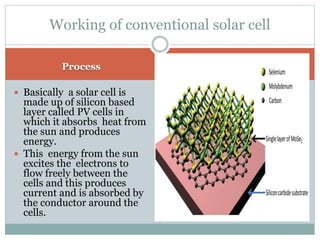
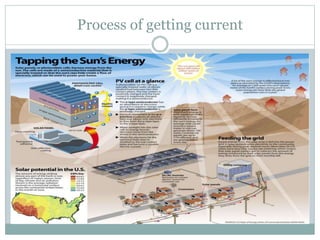
Nanotechnology applications in solar cells can improve energy efficiency. Conventional solar cells use silicon layers to absorb sunlight and produce energy by exciting electrons. Scientists have developed plastic solar cells that use nanorods and nanotechnology to absorb infrared light on cloudy days. The plastic cells are more compact and efficient than silicon cells. While initial costs may be higher, plastic solar cells could eventually be lower cost and more flexible, allowing applications like painting solar material on surfaces. Further research aims to improve light absorption and transfer of electrons for higher efficiency plastic solar cells.