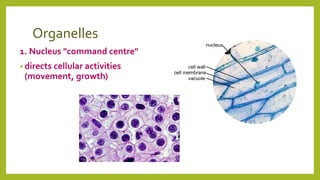
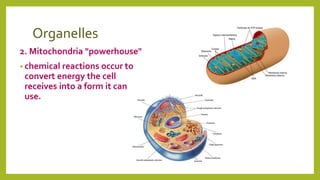
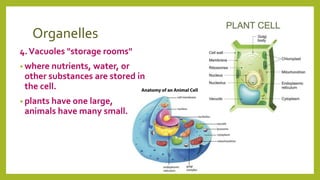
All organisms are made of cells, which contain specialized structures called organelles that each perform a specific function. Cells work together to form tissues, organs, and organ systems. Cells can be thought of as living factories containing organelles that act as the nucleus directing activities, mitochondria generating energy, a cell membrane controlling what enters and exits, vacuoles storing materials, cytoplasm providing nutrients, and in plant cells, a cell wall providing structure and chloroplasts carrying out photosynthesis.