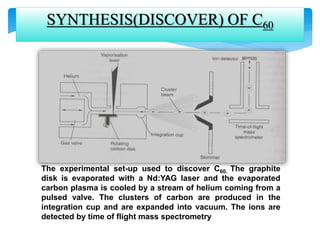
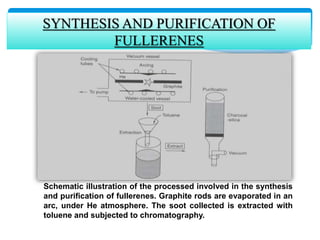
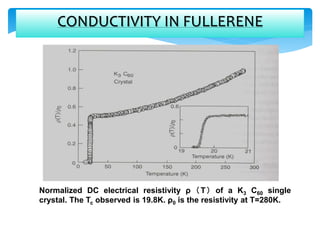
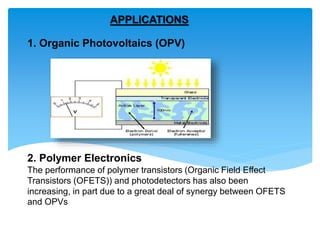
Fullerene is a molecule composed entirely of carbon atoms arranged in a hollow sphere, ellipsoid or tube shape. Buckminsterfullerene or buckyball is the spherical form with 60 carbon atoms arranged in a geodesic dome structure. Fullerenes were discovered in 1985 and their discoverers were awarded the 1996 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Common fullerenes include buckyballs (C60), nanotubes, and polymers. They are synthesized by evaporating graphite and trapping the carbon clusters, then purifying. Fullerenes are soluble in organic solvents and exhibit properties like conductivity, superconductivity, and use in applications such as photovoltaics, polymers, antioxidants, and catalysts.