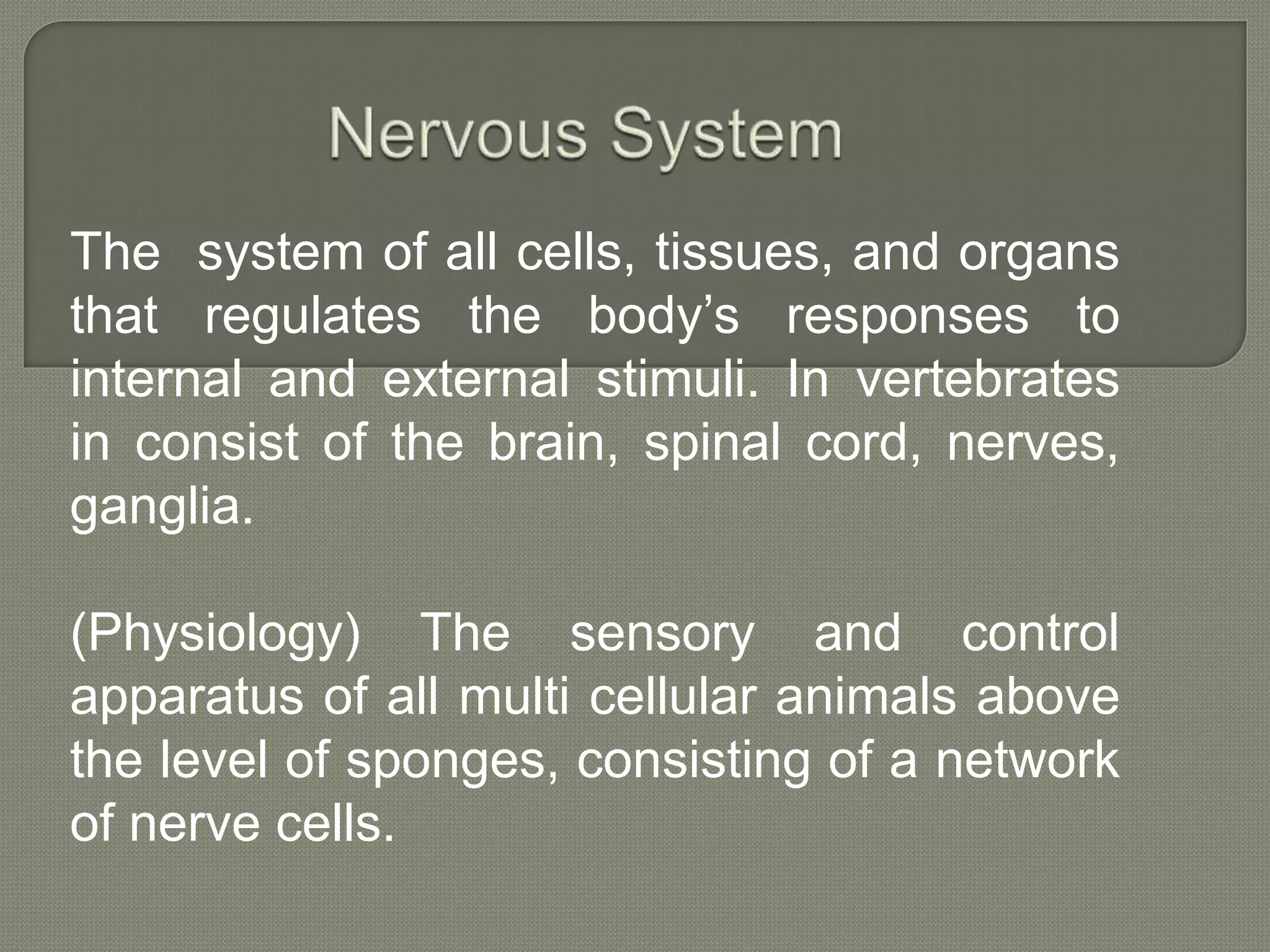
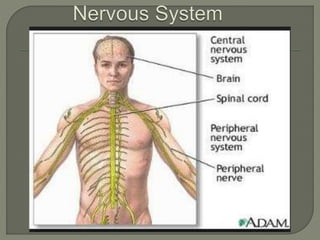
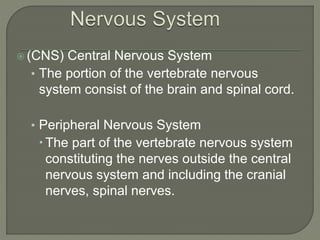
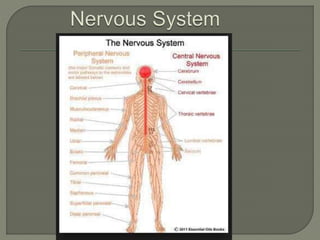
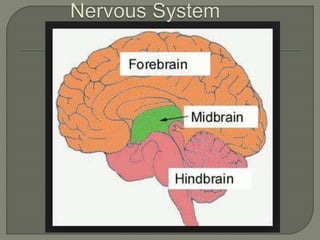
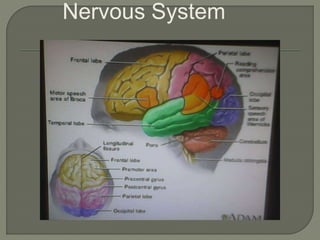
The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and ganglia. It regulates responses to internal and external stimuli. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is outside the central nervous system and includes cranial and spinal nerves. The brain is divided into the hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain. It serves functions like imagination, memory, speech, movement, and hormone secretion. Neurons and glial cells make up brain tissue and neurons communicate via synapses.