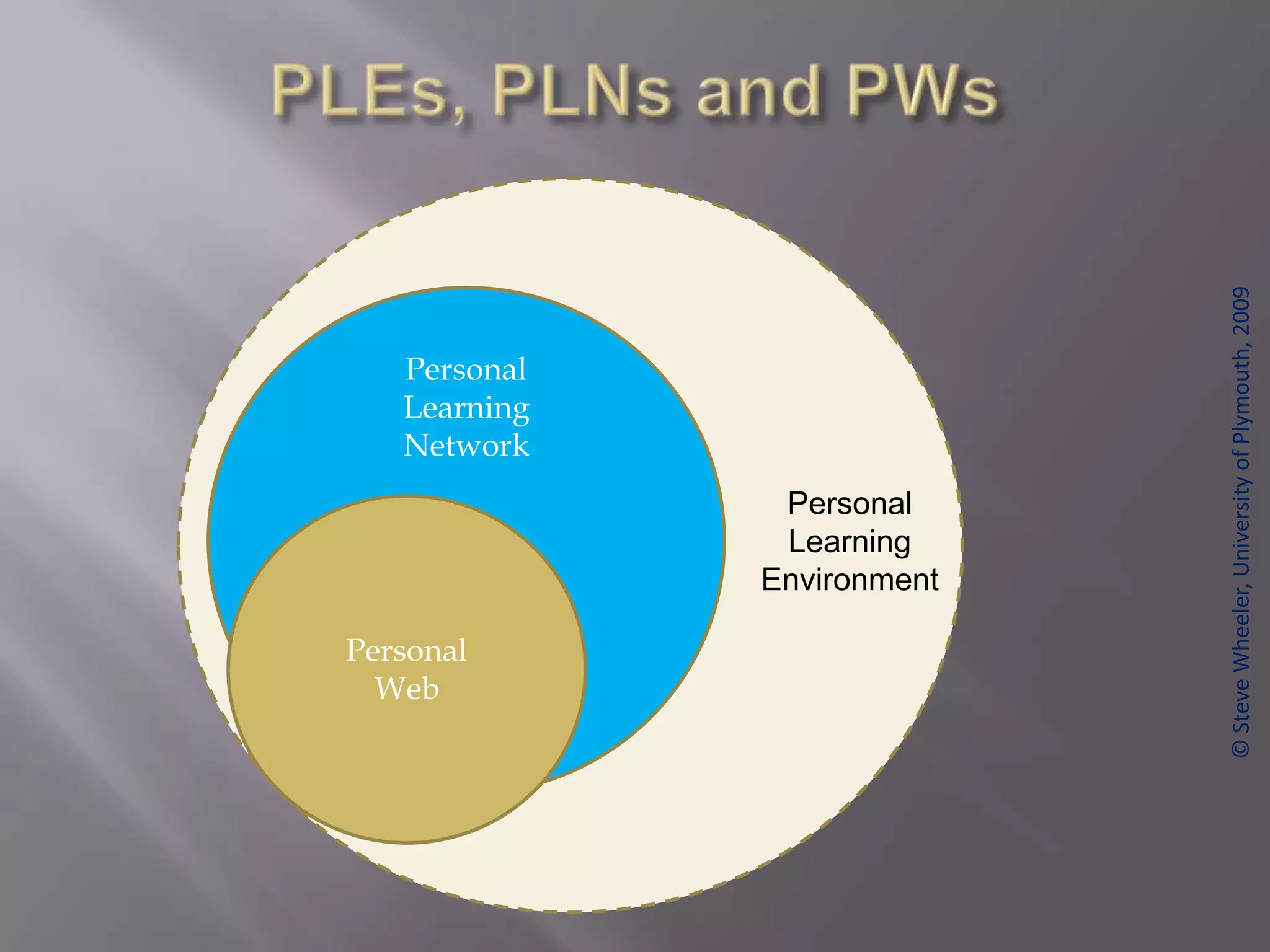
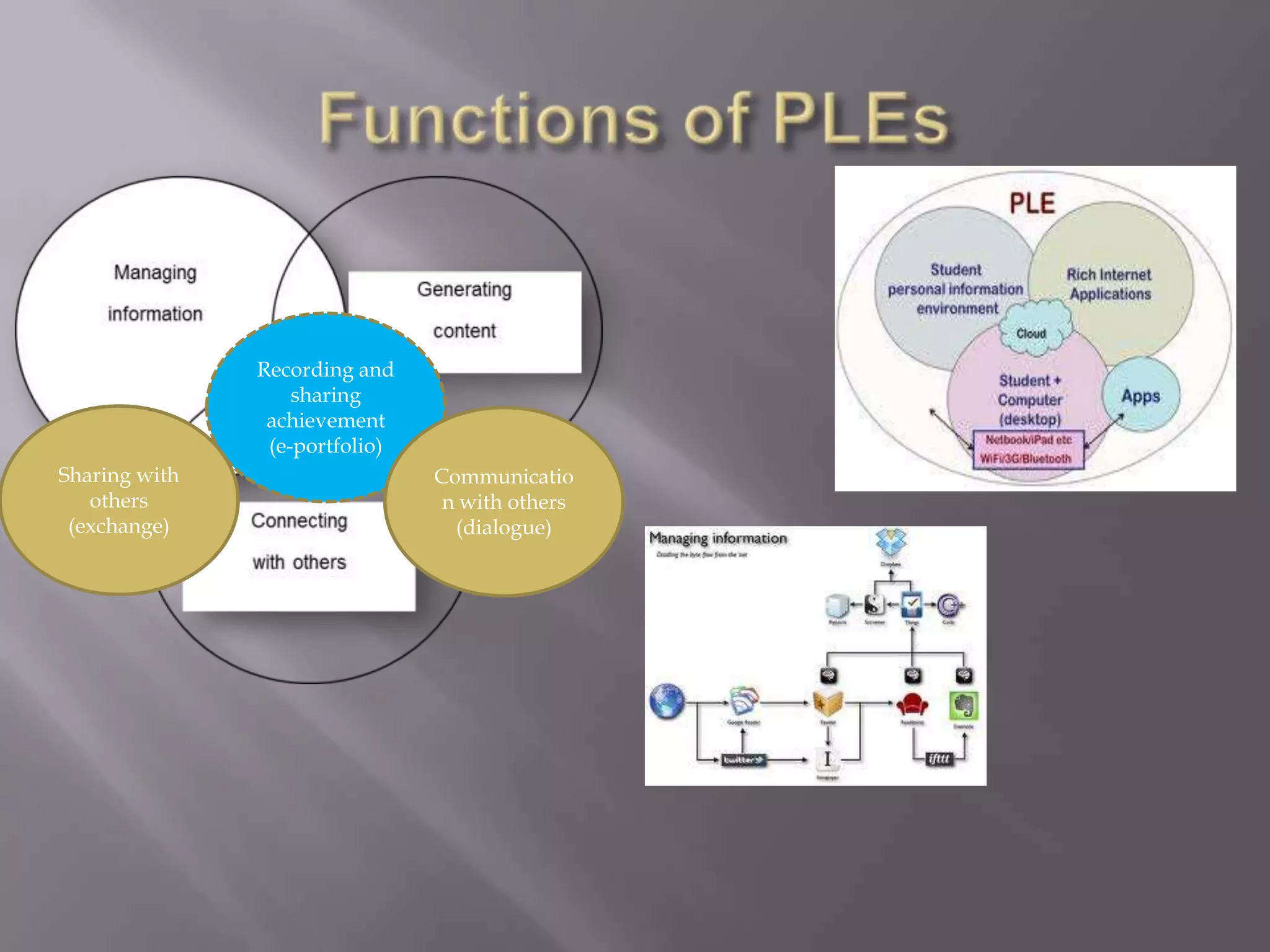
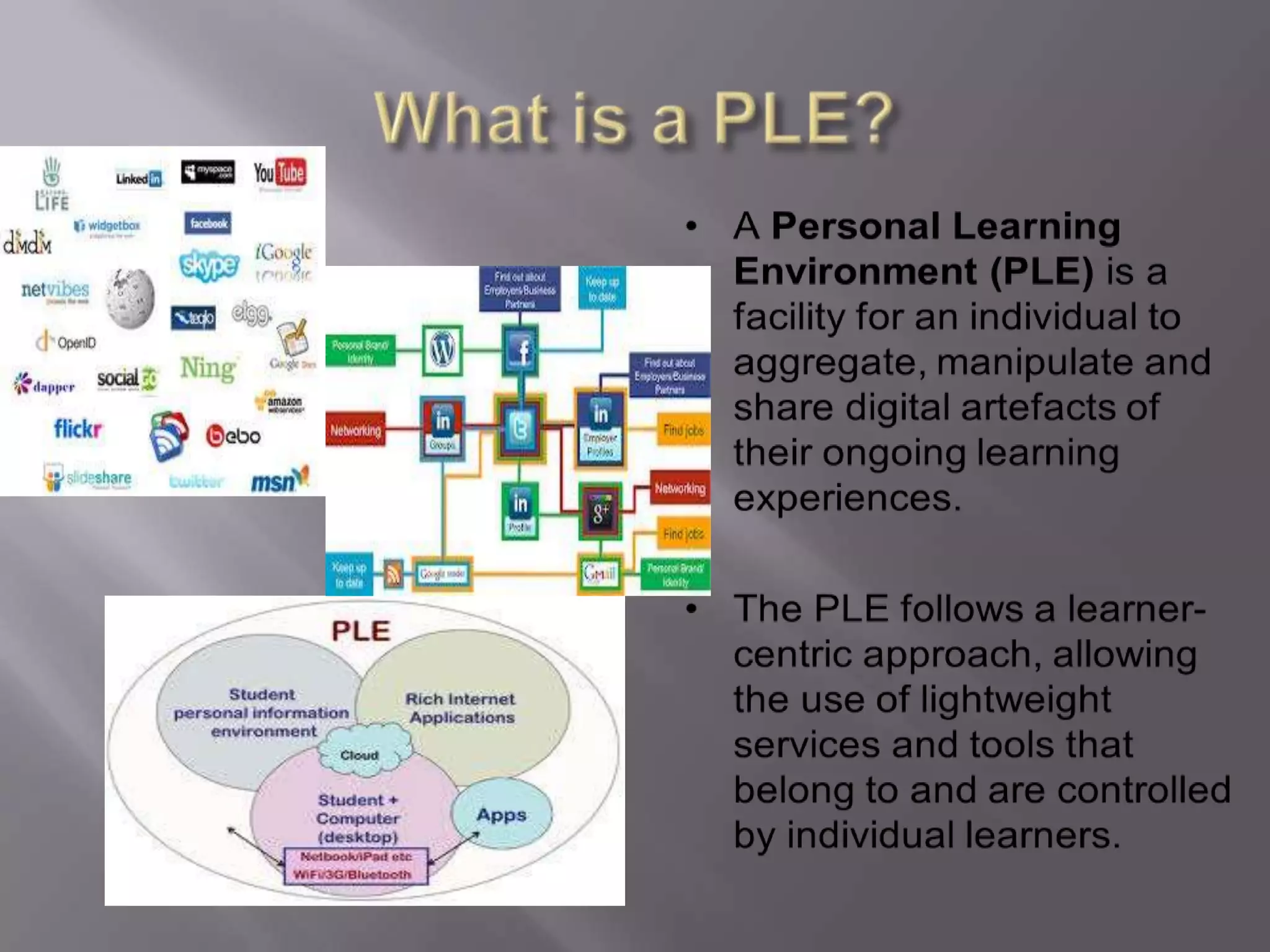
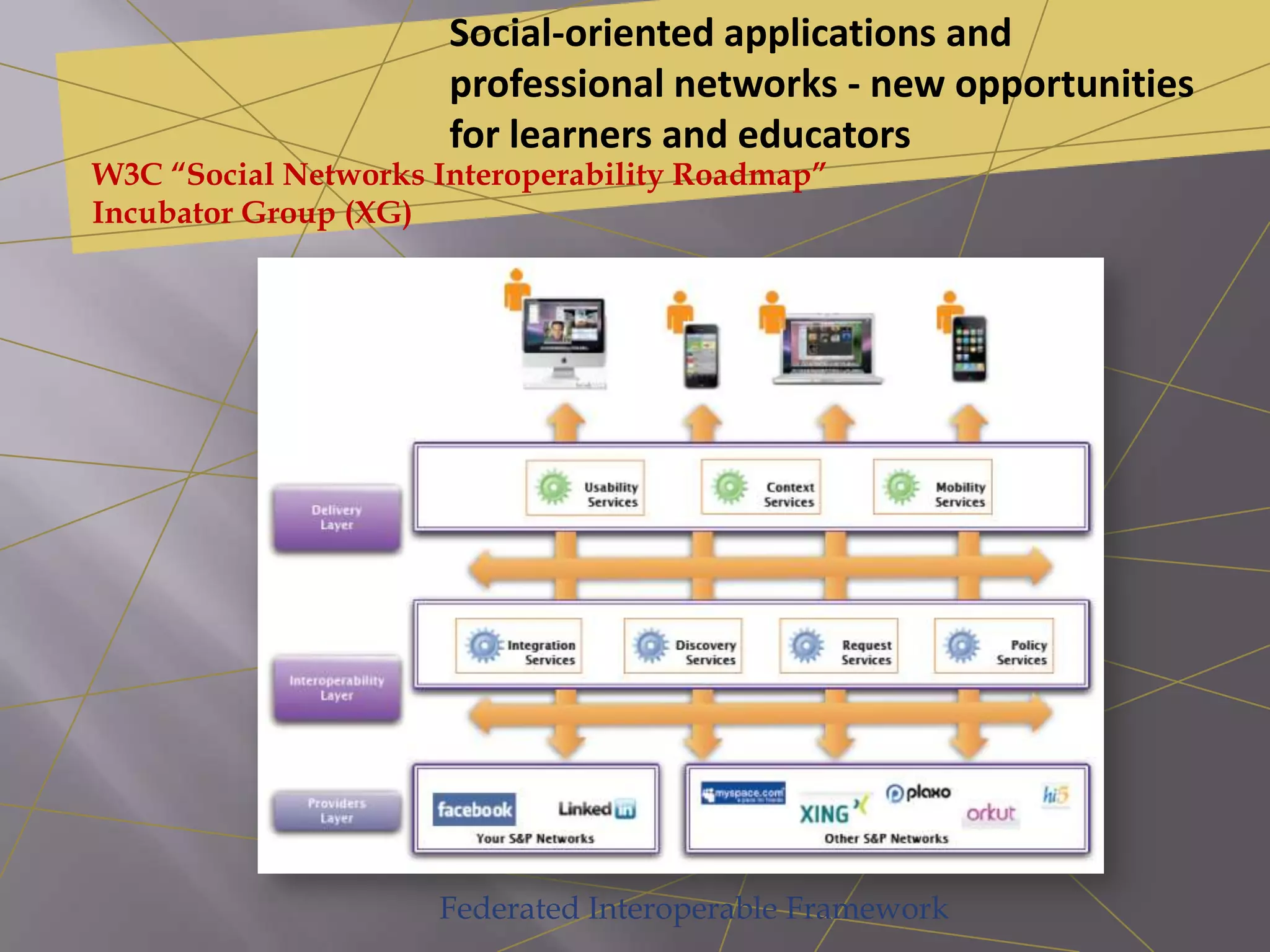
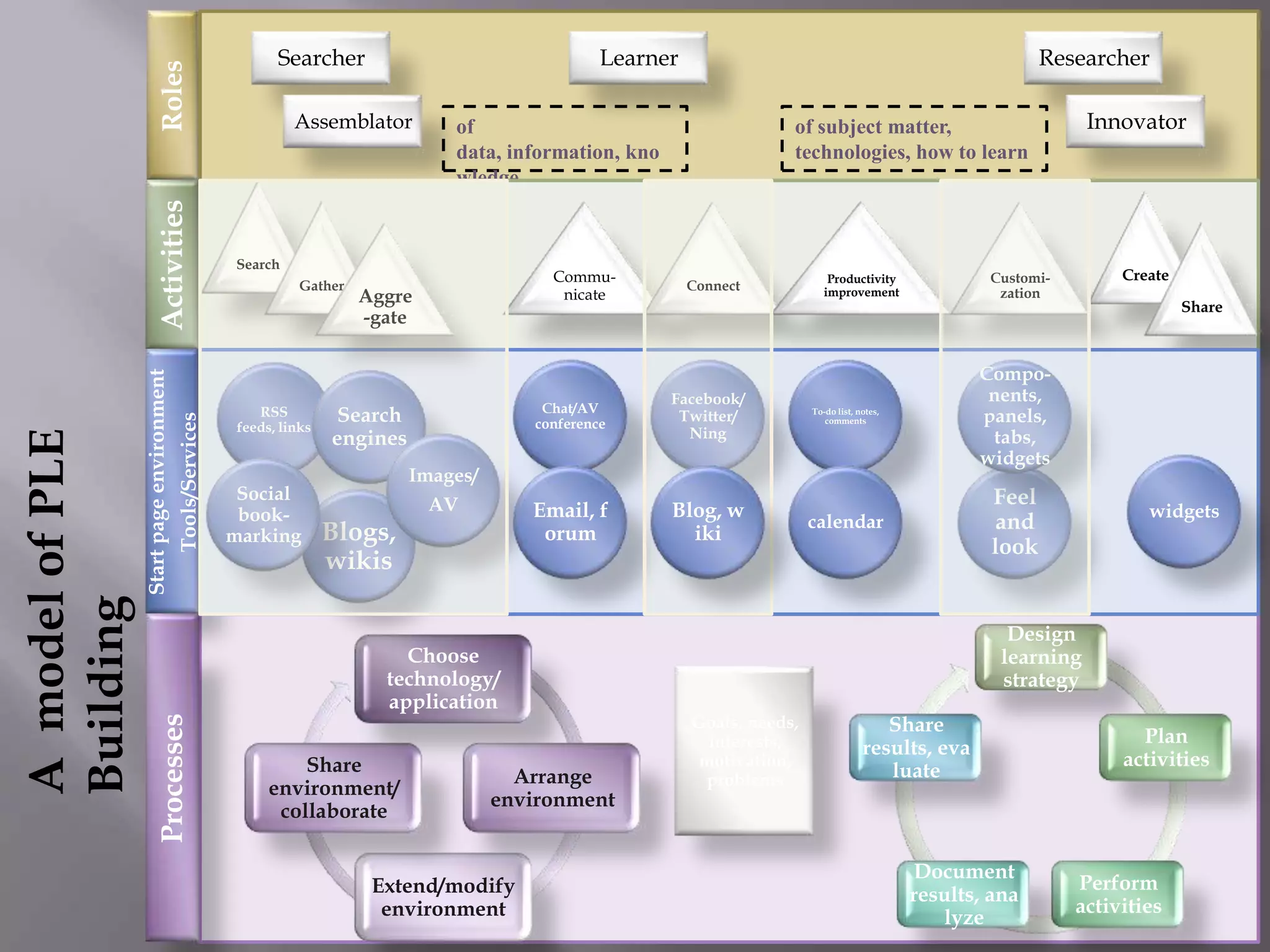
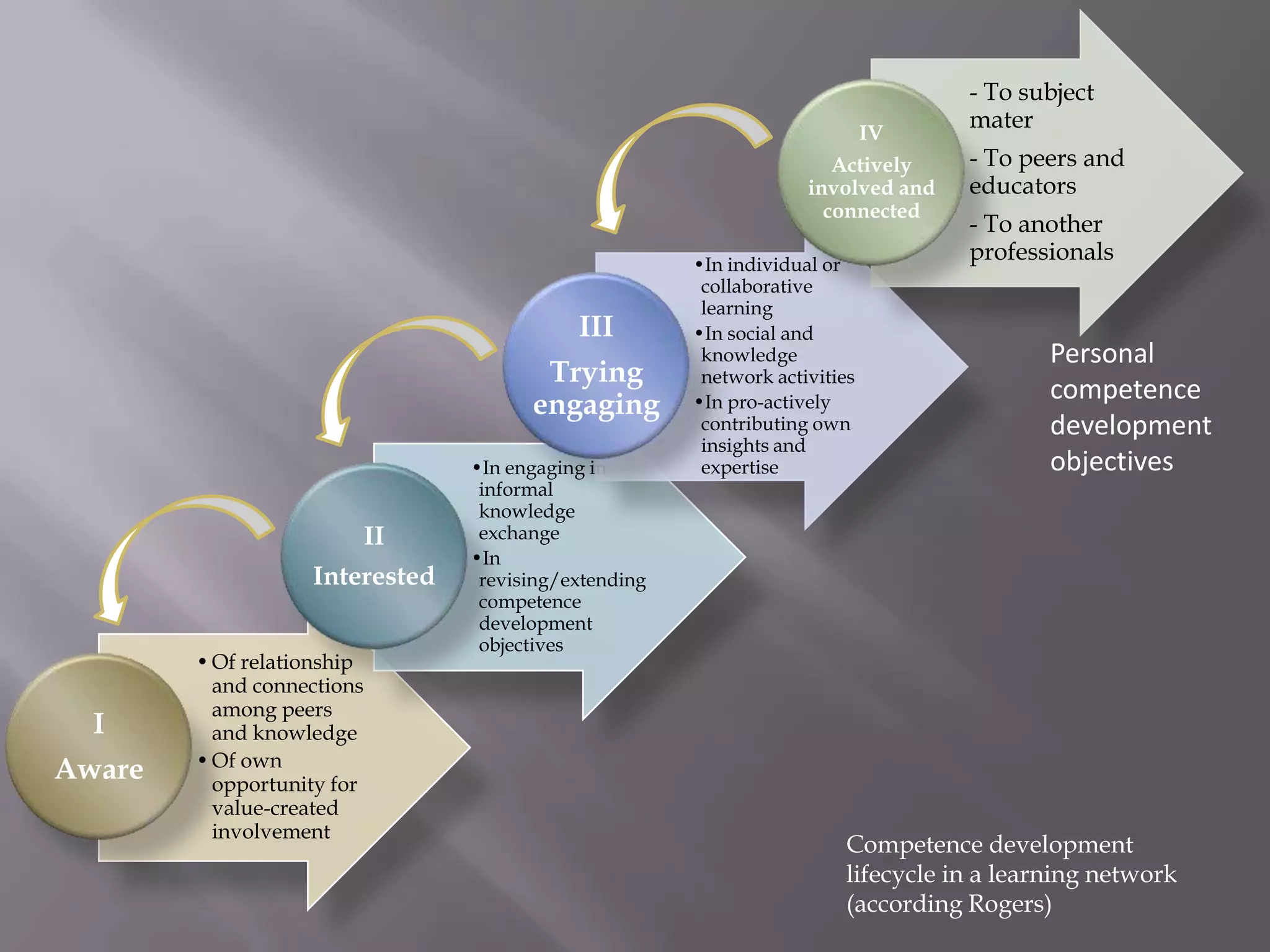
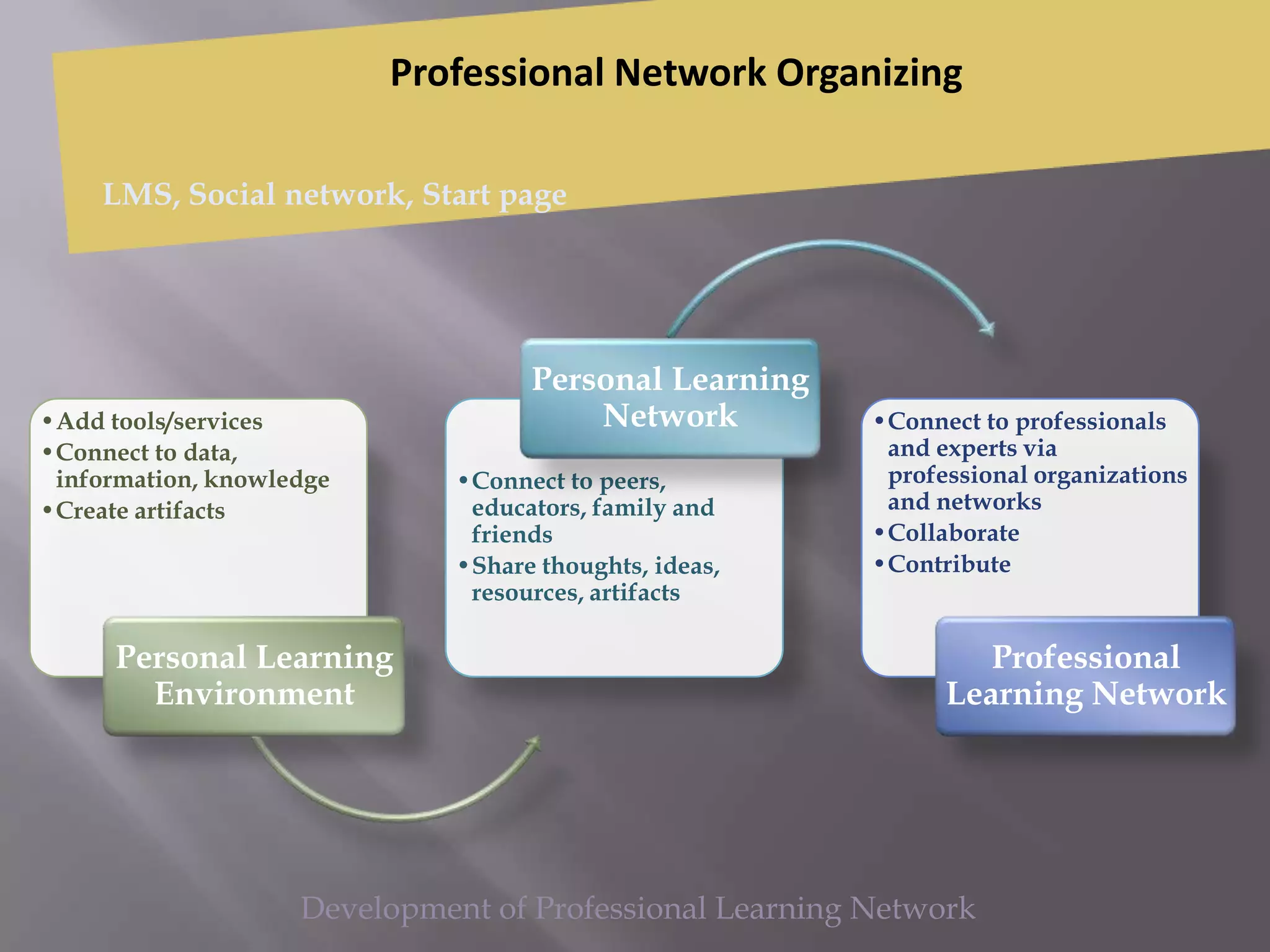
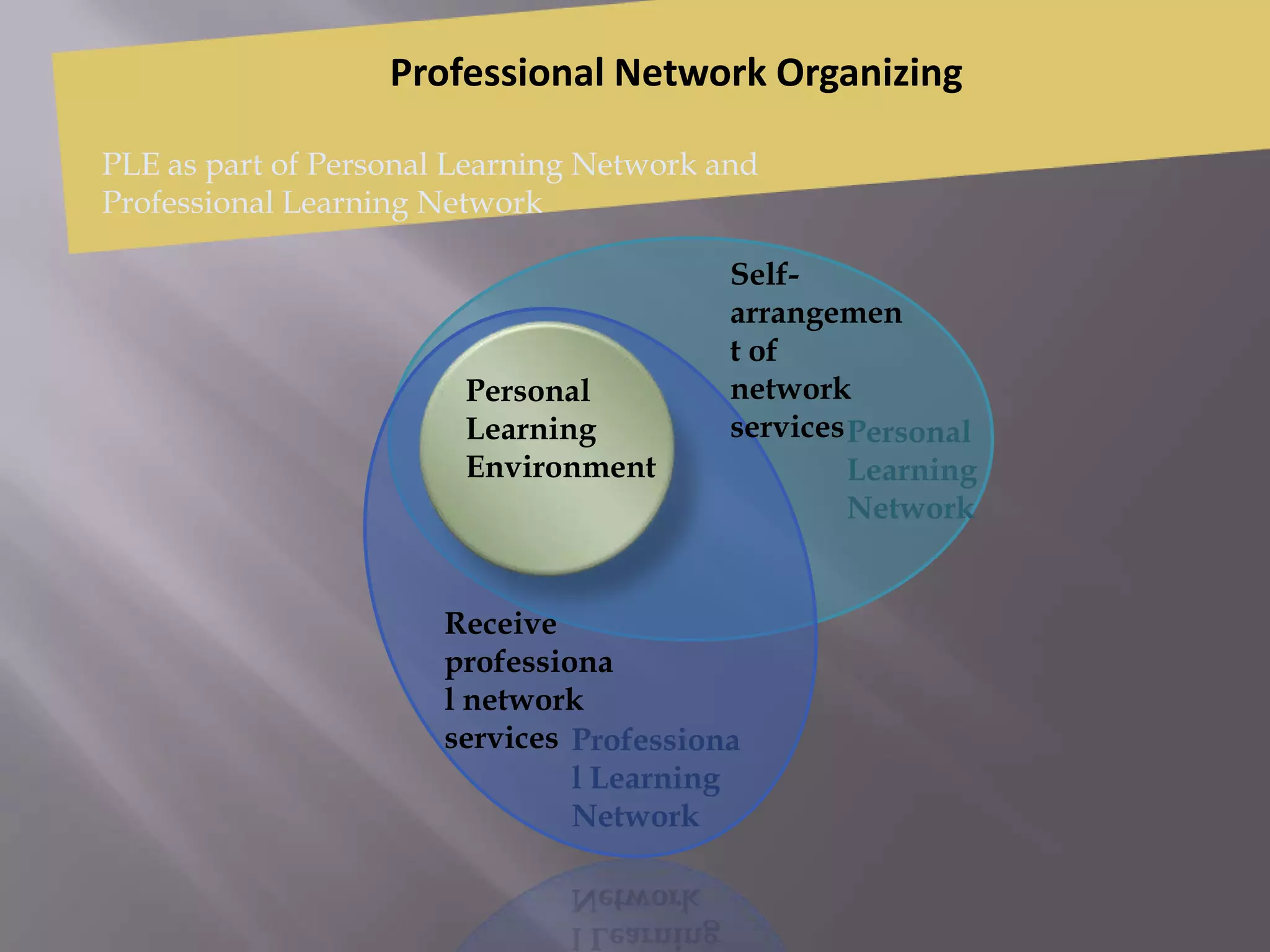
This document discusses personal learning environments (PLEs), personal learning networks (PLNs), and professional learning networks (PLNs). It addresses how PLEs allow learners to manage their own learning goals and processes. PLEs can then develop into PLNs for collaborating with others and sharing knowledge. Finally, PLNs form for connecting with professionals in fields of interest and contributing expertise on an ongoing basis after course completion. The document provides examples of roles and activities in these networks and models for developing competencies through them.