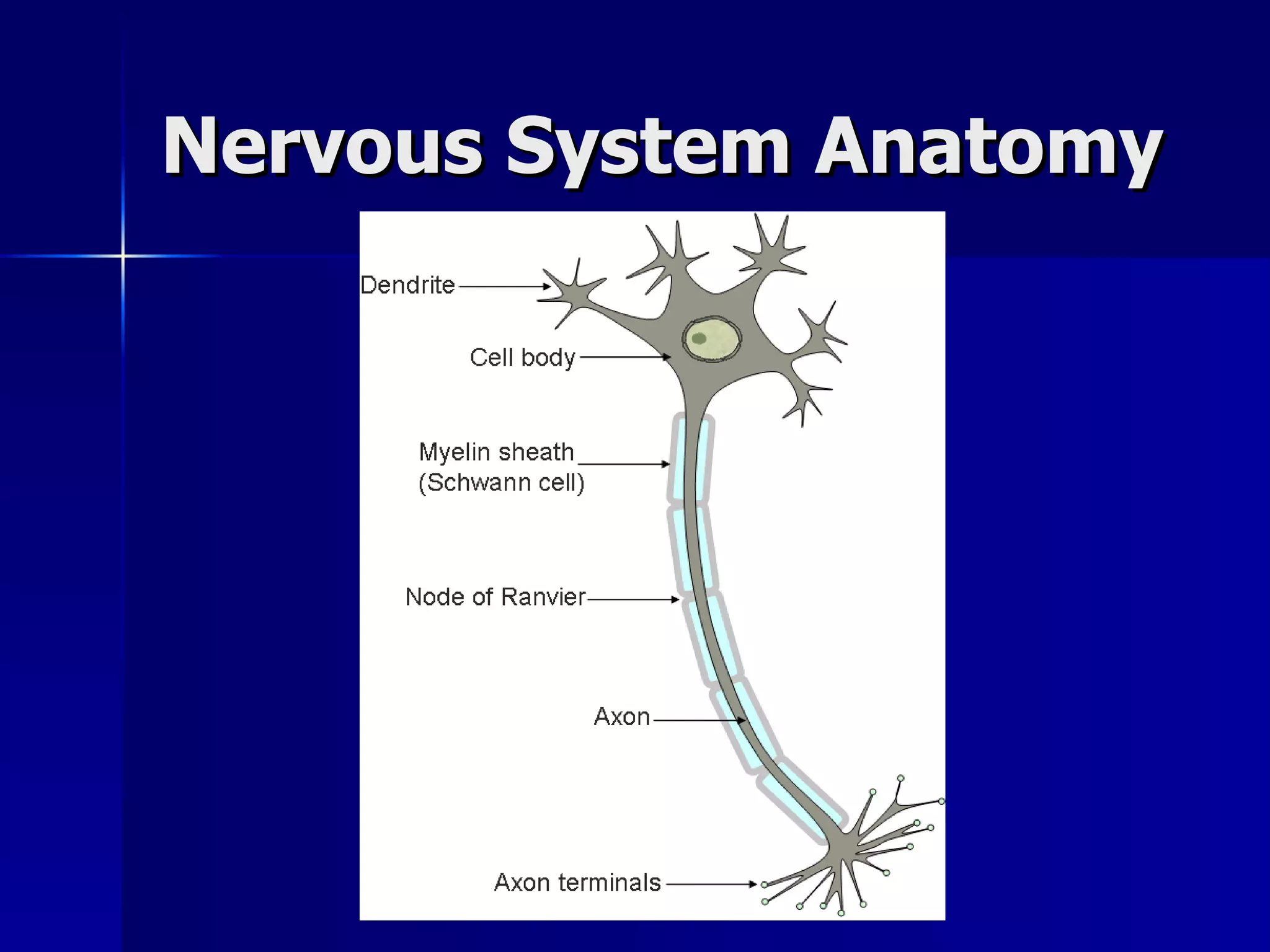
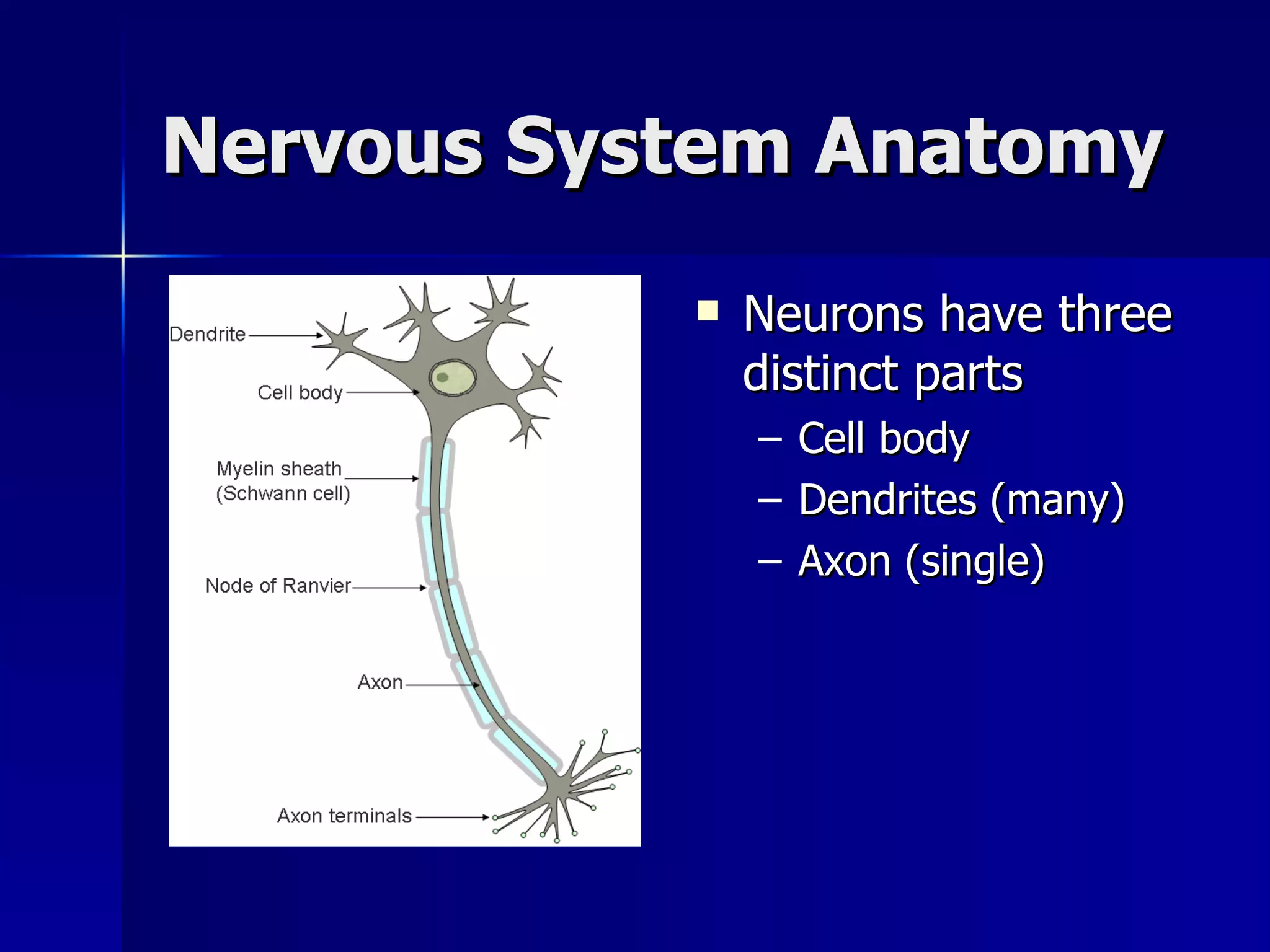
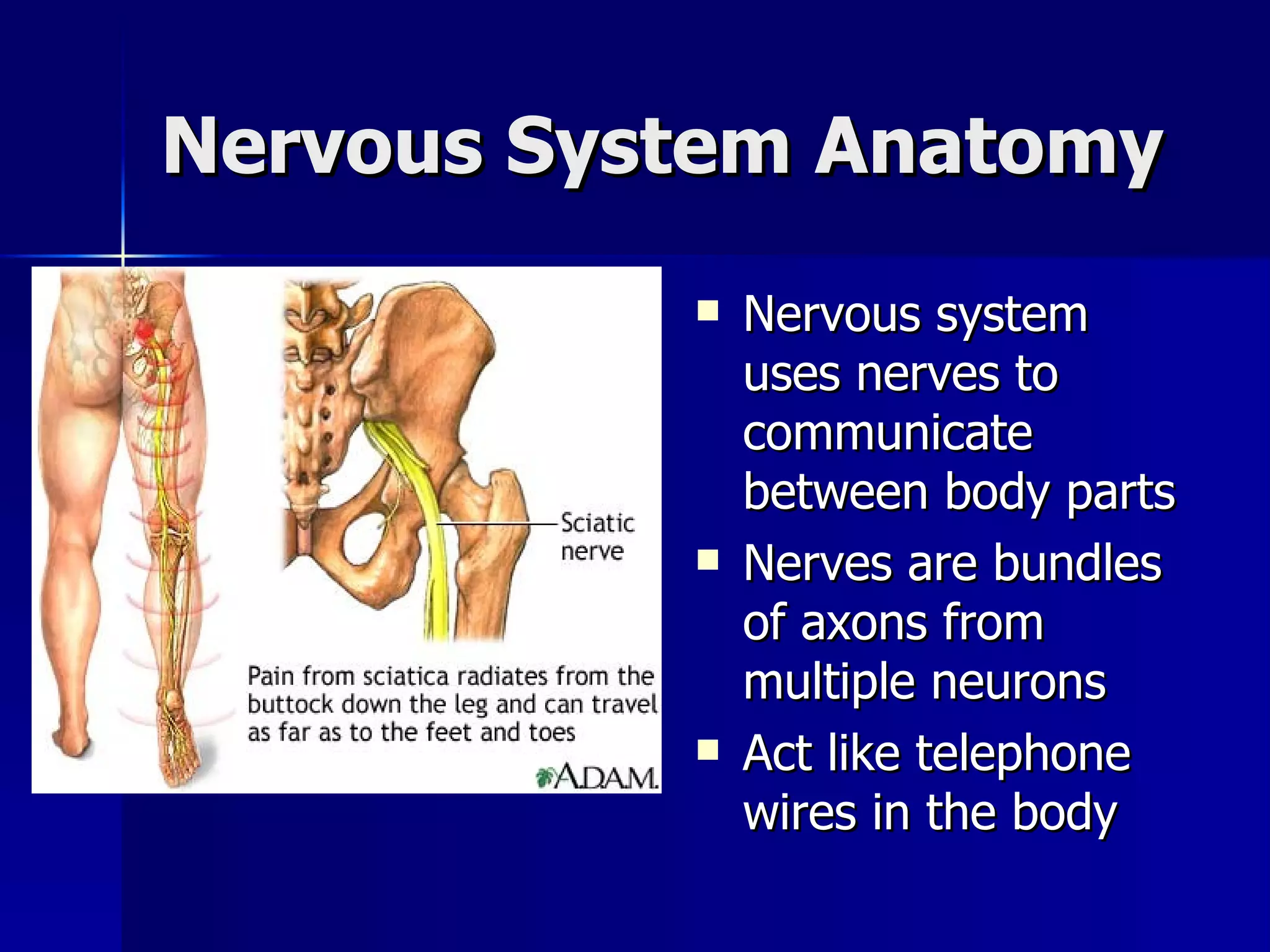
The document provides an overview of the nervous system, including its main functions, anatomy, and divisions. The nervous system coordinates movement, senses the environment, and integrates senses. It is composed of neurons and neuroglial cells and uses electrochemical signals to communicate via nerves between parts of the body. The nervous system can be divided into the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which connects the CNS to the rest of the body. The PNS is further divided into the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions, and the somatic nervous system, which controls voluntary functions.