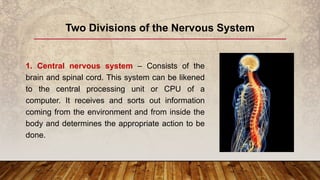
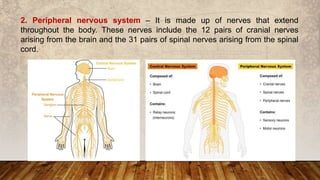
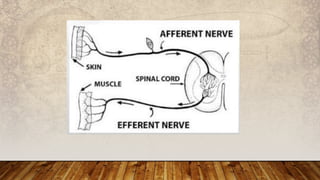
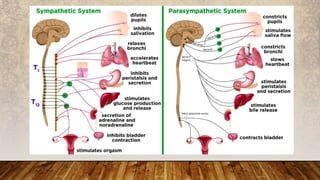
The nervous system has three main functions: (1) receive information from inside and outside the body, (2) interpret received information, and (3) make the body respond accordingly. It consists of the central nervous system, made up of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system of nerves throughout the body. The peripheral nervous system has two divisions - the somatic division for voluntary movement and reflexes, and the autonomic division for involuntary functions like digestion.