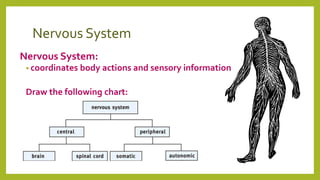
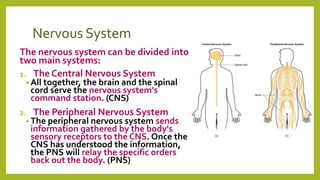
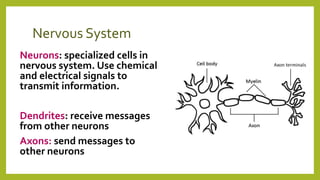
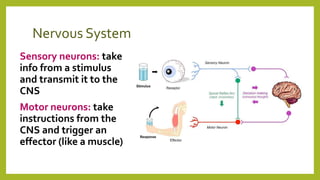
The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The PNS sends sensory information to the CNS and carries out the CNS's instructions through the body. The peripheral nervous system consists of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions, and the somatic system, which controls voluntary movement and reflexes. Neurons are the basic functional units that transmit chemical and electrical signals throughout the nervous system.