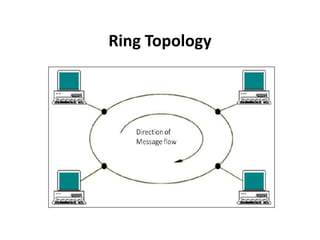
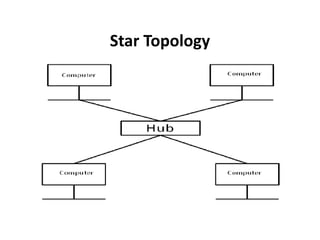
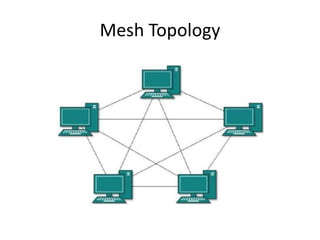
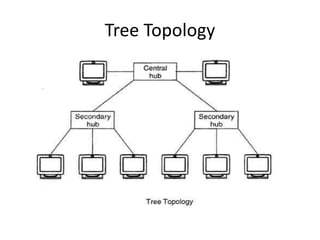
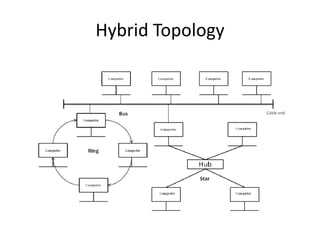
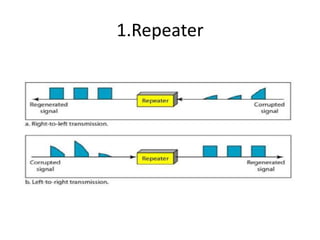
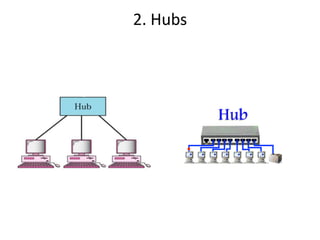
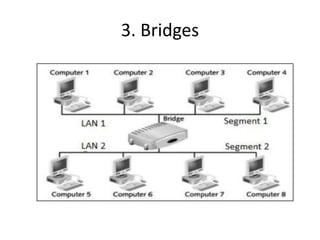
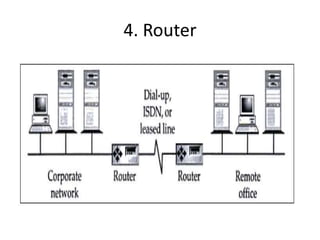
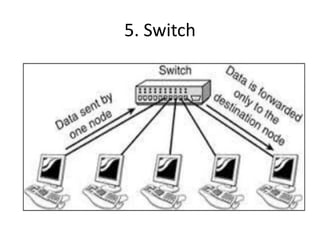
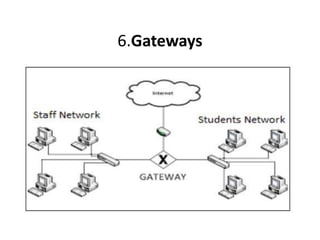
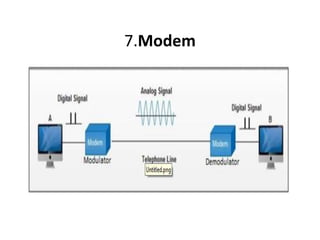
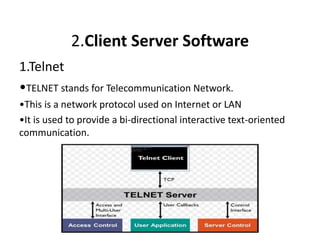
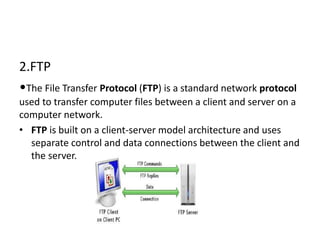
The document outlines various network topologies, including bus, ring, star, mesh, tree, and hybrid topologies, highlighting their physical and logical structures as well as advantages and disadvantages. It also discusses the need for network control devices such as repeaters, hubs, bridges, routers, switches, gateways, and modems, detailing their functions and operational layers. Additionally, the document touches on network software used for communication applications like email and file transfer protocols.