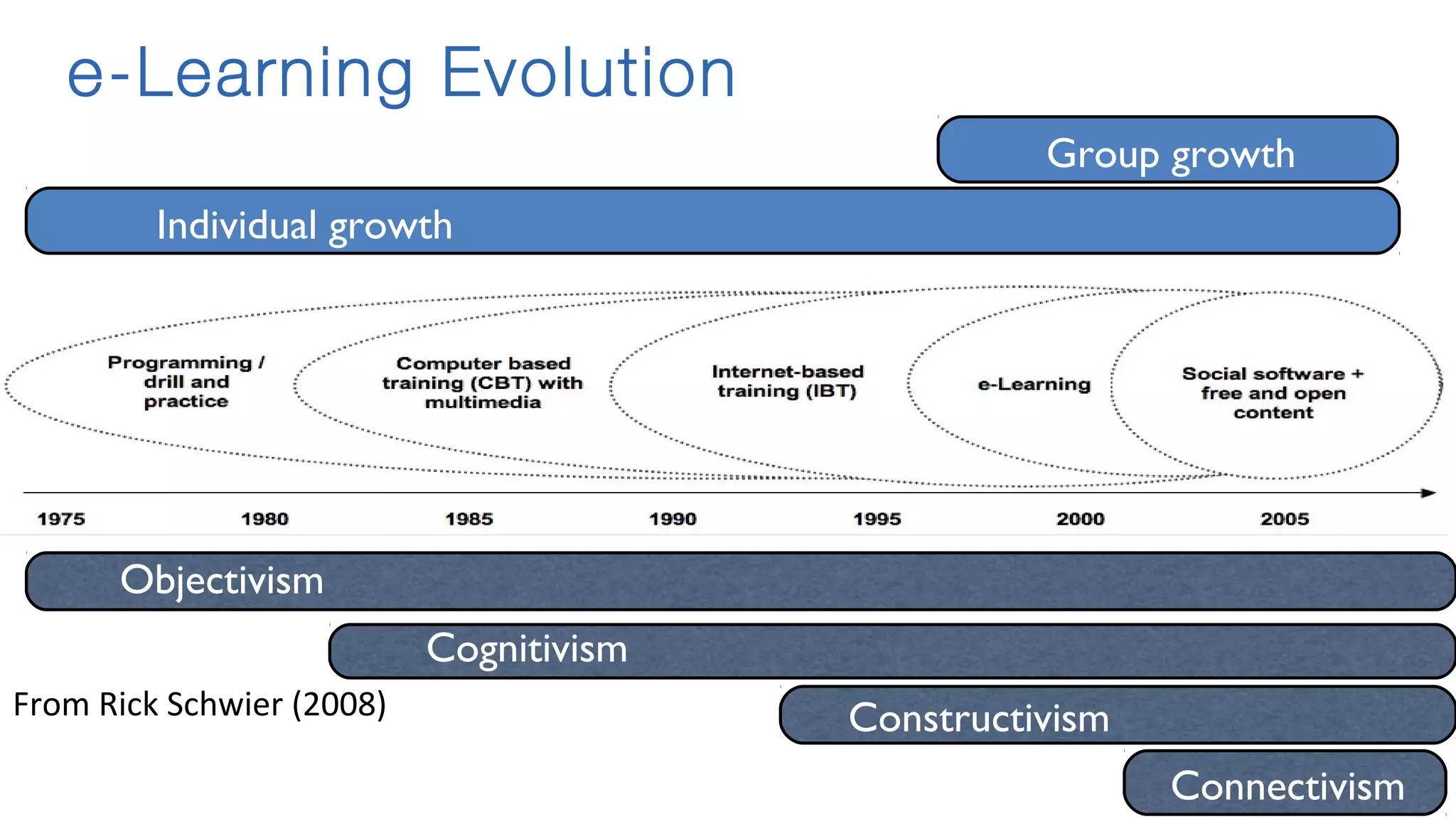
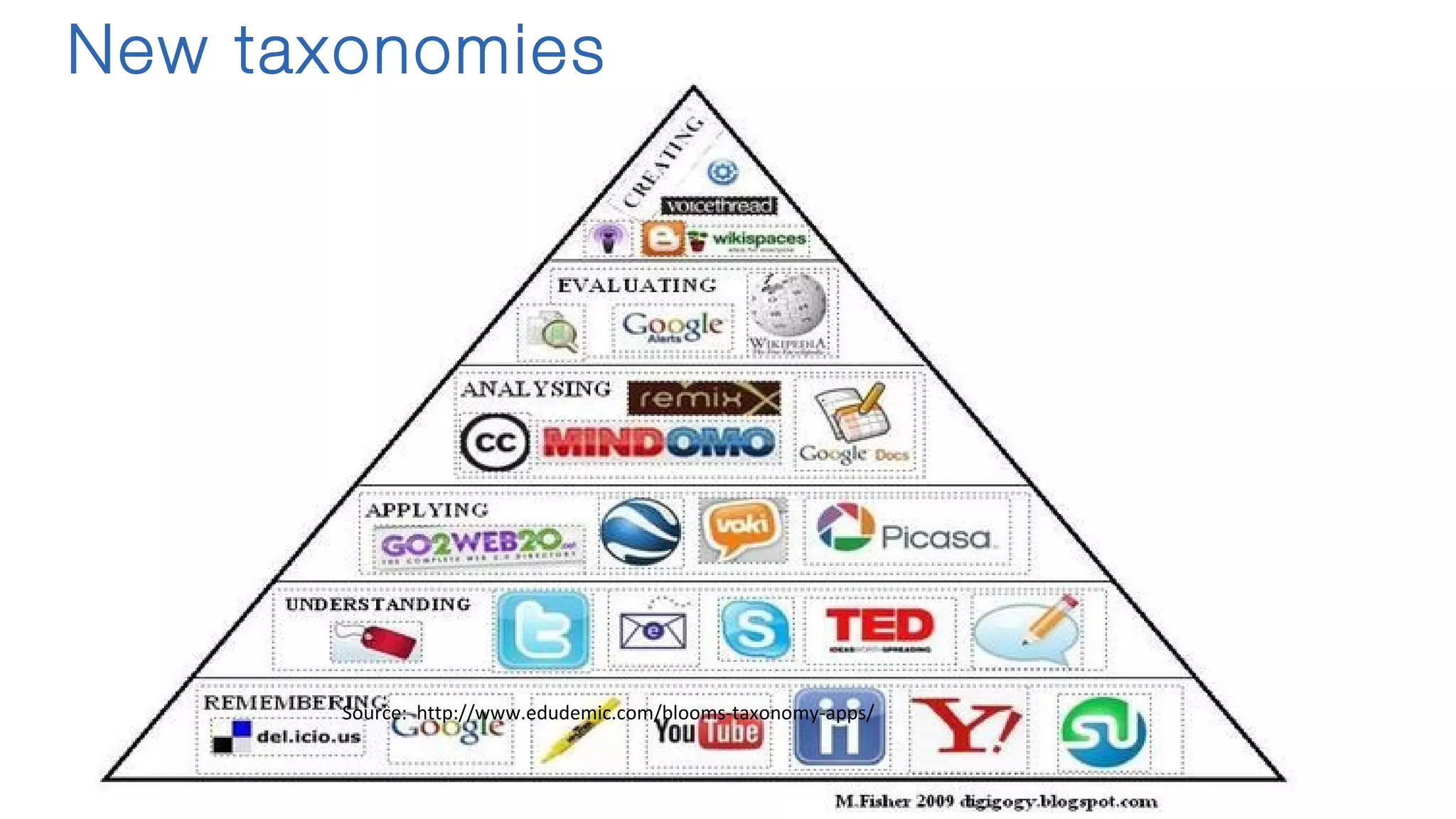
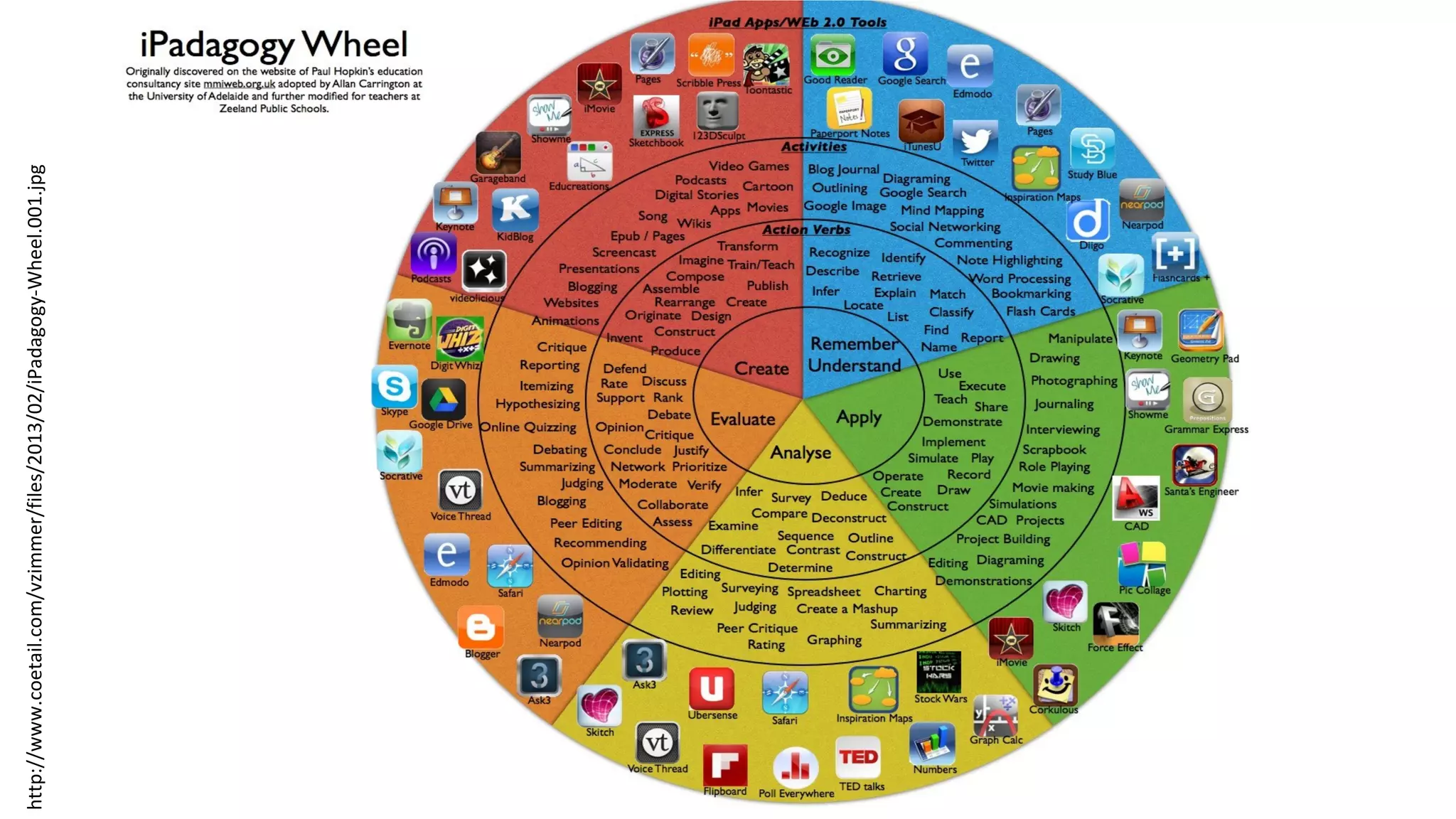
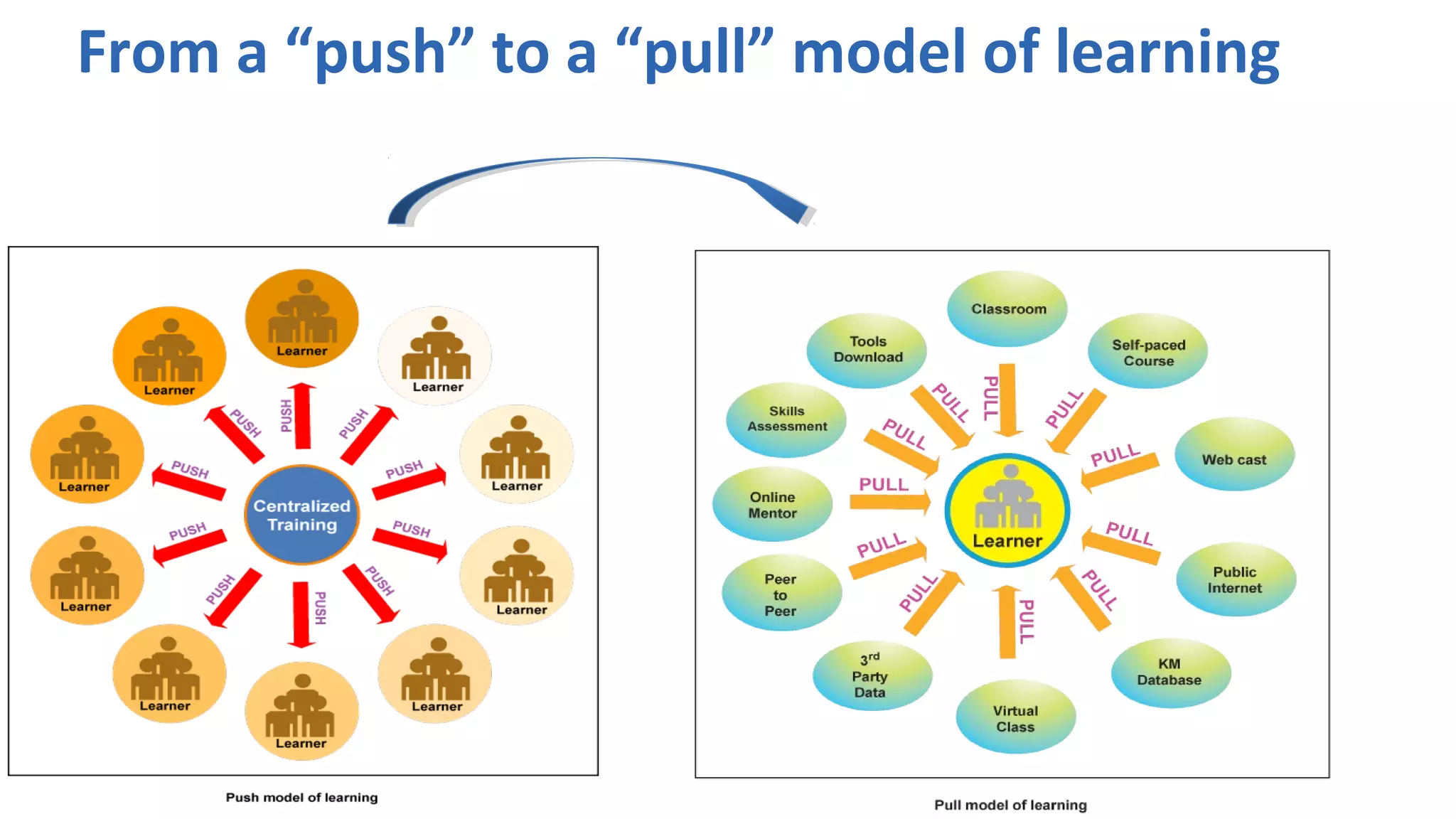
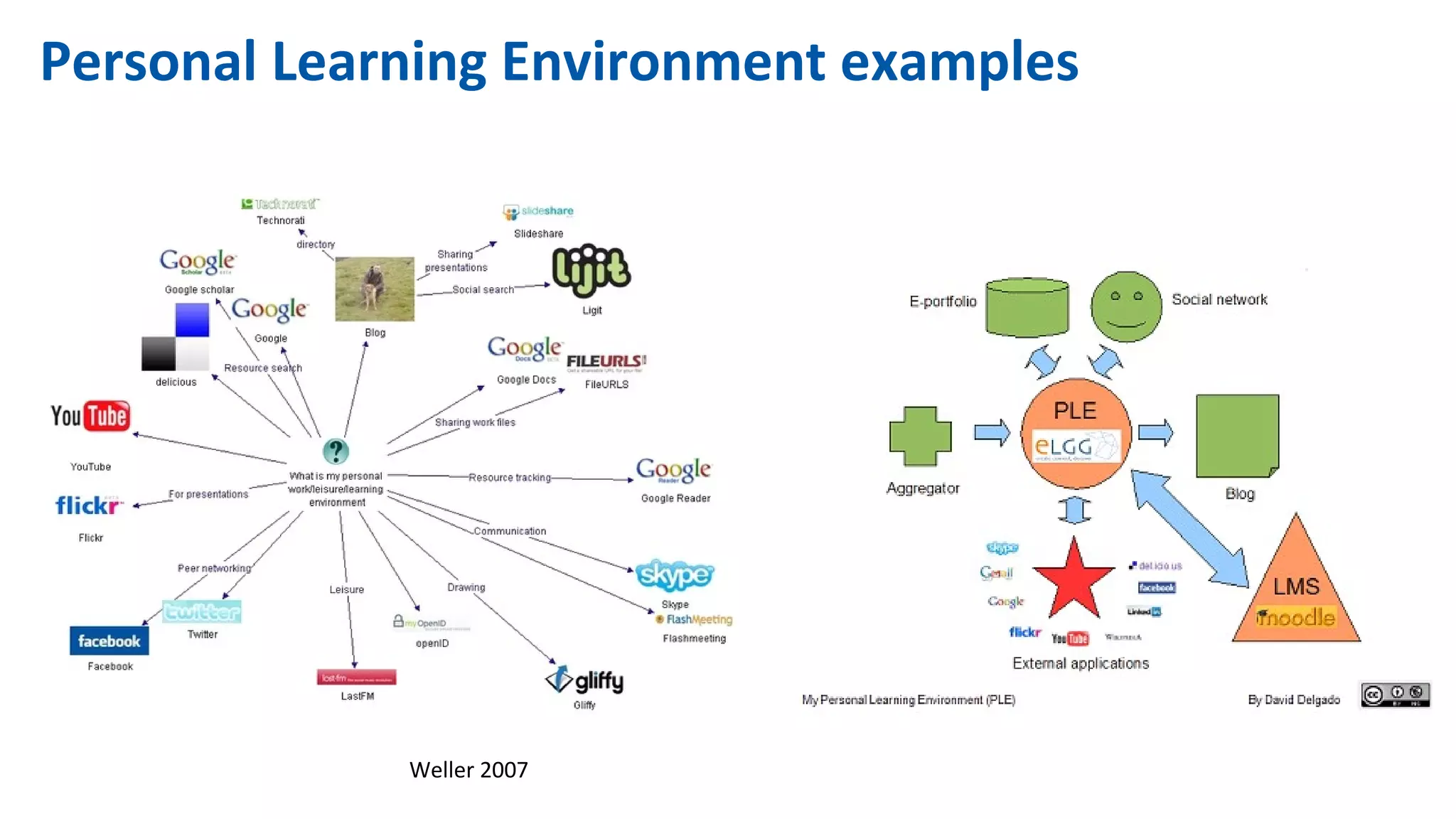
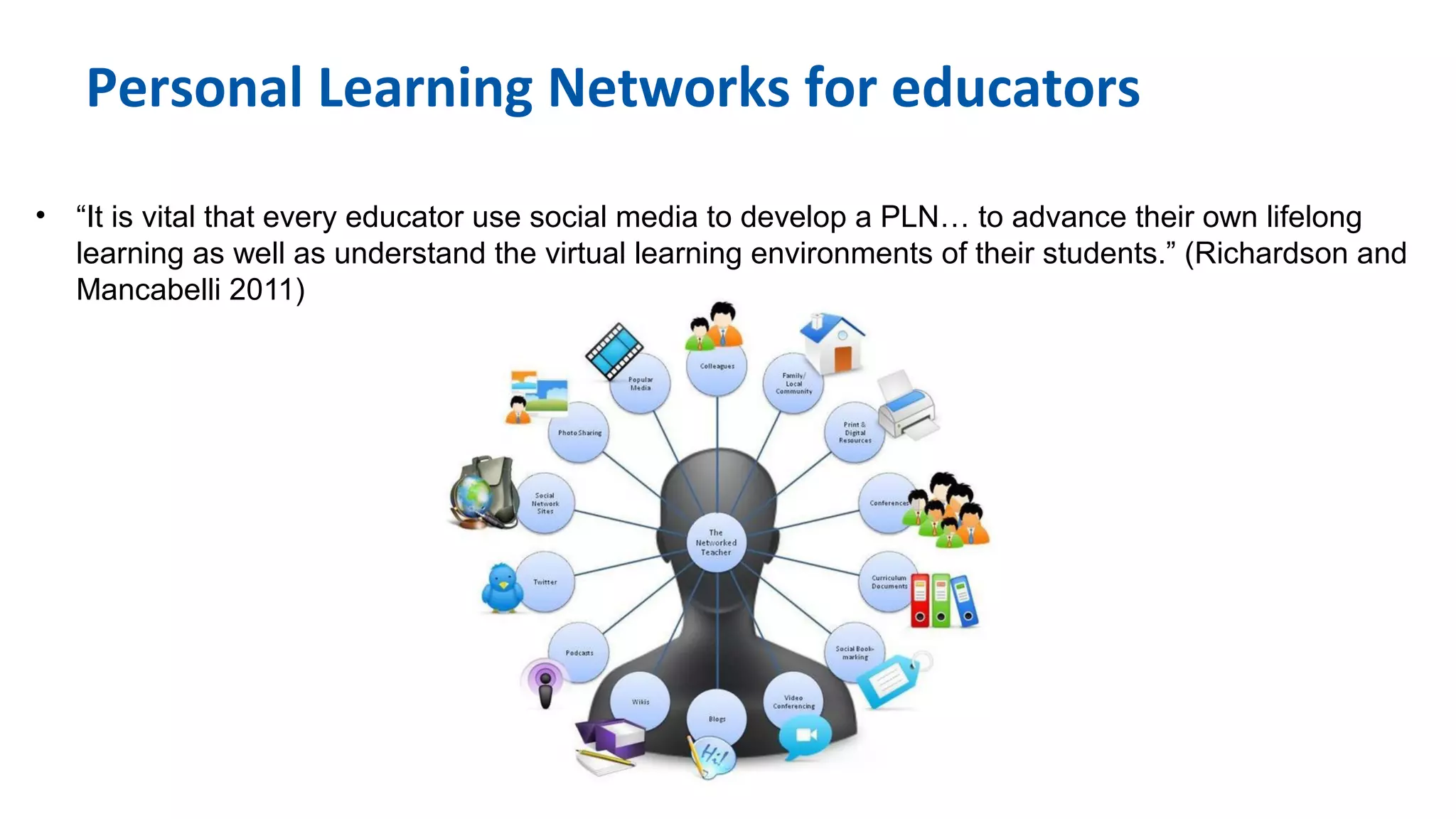
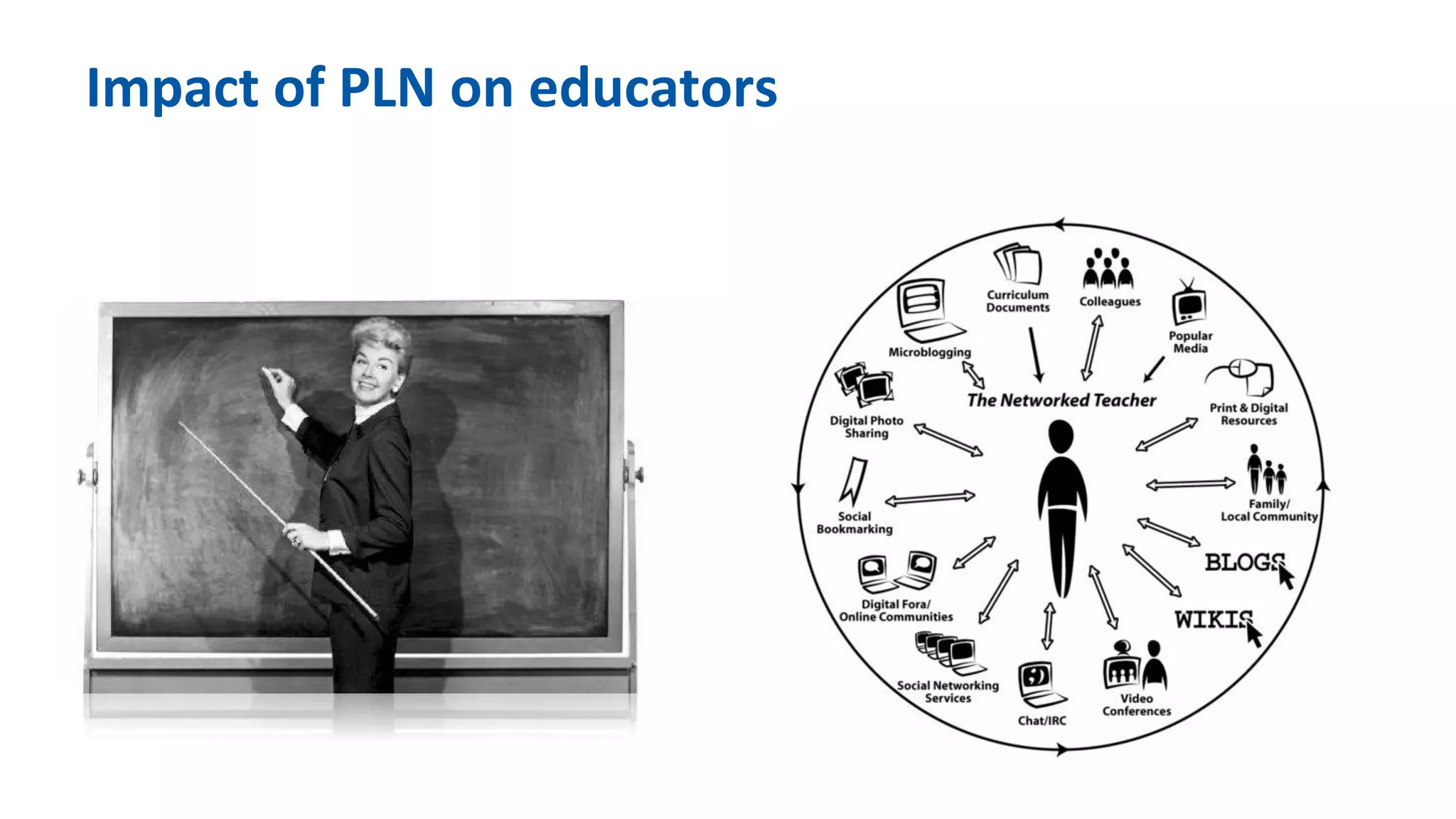
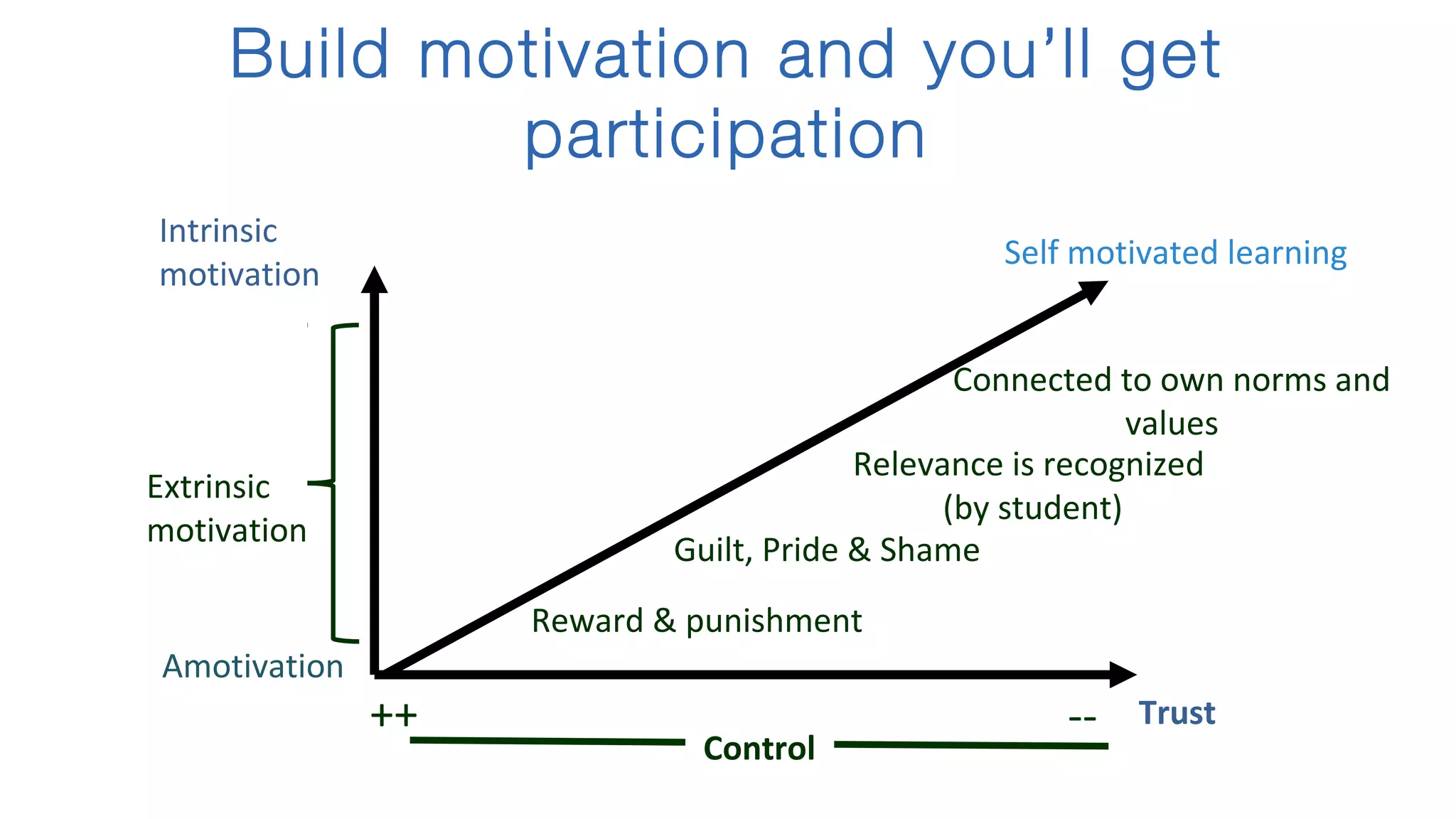
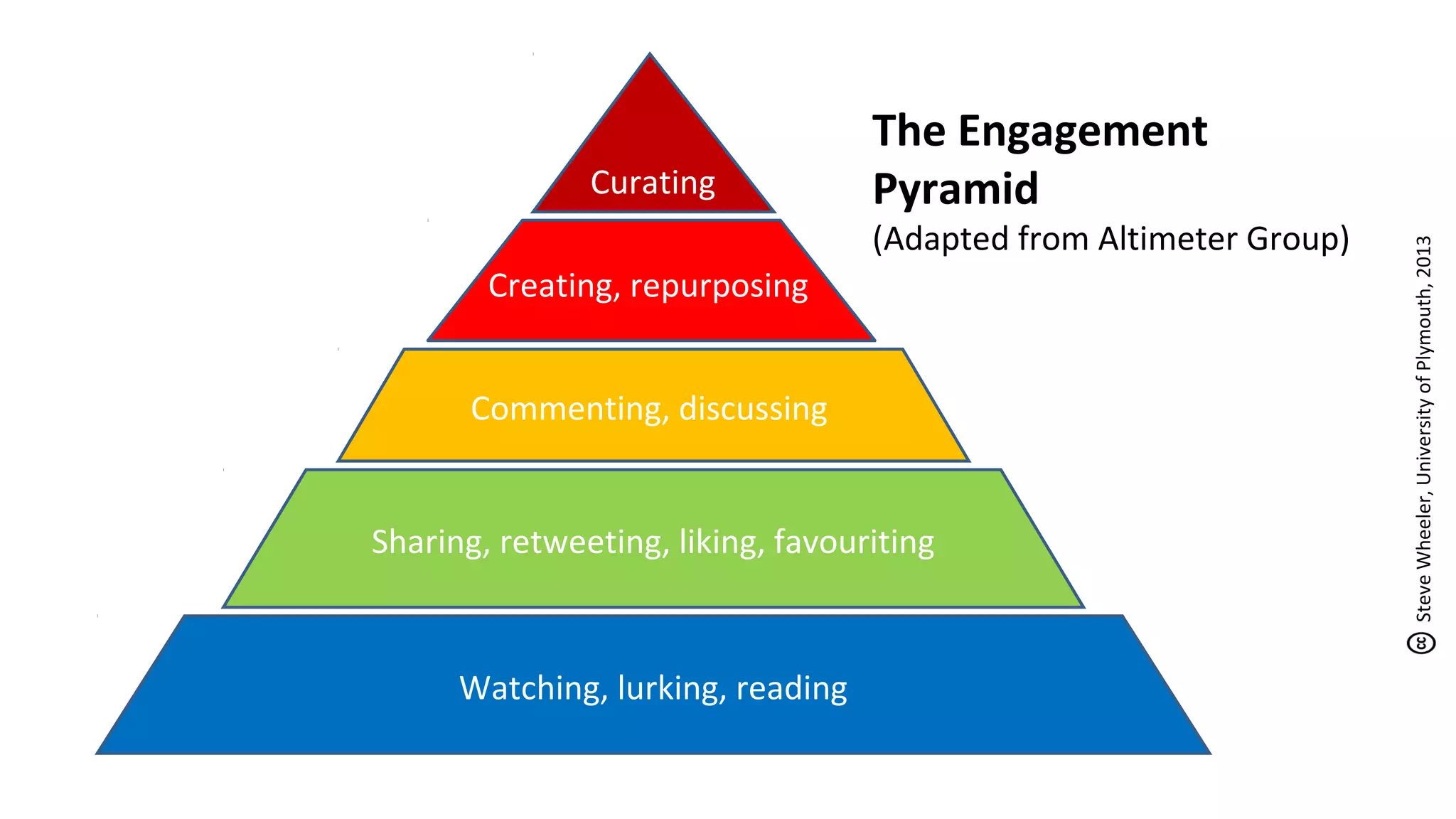
The document discusses the evolution of learning through networked teaching and personal learning networks (PLN), emphasizing the importance of connections and social media in developing knowledge. It highlights the concept of a personal learning environment (PLE) as a self-directed virtual space for personalized learning. Practical tips for building and enhancing a PLN are provided, focusing on various digital platforms and the significance of intrinsic motivation for active participation.