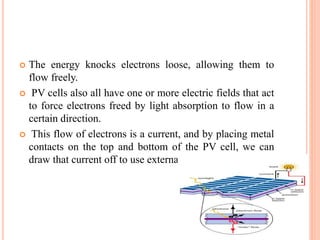
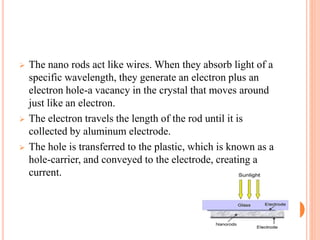
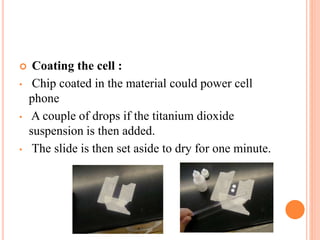
This document discusses infrared plastic solar cells that use nanotechnology to harness energy from infrared light. It can work even on cloudy days. The cell contains a layer of nano rods dispersed in a polymer sandwiched between electrodes. When light is absorbed, electrons are generated and travel through the nano rods to be collected at the electrodes, producing a current. These plastic solar cells have potential applications such as powering devices, cars, and may eventually supply power needs through large solar farms. However, their high cost currently limits widespread use.