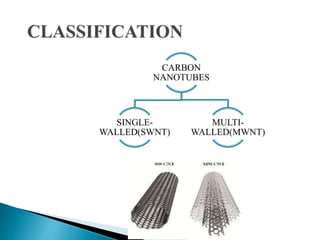
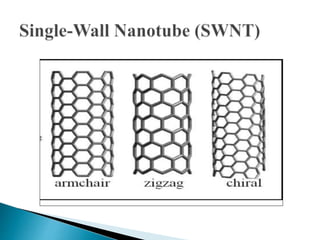
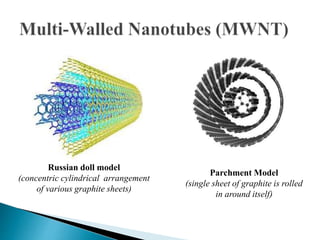
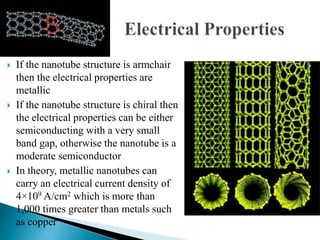
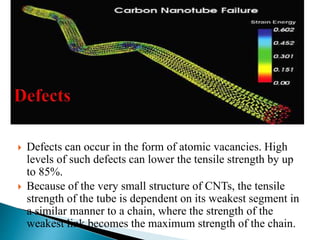
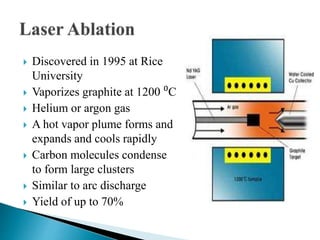
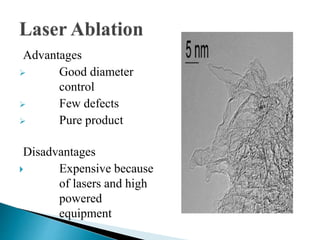
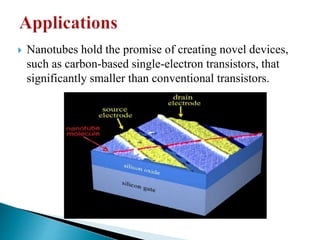
This document discusses carbon nanotubes, including their discovery in the 1950s, classification as single-walled or multi-walled nanotubes, properties like strength and conductivity, common synthesis methods like arc discharge and chemical vapor deposition, and potential applications such as for solar cells, sporting goods, and neural networks. It also notes potential health risks from short carbon nanotubes and the need for further research on impacts.