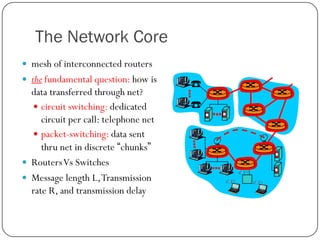
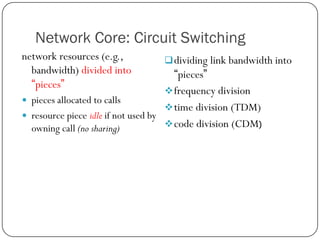
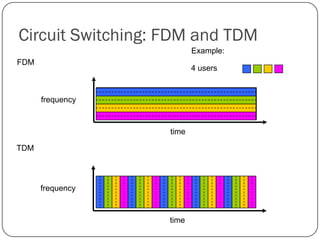
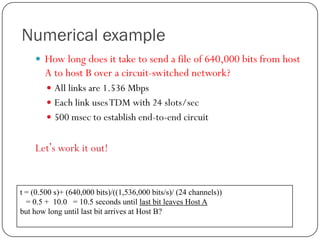
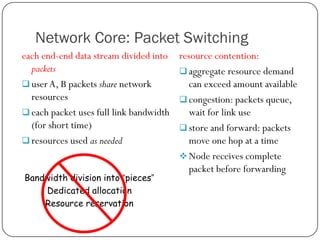
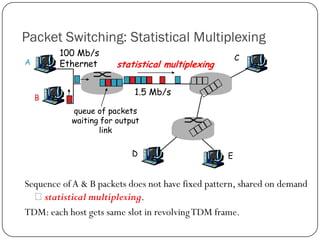
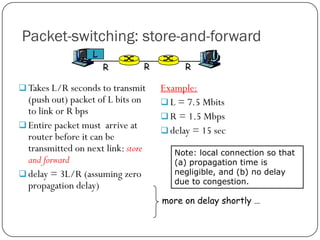
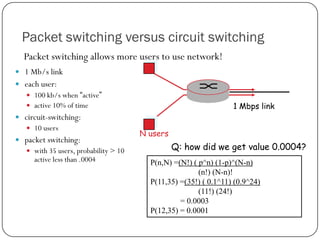
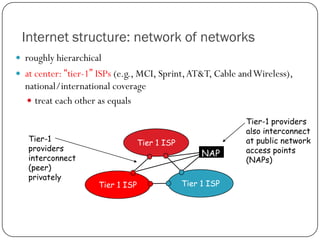
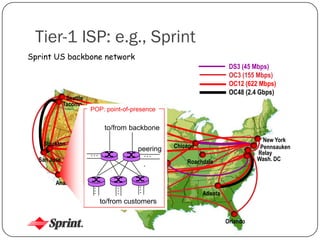
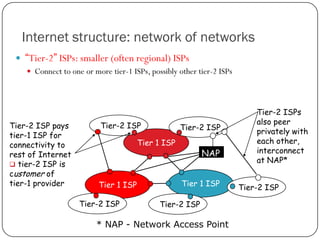
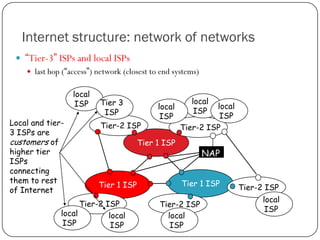
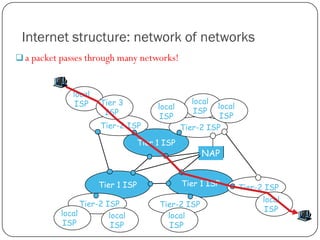
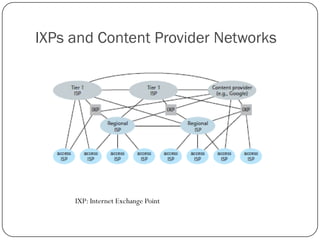
The document discusses packet switching and circuit switching in computer networks. It defines packet switching as dividing data into discrete chunks or packets that are sent through the network and shared across network resources. In circuit switching, dedicated circuits are established for each connection, reserving bandwidth for the duration even if not in use. The document also outlines the hierarchical structure of the Internet, made up of tier 1, 2, and 3 ISPs that connect end users and pass traffic through multiple networks of routers and switches.