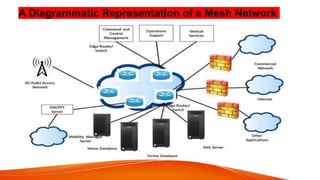
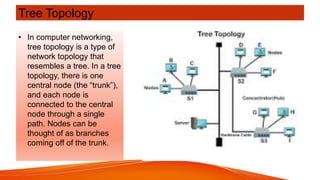
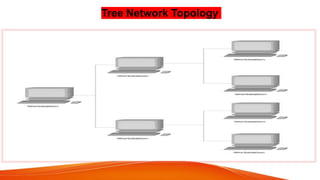
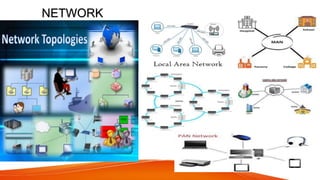
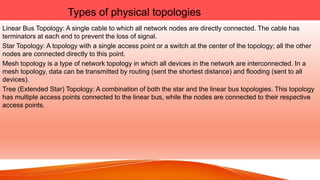
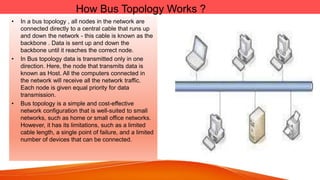
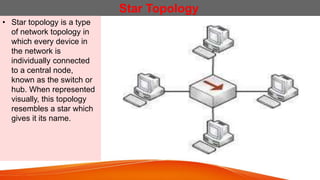
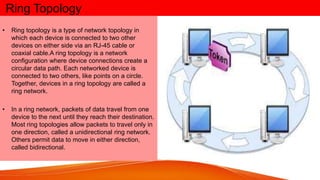
Network topologies define the layout of connections between nodes in a computer network. The physical topology refers to the actual layout of cables and connections, while the logical topology defines how data is transmitted. Common network topologies include bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree. Each has advantages and disadvantages depending on the network size and needs. The bus topology is inexpensive but has limitations on cable length and number of devices. Star topology is robust but requires more cable and hardware. Ring topology has no central point of failure but a single fault disables the whole network. Mesh networks are highly redundant but also complex and expensive to implement.







![Advantages and Disadvantages of Ring Topology
• Advantages
• Performs better than a bus topology under heavy network
load
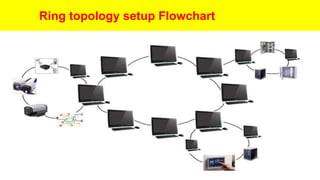
• Does not require a central node to manage the connectivity
between the computers
• Due to the point-to-point line configuration of devices with a
device on either side (each device is connected to its
immediate neighbor), it is quite easy to install and reconfigure
since adding or removing a device requires moving just two
connections.
• Point-to-point line configuration makes it easy to identify and
isolate faults.
• Ring Protection reconfiguration for line faults of bidirectional
rings can be very fast, as switching happens at a high level,
and thus the traffic does not require individual rerouting.
• Ring topology helps mitigate collisions in a network.[5]
• Very orderly network where every device has access to the
token and the opportunity to transmit
• Disadvantages
• One malfunctioning workstation can create
problems for the entire network. This can be
solved by using a dual ring or a switch that closes
off the break.[6]
• Moving, adding and changing the devices can
affect the network
• Communication delay is directly proportional to
number of nodes in the network
• Bandwidth is shared on all links between devices
• More difficult to configure than a Star: node
adjunction = Ring shutdown and reconfiguration[7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internetnetworktopologypresentationpowerpointaditya-230630080702-915393fa/85/INTERNET-NETWORK-TOPOLOGY-PRESENTATION-POWERPOINT-ADITYA-pptx-15-320.jpg)