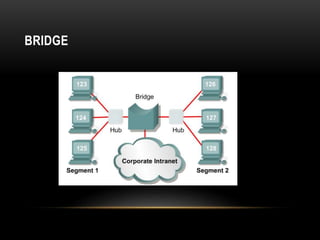
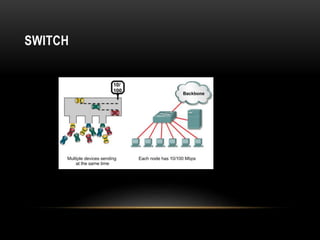
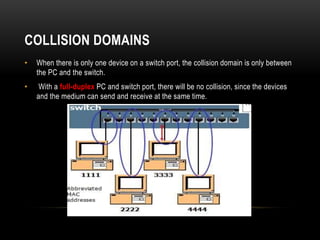
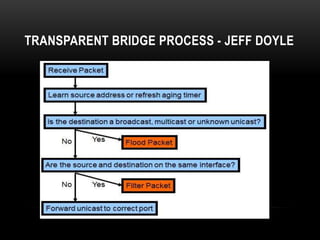
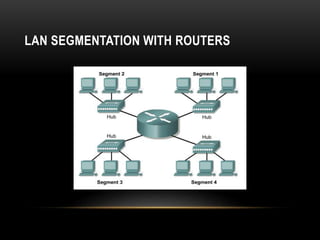
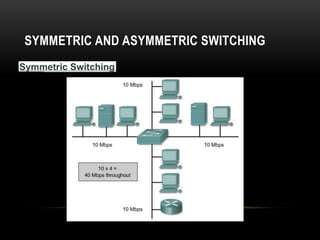
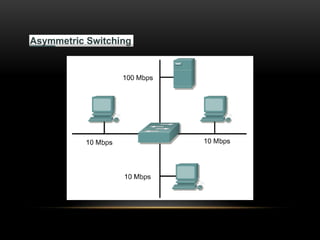
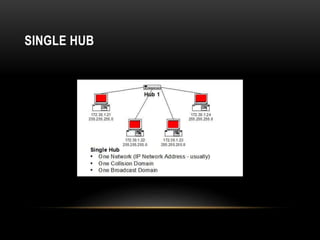
This document discusses different networking devices and concepts for connecting devices in a local area network (LAN). It describes bridges, switches, routers, hubs, and repeaters. Bridges segment networks at layer 2, switches create virtual circuits to maximize bandwidth, and routers route traffic between layer 3 networks. The document also covers half and full duplex transmissions, collision domains, broadcast domains, and how devices such as hubs, switches, and routers handle sending and receiving Ethernet frames. It discusses using VLANs to create separate broadcast domains within a switch and needing routers to pass traffic between VLANs.