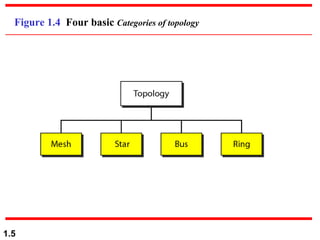
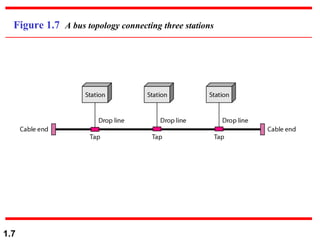
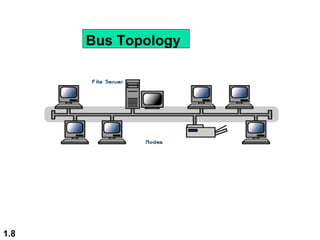
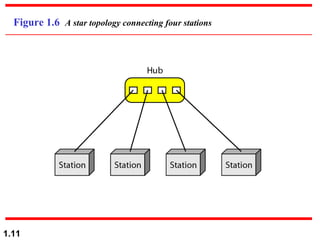
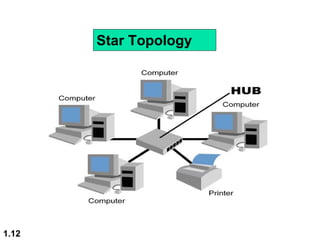
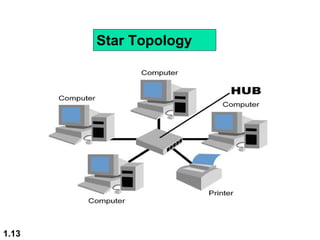
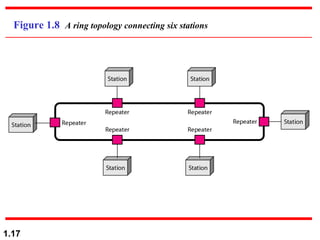
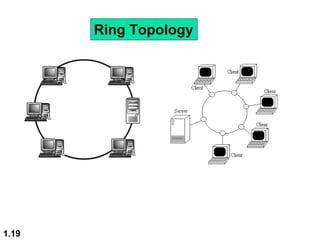
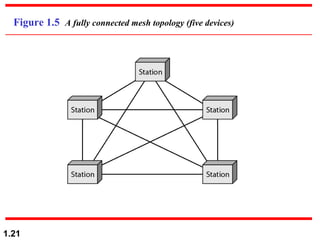
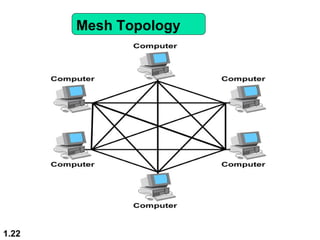
This document discusses different network topologies and modes of data communication. There are three main modes of communication: simplex (unidirectional), half duplex (bidirectional but not simultaneous), and full duplex (simultaneous bidirectional). The four basic network topologies covered are bus, star, ring, and mesh. A bus topology connects all devices to a single cable backbone. A star topology connects each device to a central hub/switch. A ring topology connects each device in a continuous loop, passing signals in one direction. A mesh topology connects each device to every other device through dedicated links, providing redundancy if one link fails.