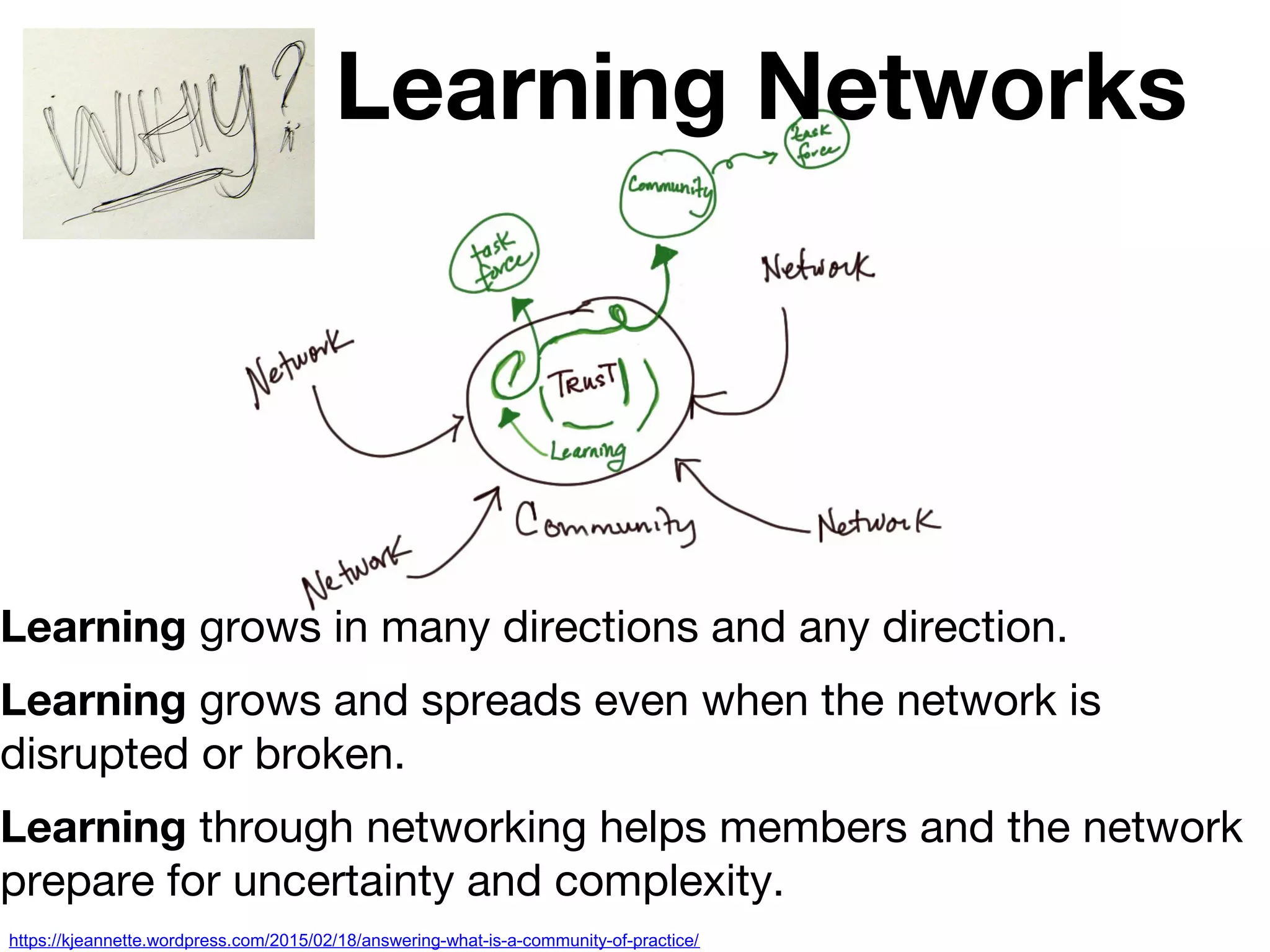
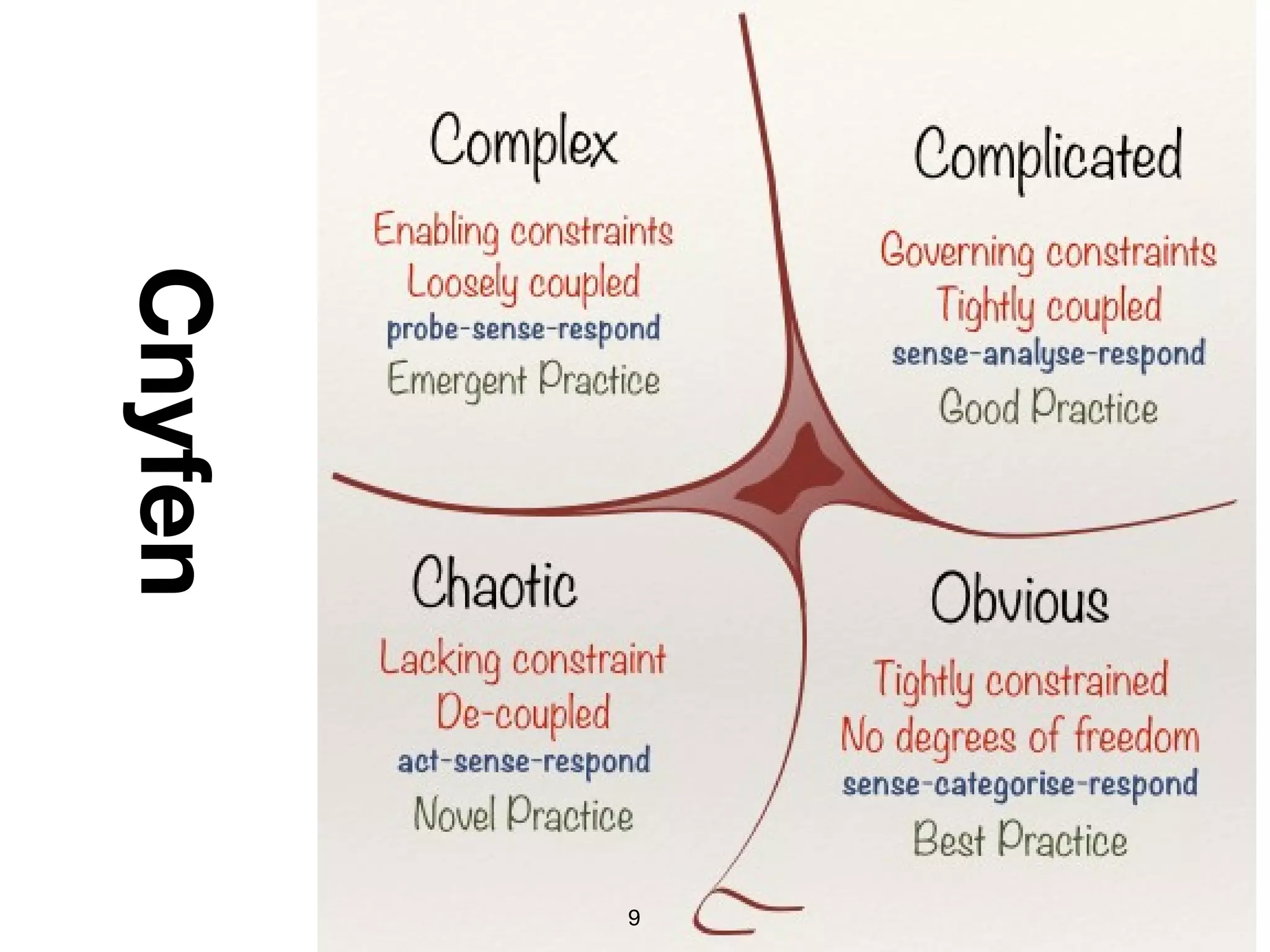
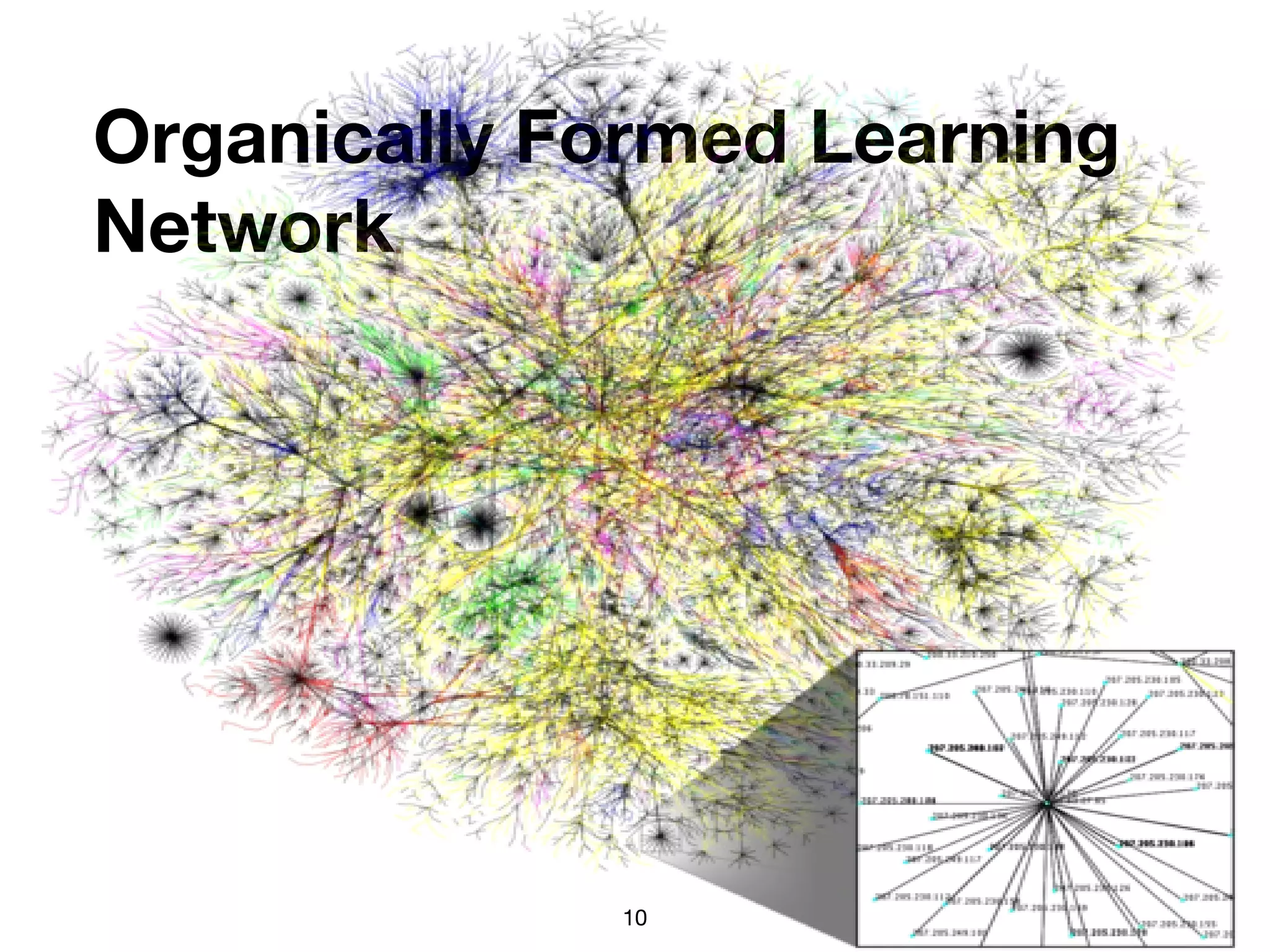
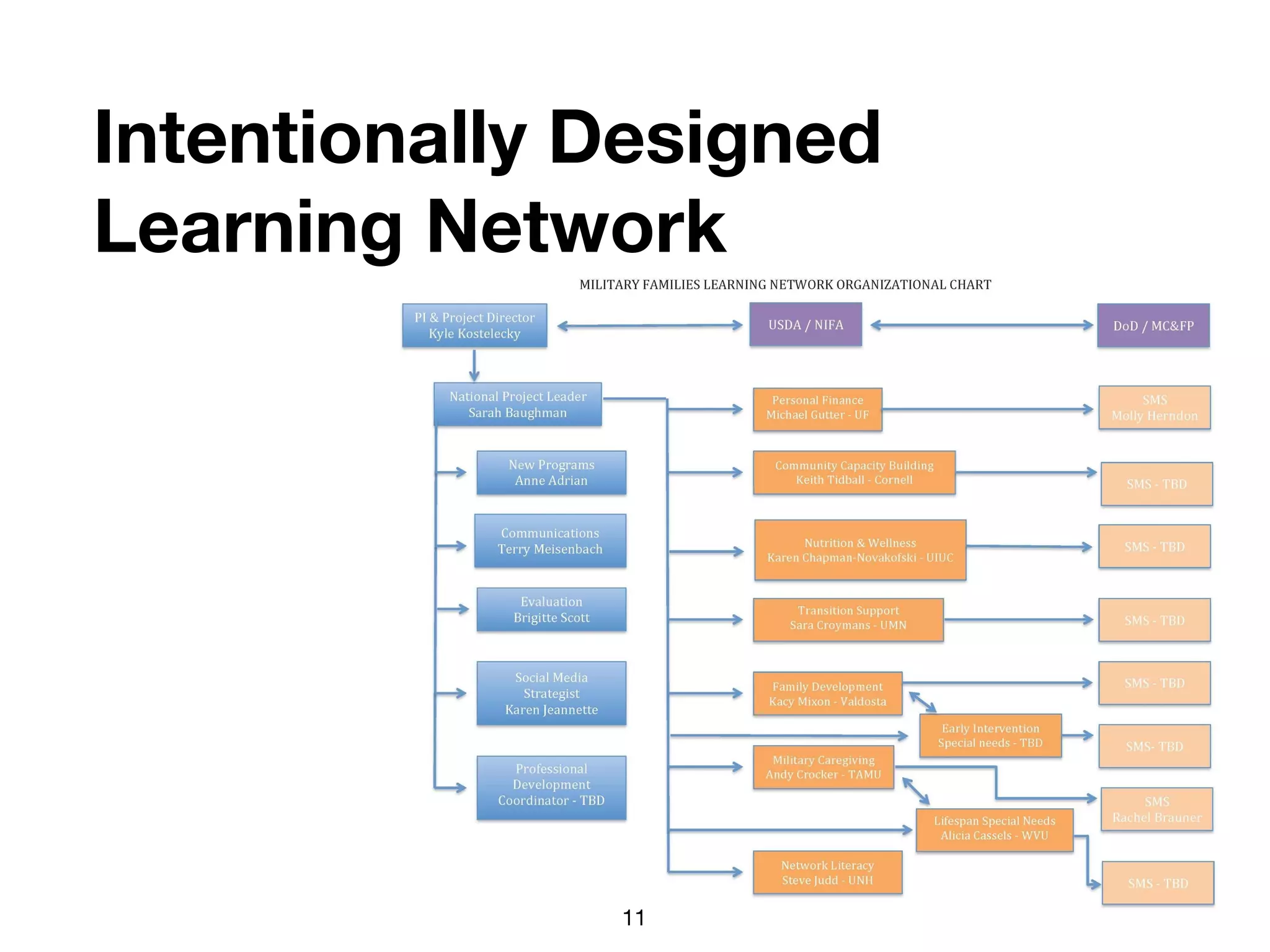
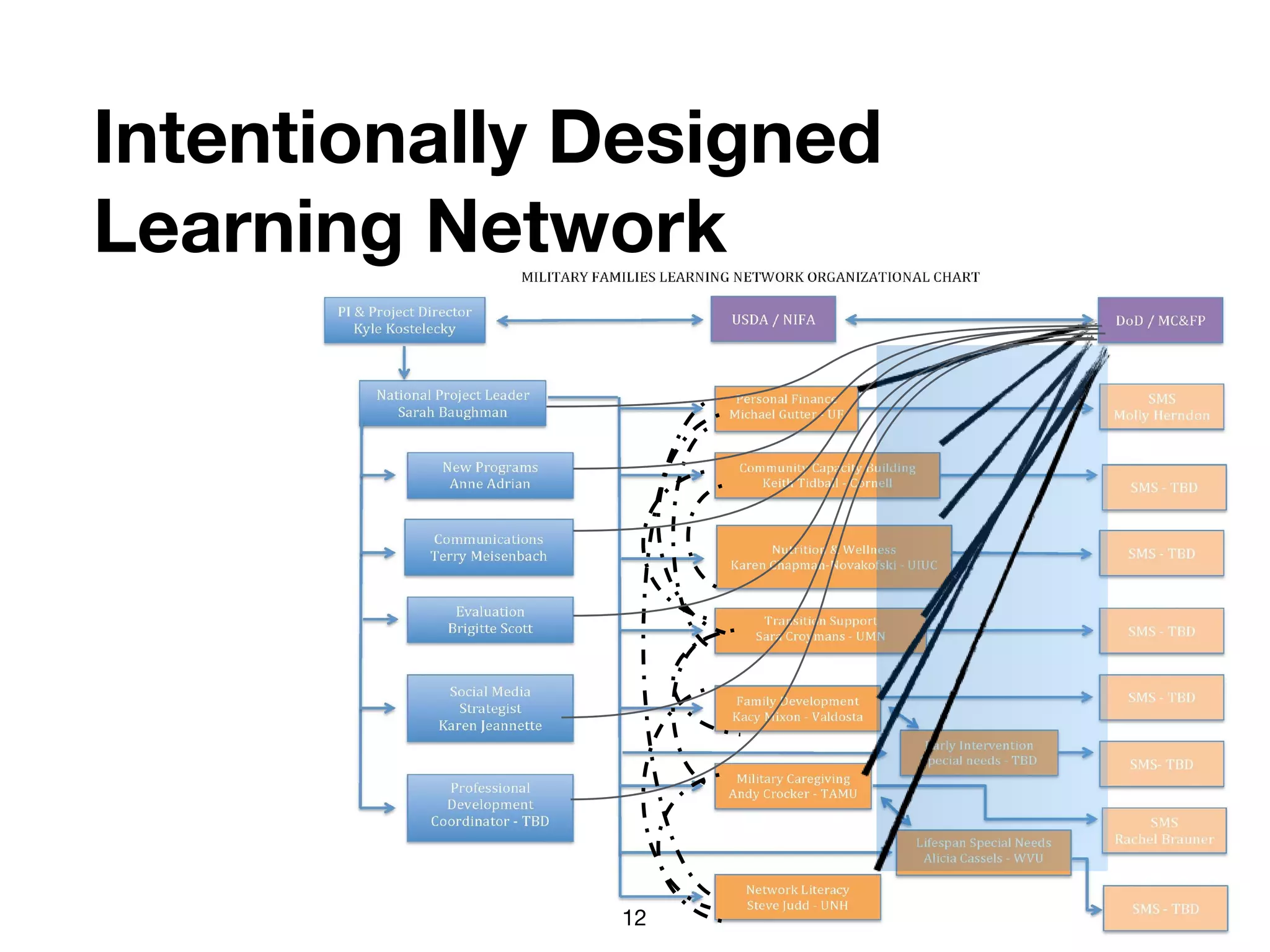
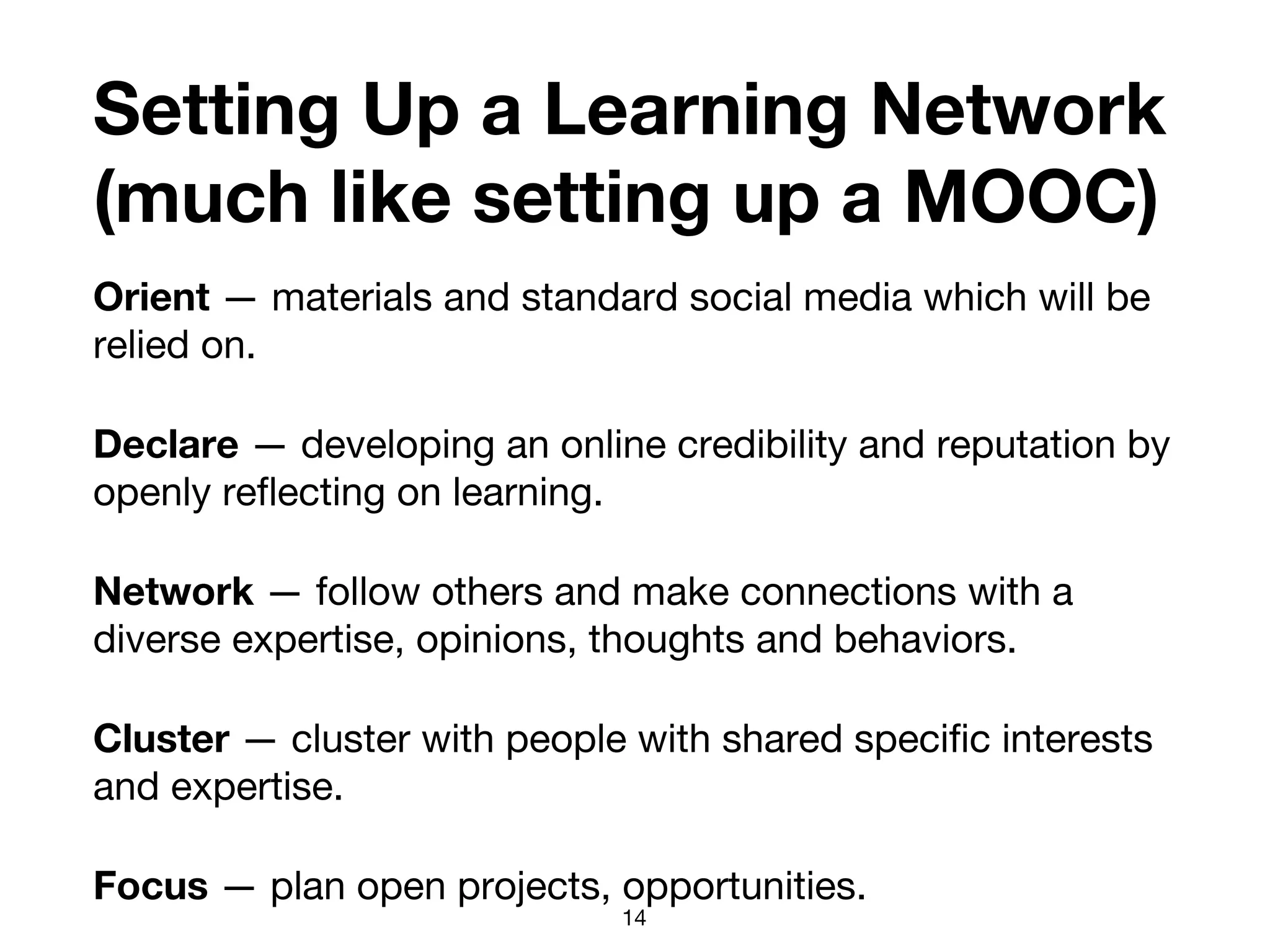
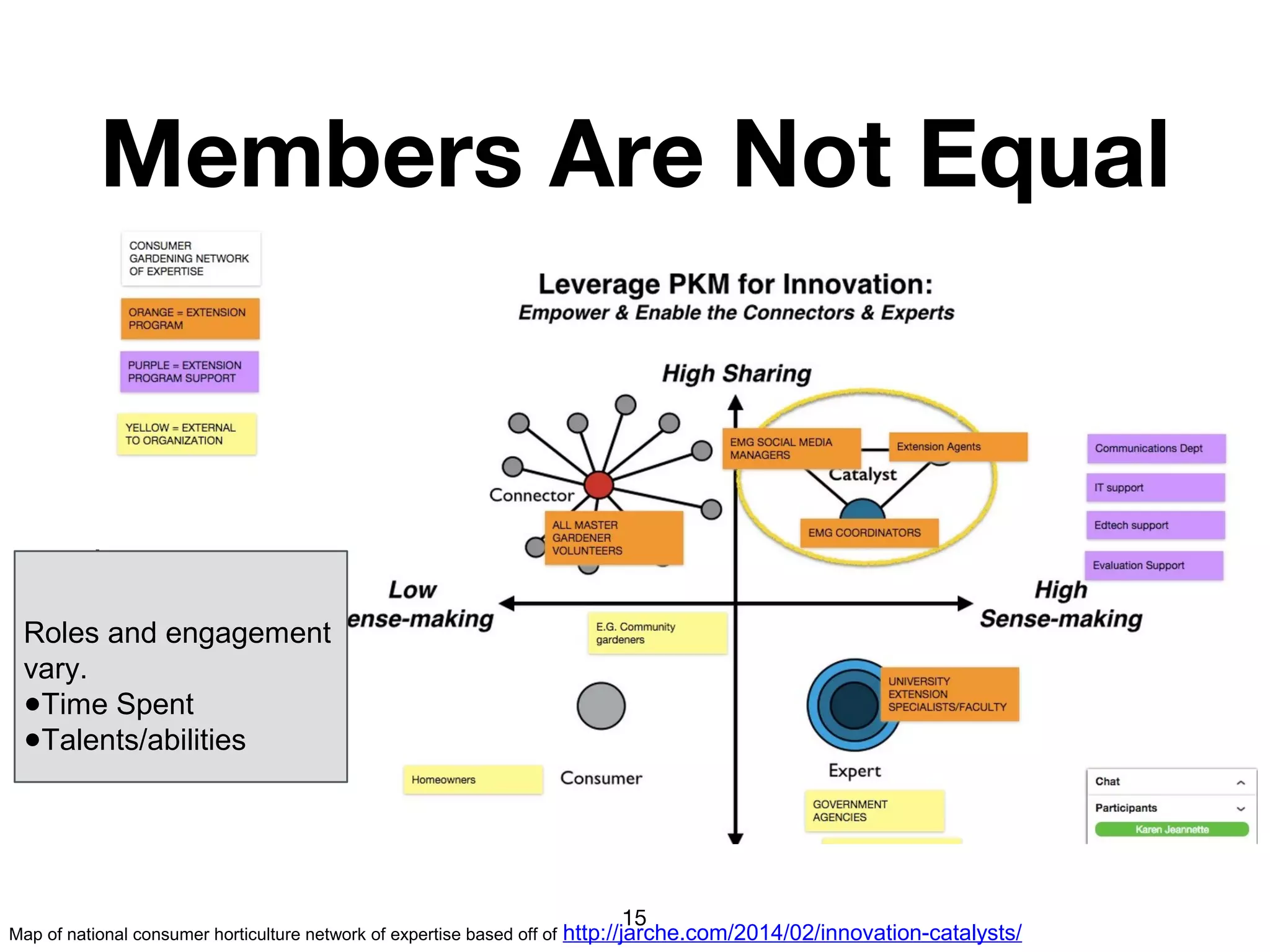
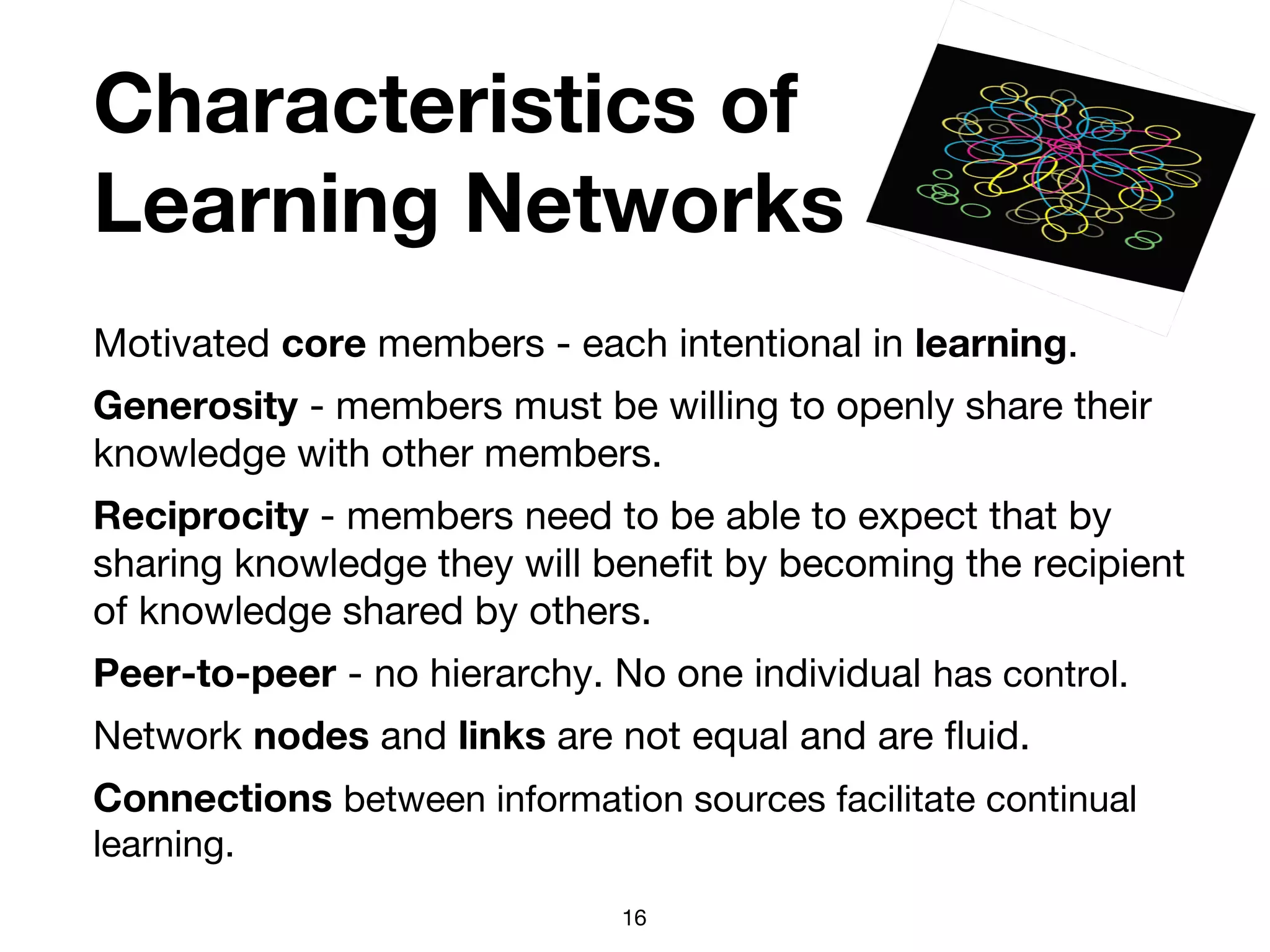
The document discusses the concept of learning networks, emphasizing that learning is a social process occurring through connections among people with shared knowledge and goals. It outlines the phases of network connectivity, alignment, and production, and highlights the importance of diversity and reciprocity within these networks. Ultimately, learning networks foster resilience and agility in individuals and organizations, enabling innovative collaboration to address complex challenges.