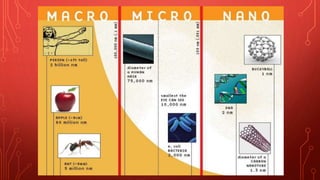
The document discusses nanotechnology, which involves manipulating materials at the nanoscale of 1 to 100 nanometers. It describes how nanotechnology can be used across various fields like materials science, biology and medicine. Some key applications mentioned include using carbon nanotubes to create strong lightweight materials, using quantum dots in displays and electronics, developing nanobots for detection and drug delivery, and employing nanoparticles in fabrics, drugs, and electronics like flexible screens. The document also notes some potential risks of nanotechnology like nanoparticles entering the body and crossing the blood-brain barrier.