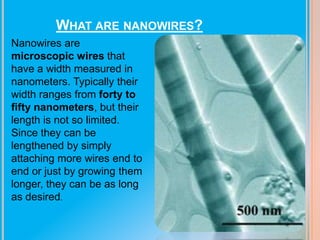
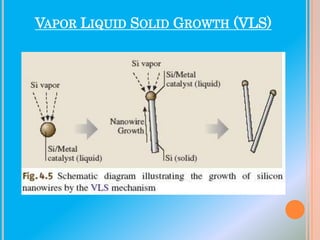
Nanowires are microscopic wires that have widths measured in nanometers, ranging from 40-50 nanometers. They have potential applications in electronics, energy storage, sensing and optoelectronics due to their unique properties. Specifically, semiconductor nanowires and carbon nanotubes have shown promise as building blocks for future nanoscale devices and circuits due to their ability to efficiently transport electrical carriers and exhibit critical device functions. However, carbon nanotubes have faced challenges in controlling their semiconducting or metallic properties and manipulating individual tubes, while nanowires allow for more rational and predictable assembly through control of their synthesis.