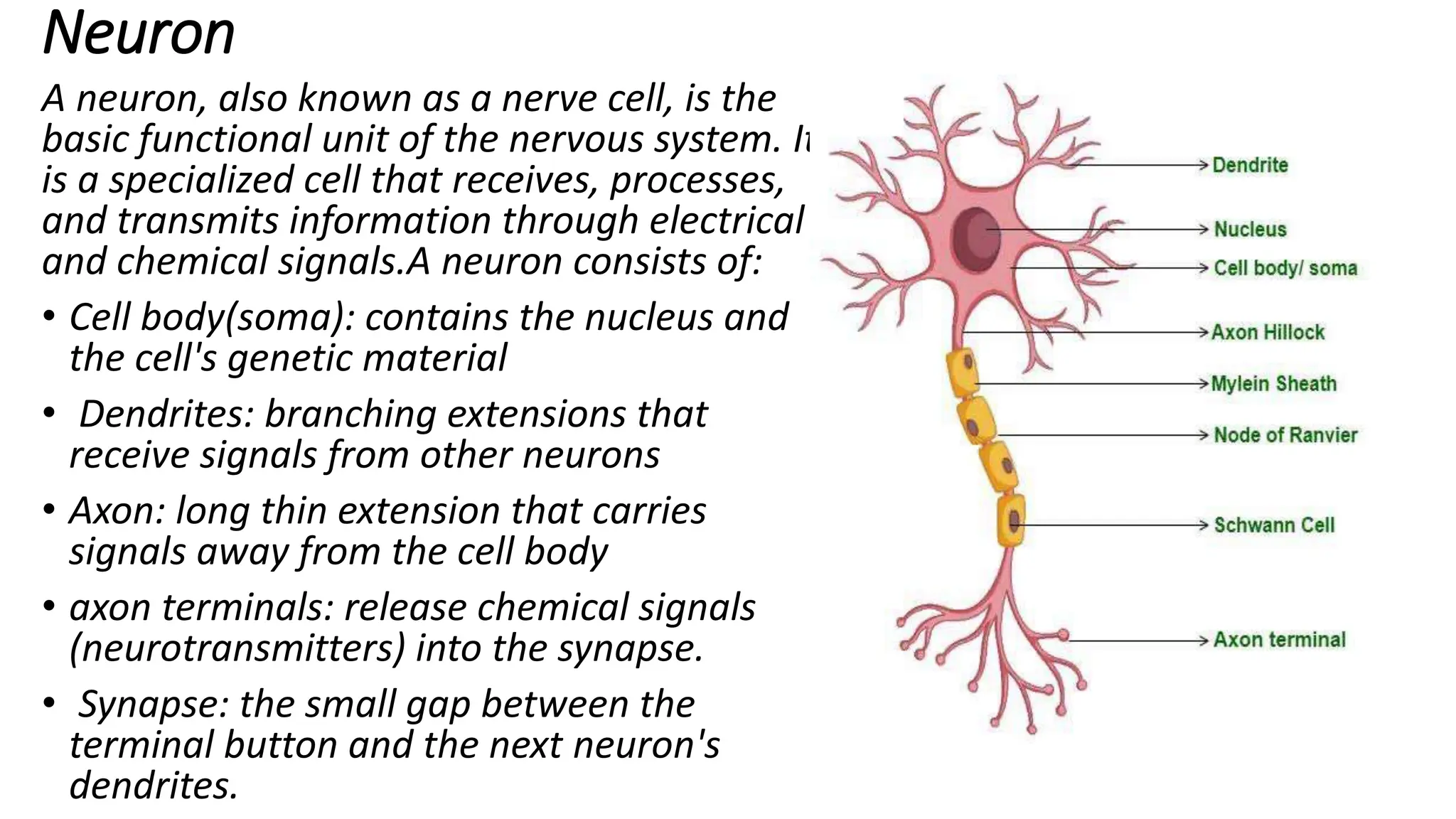
The nervous system is a complex network that coordinates body functions through the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord, managing voluntary actions and cognitive processes, while the PNS connects sensory receptors, muscles, and glands, further divided into the somatic and autonomic systems. Neurons, the functional units of the nervous system, transmit information through specialized structures including dendrites, axons, and synapses.