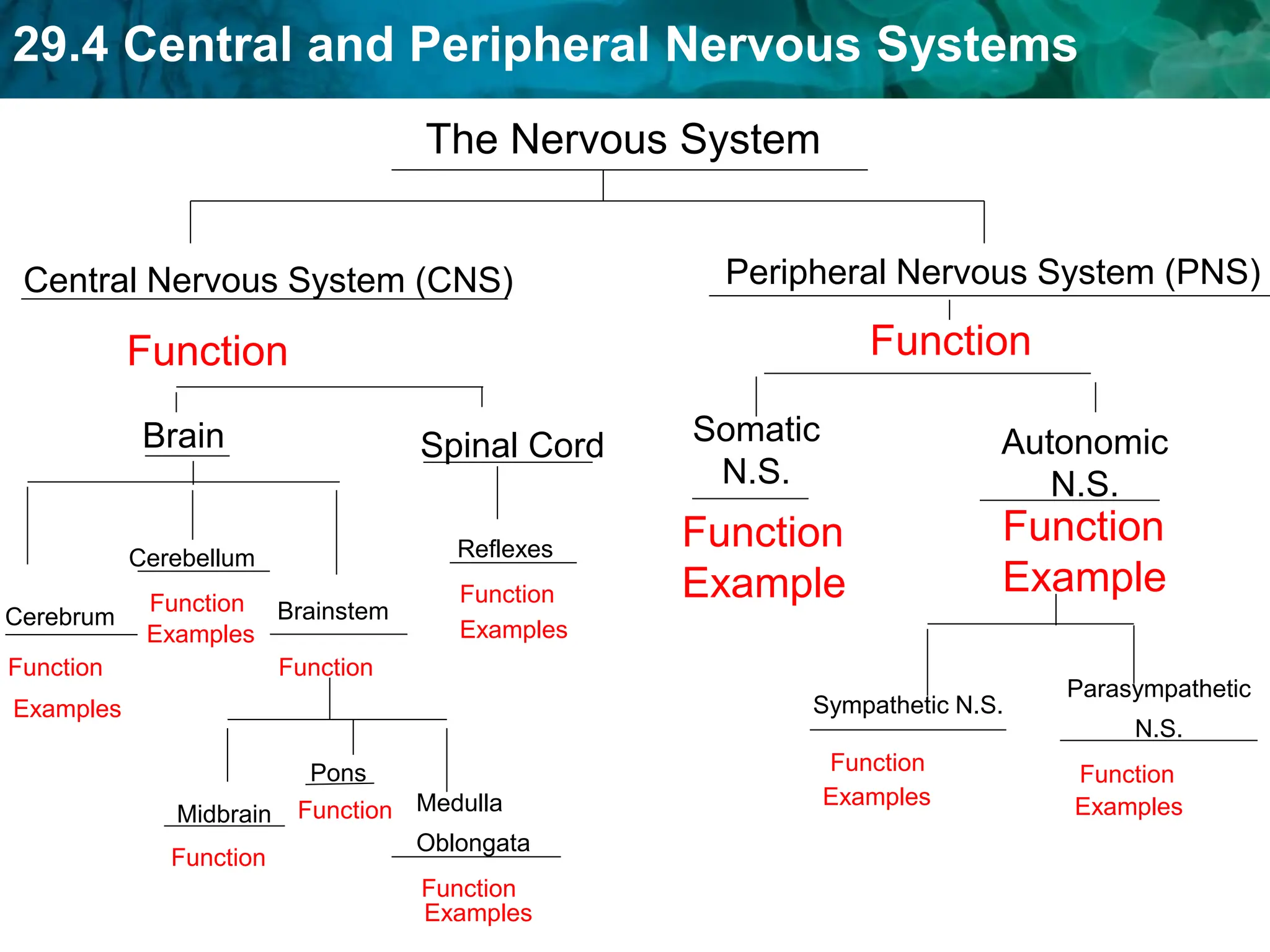
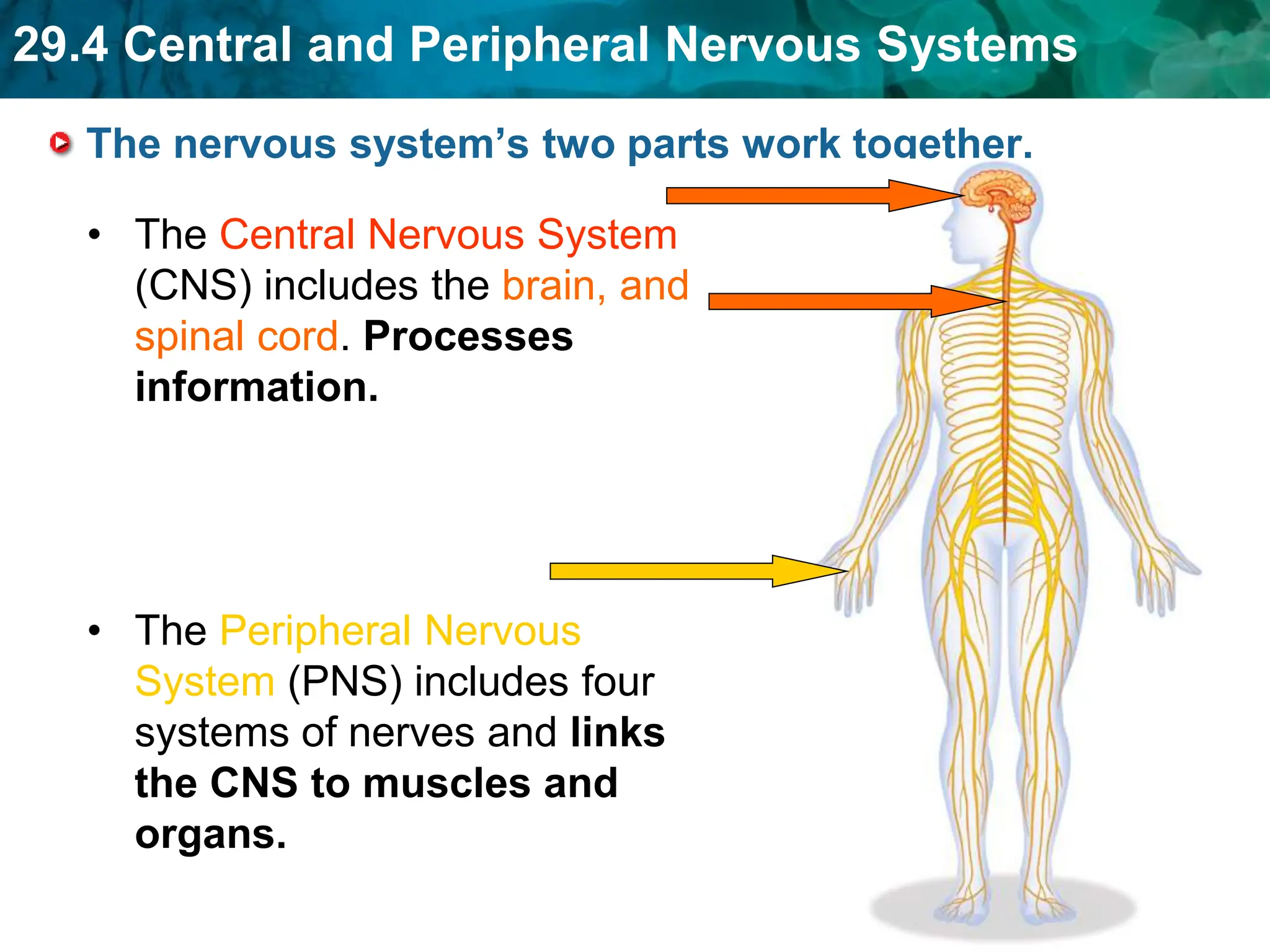
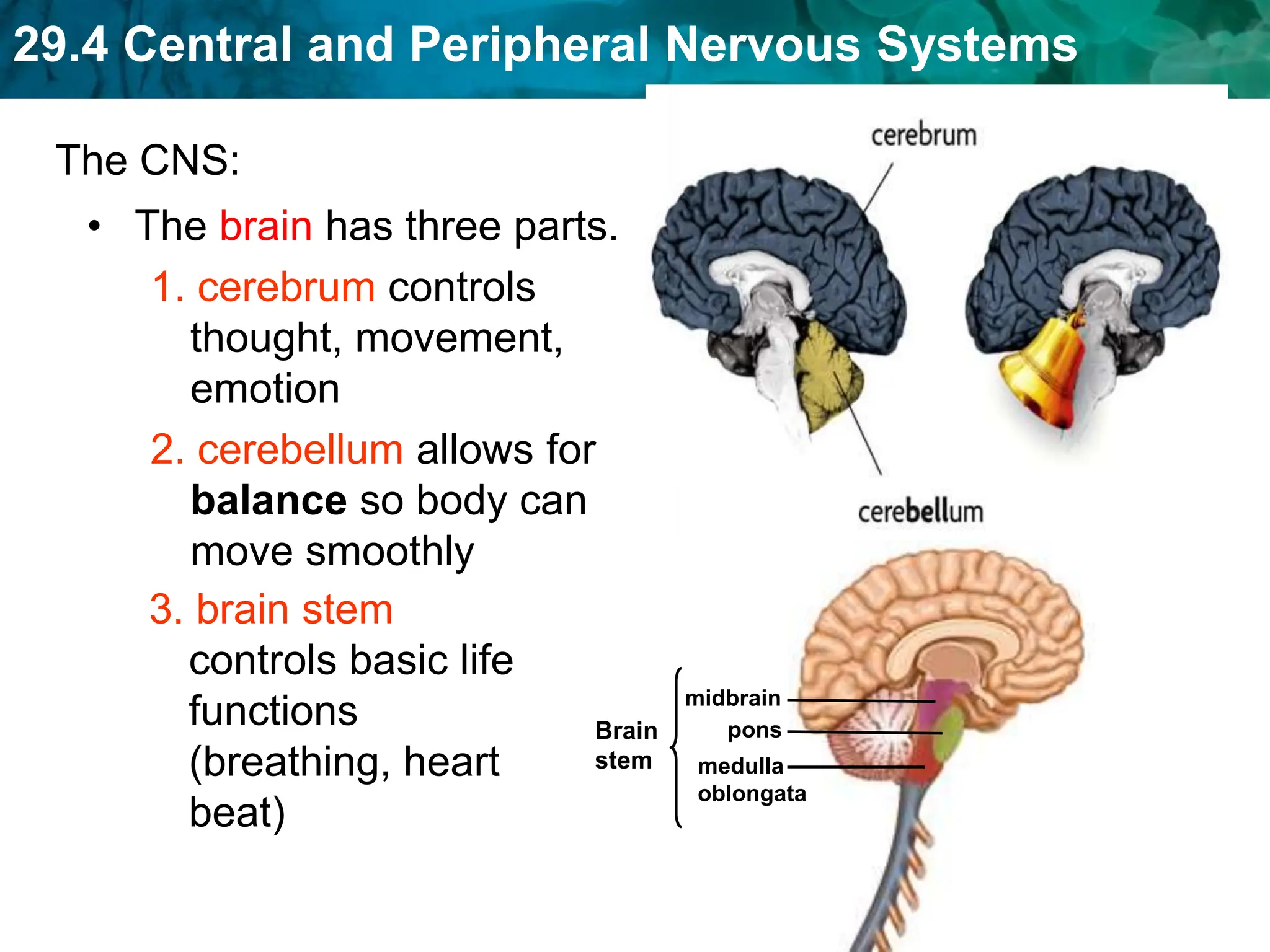
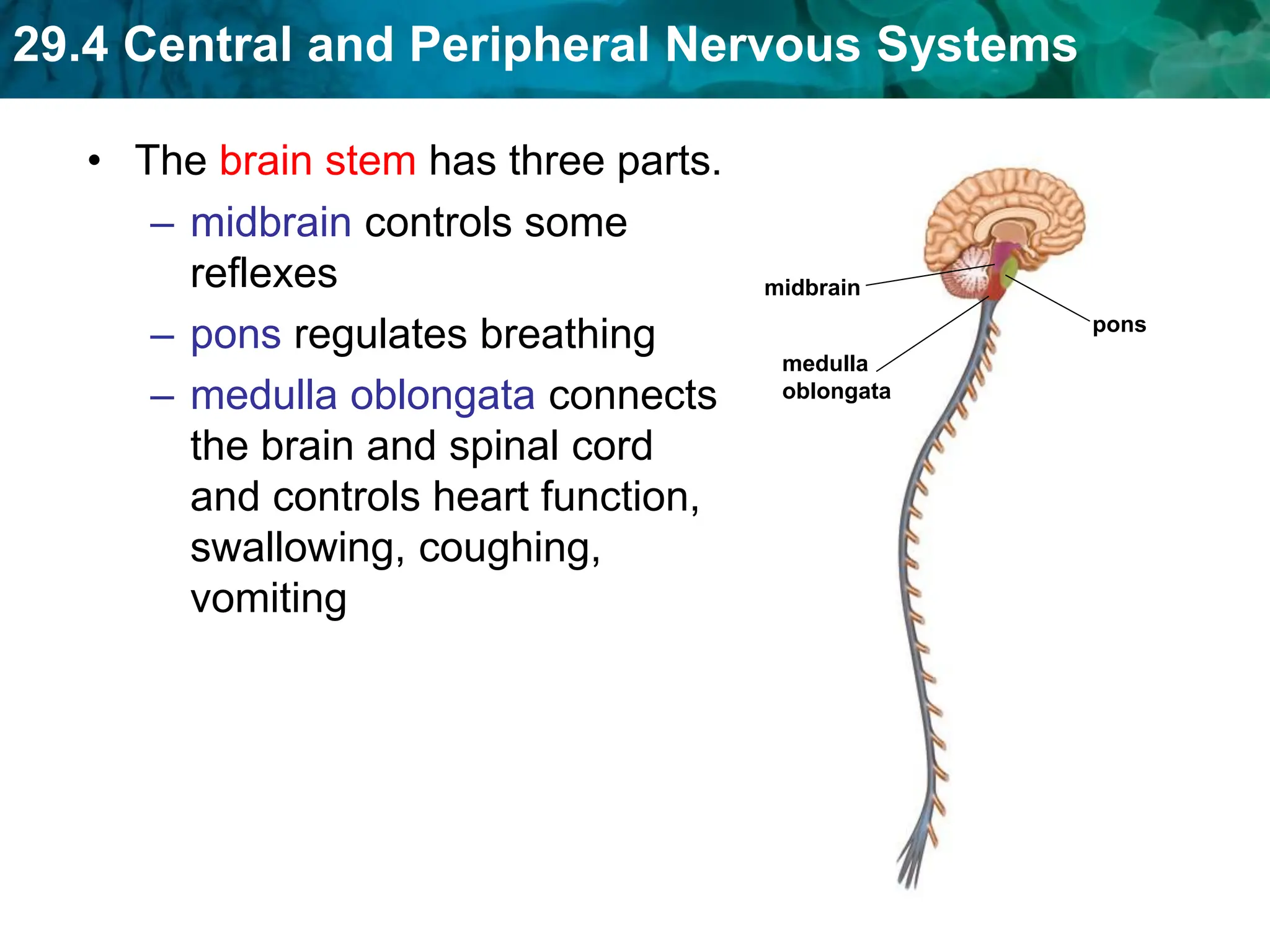
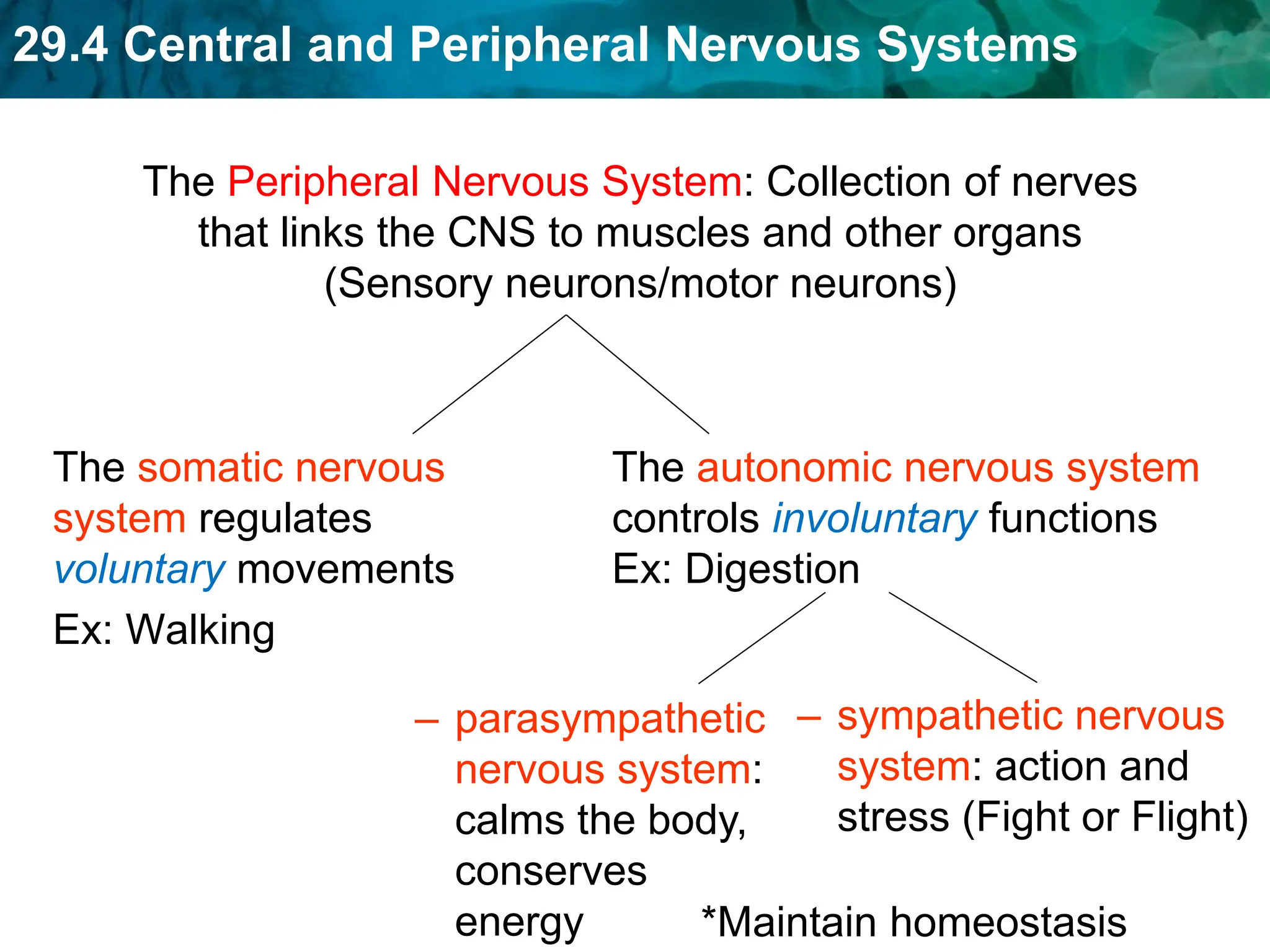
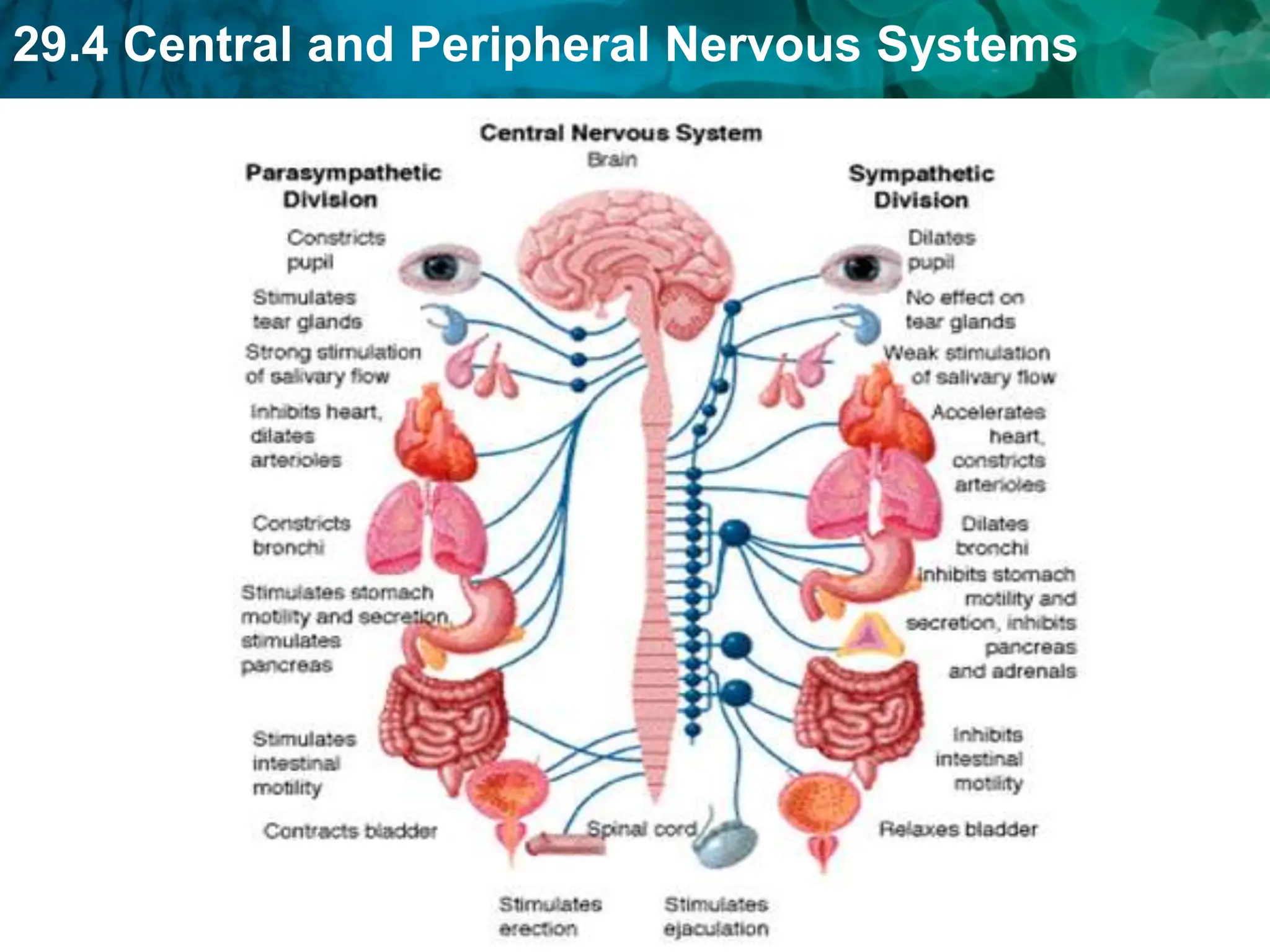
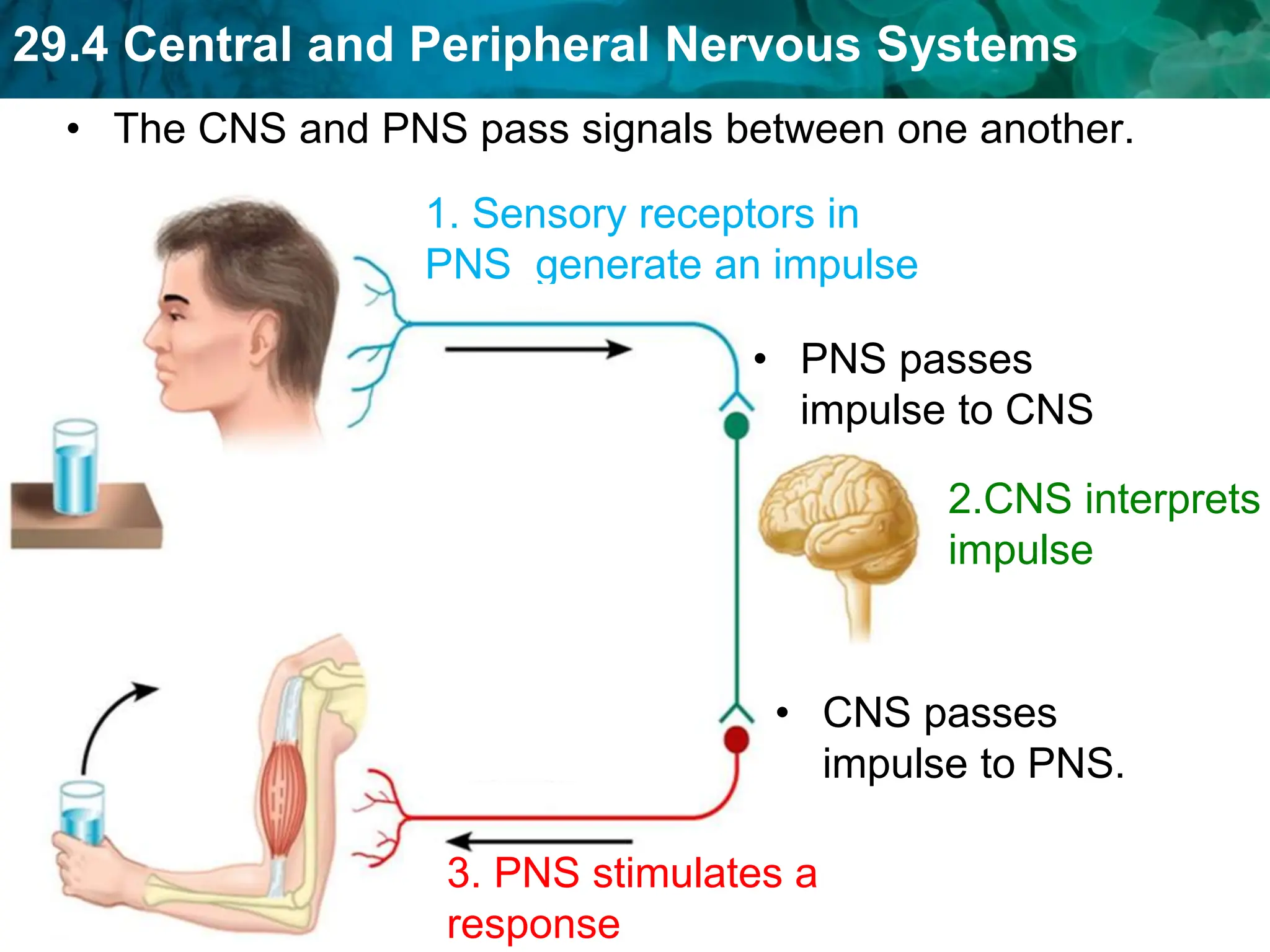
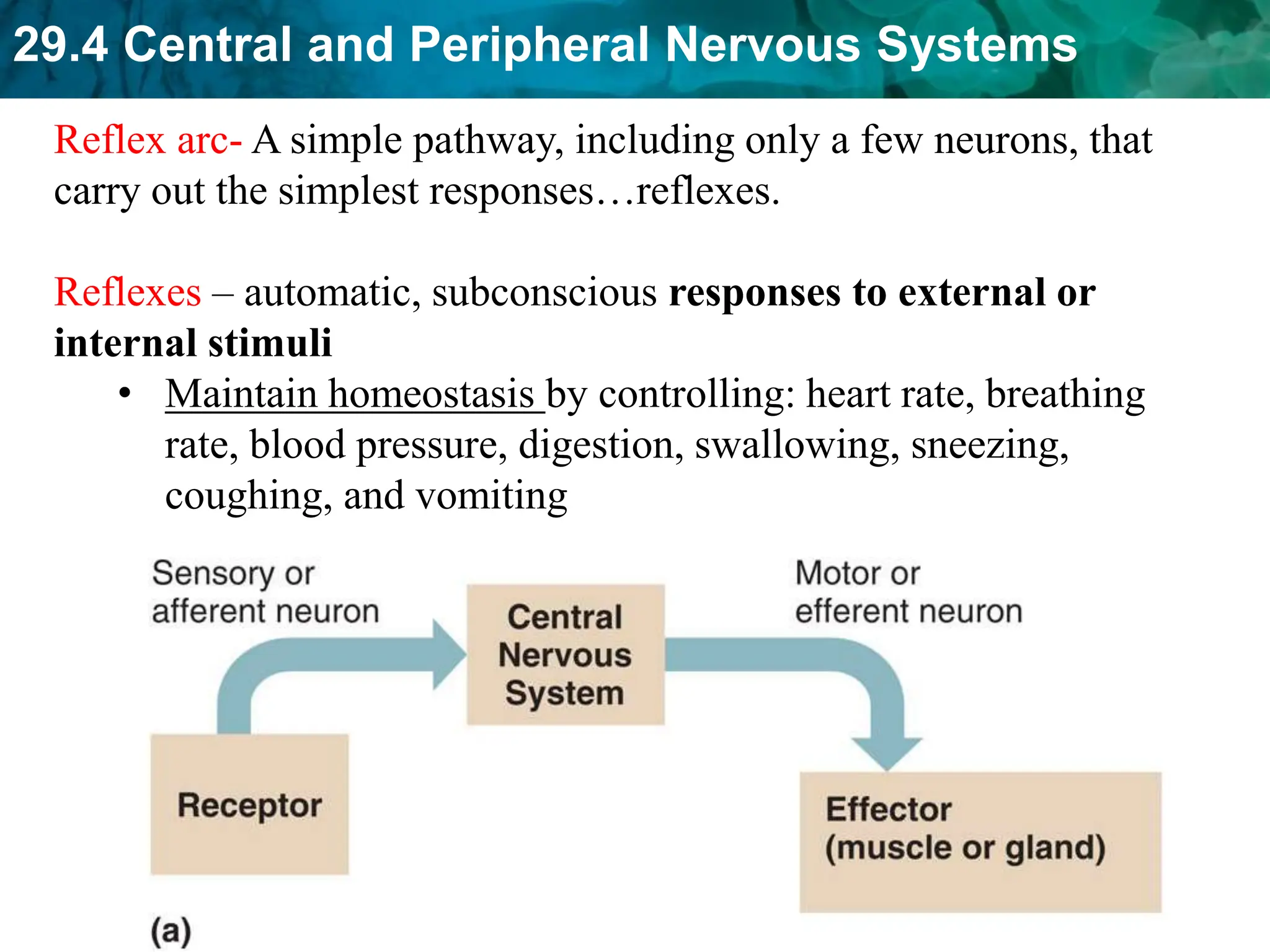
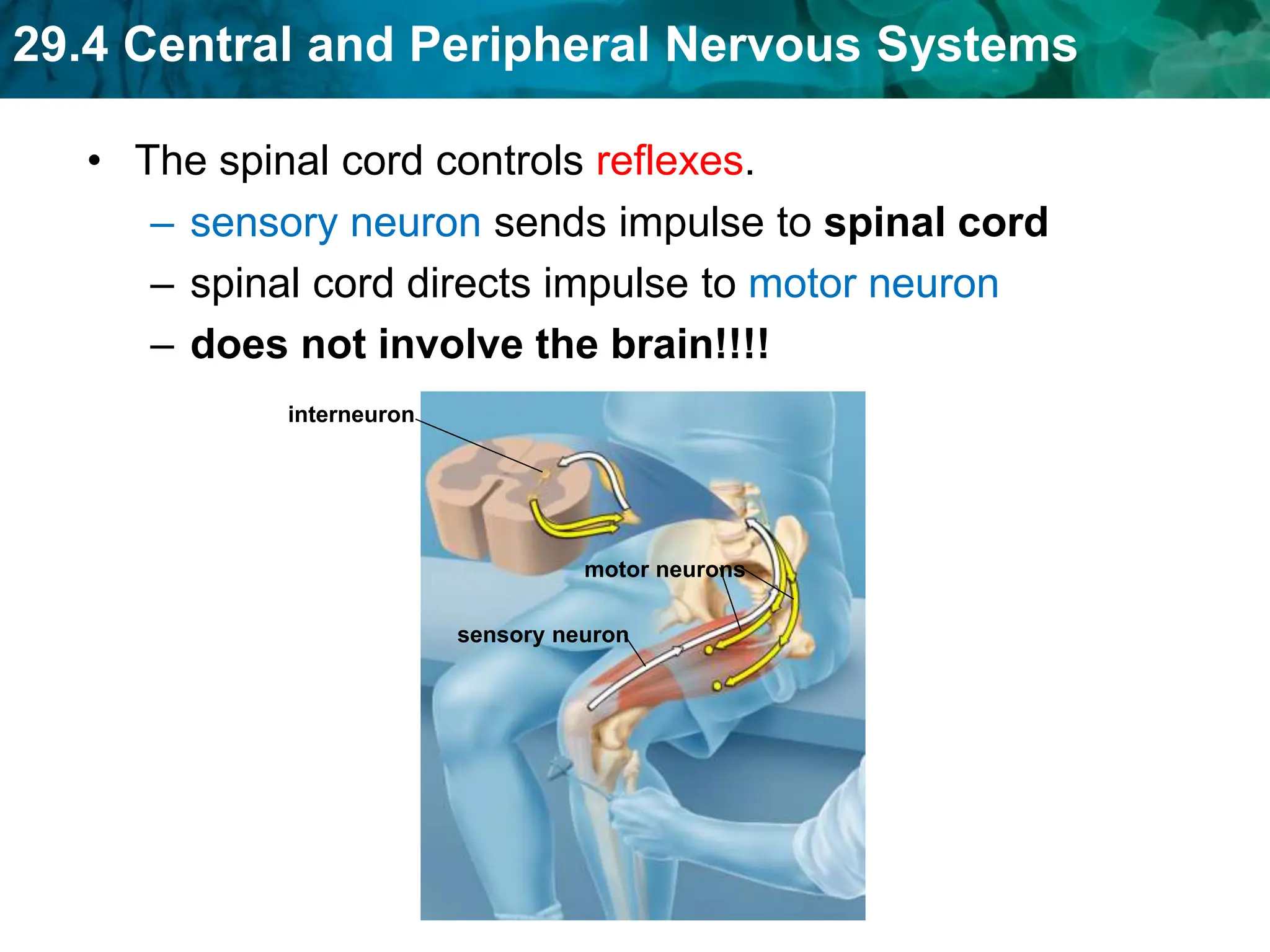
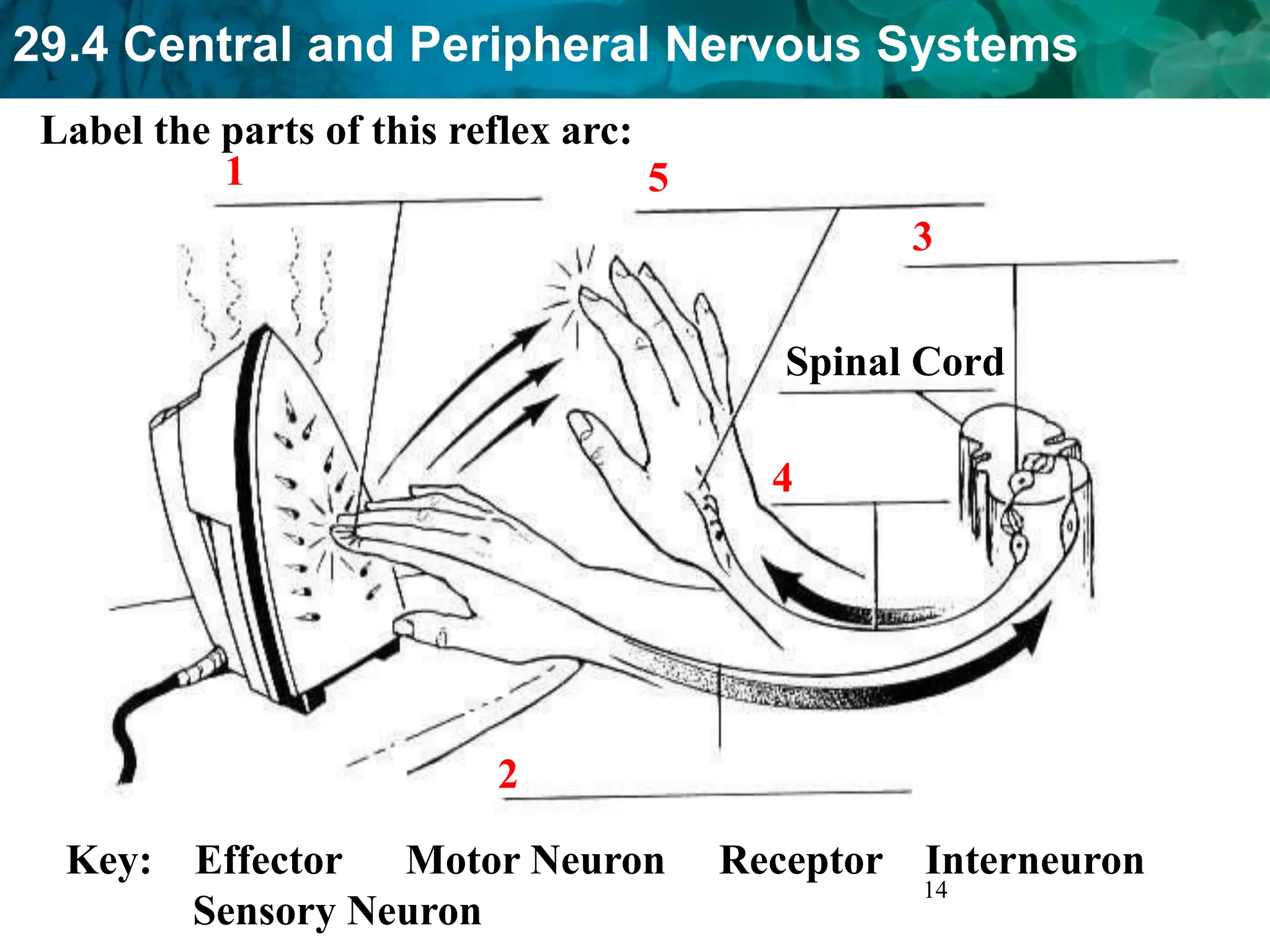
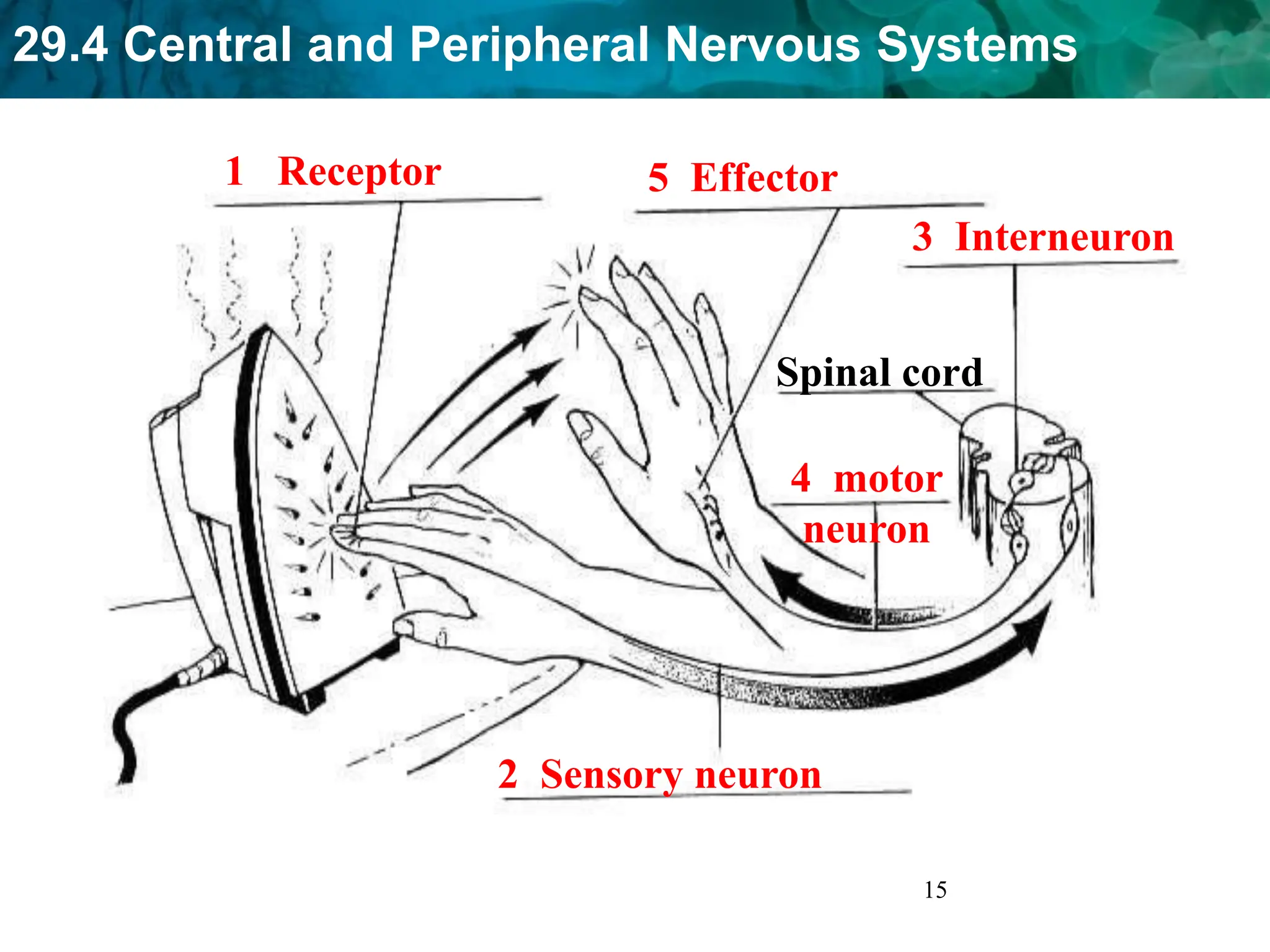
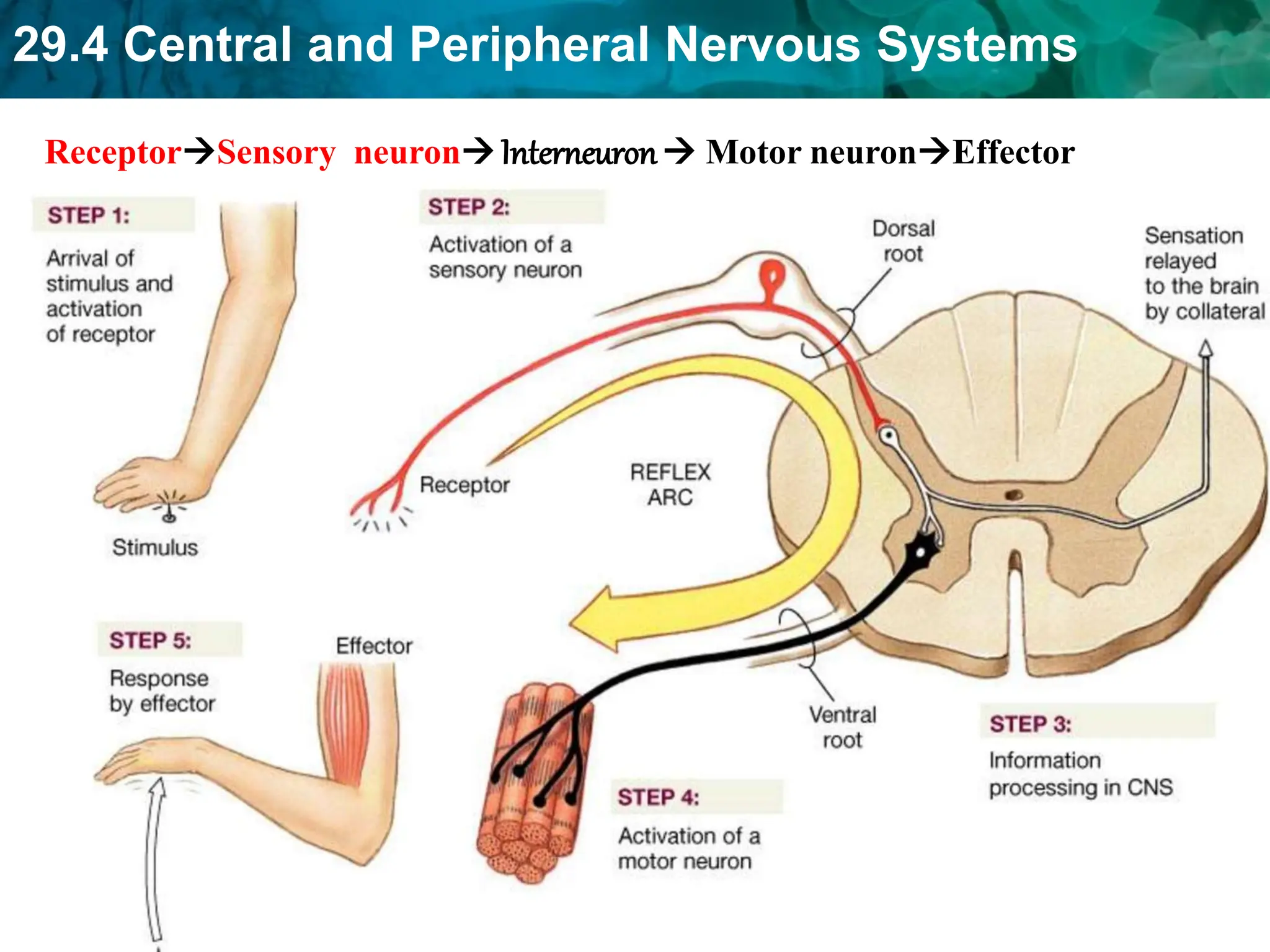
The document outlines the functions and components of the central and peripheral nervous systems, highlighting the roles of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in processing and transmitting signals. It describes how the central nervous system (CNS) processes information while the peripheral nervous system (PNS) connects the CNS to muscles and organs, maintaining homeostasis. Additionally, it explains the reflex arc as a simple pathway for automatic responses that do not involve the brain.