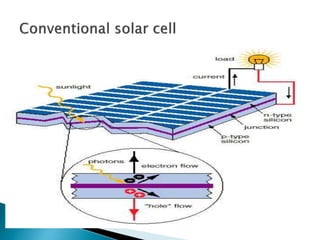
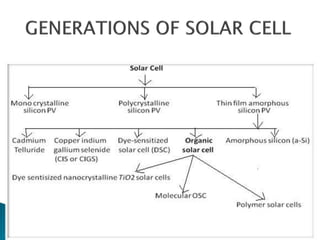
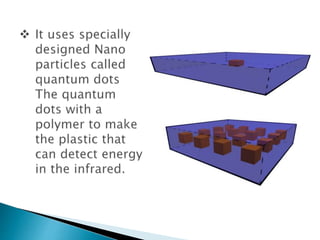
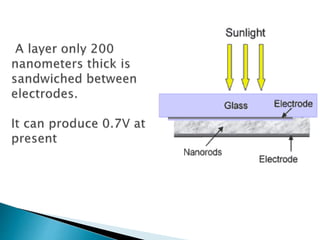
This document summarizes a seminar on infrared plastic solar cells. It discusses how plastic solar cells use nanotechnology to harness infrared radiation from the sun through semiconductor nanorods, allowing them to generate electricity even on cloudy days. This overcomes limitations of conventional solar panels. While plastic cells are more efficient, a current limitation is their higher cost compared to traditional panels. The seminar covers solar energy basics, nanotechnology applications, infrared radiation properties, types of solar cells, and advantages of plastic cells for harnessing more of the sun's energy spectrum.