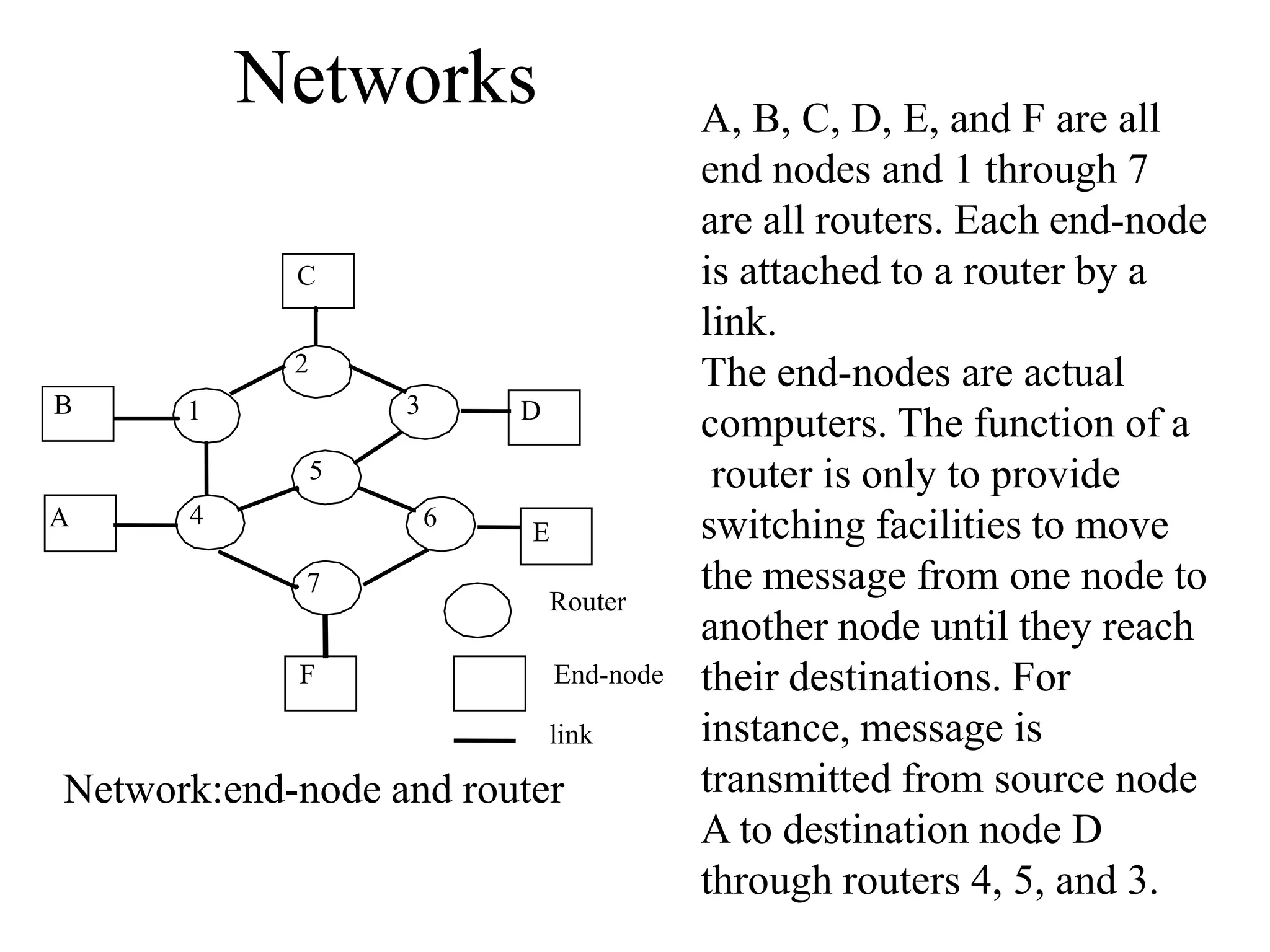
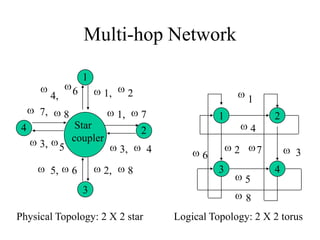
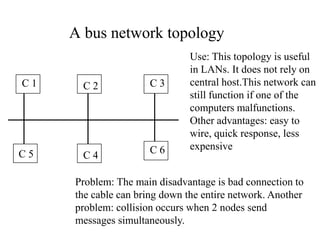
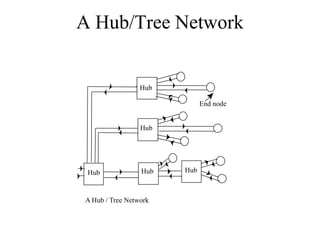
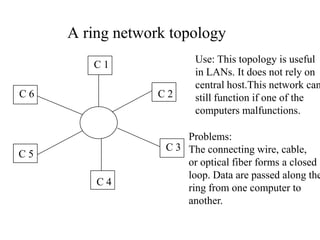
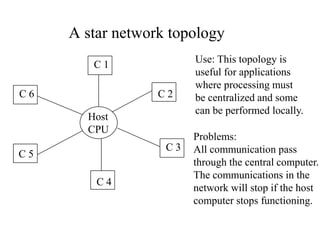
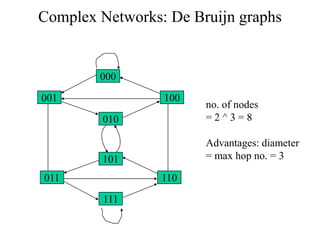
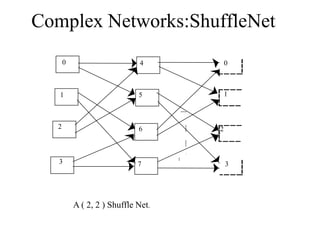
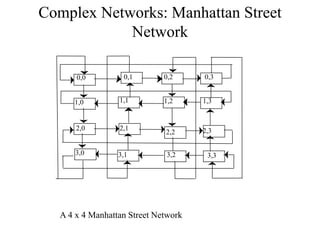
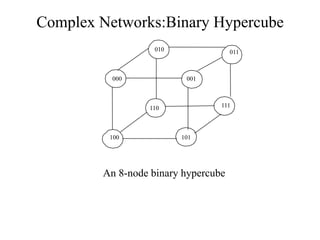
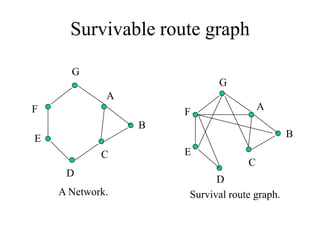
Networks consist of end nodes, routers, and links that connect them. End nodes are actual computers while routers only provide switching facilities to move messages between nodes. There are two main routing techniques - static routing where routes are predetermined, and dynamic routing where routes are calculated when needed and are more efficient. Physical topology defines the physical connections between nodes while logical topology defines the logical connections using the physical topology to optimize performance. Faults in optical networks include channel faults affecting a single wavelength, link faults affecting an entire fiber, and node faults affecting an entire node. These faults can be managed through redundancy and alternate routing.