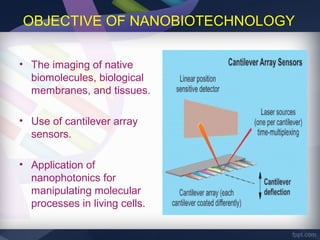
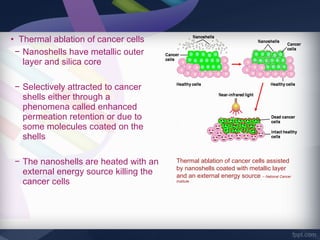
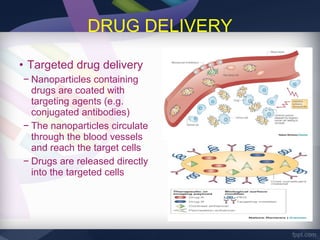
Nanobiotechnology combines nanotechnology and biotechnology to create functional materials and devices at the nanoscale (1-100 nm) where new properties emerge. It allows for imaging and manipulation of biomolecules, development of biosensors, targeted drug delivery for cancer treatment, and regenerative medicine using biomimetic tissues. While offering promising applications, nanobiotechnology may also pose toxicity risks if nanoparticles are able to penetrate tissues and cells and cause biochemical damage.