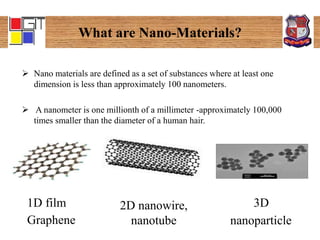
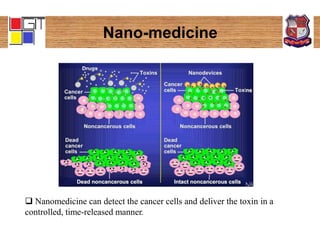
The document is an active learning assignment on nano-materials, detailing their definition, classification, synthesis methods, properties, applications, and disadvantages. It describes two main synthesis processes: top-down and bottom-up, alongside various techniques for each. Additionally, it outlines specific applications in concrete, vehicle technology, and nanomedicine, while noting potential disadvantages such as impurity and higher production costs.