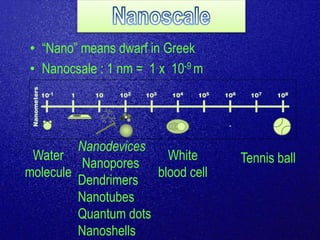
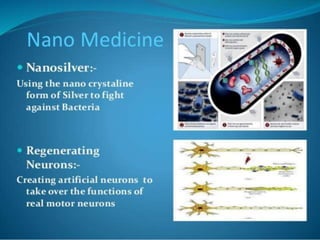
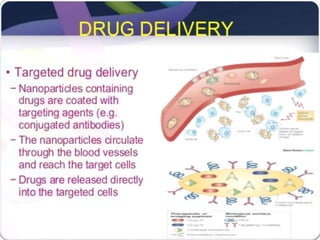
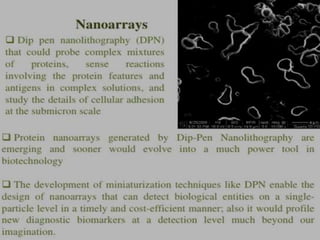
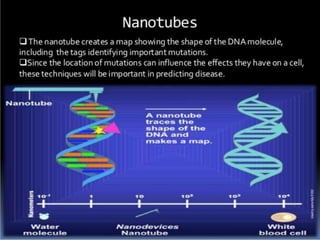
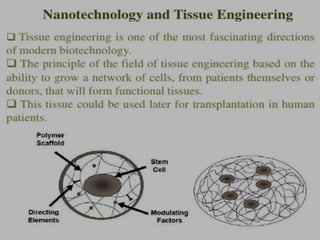
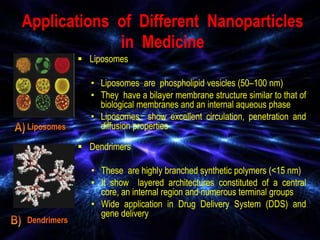
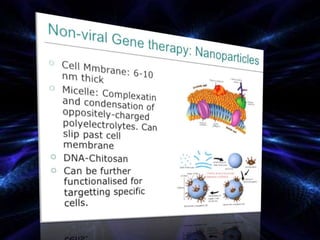
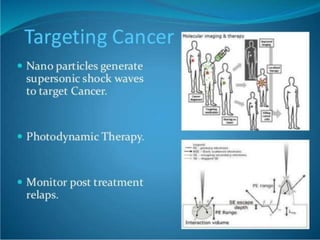
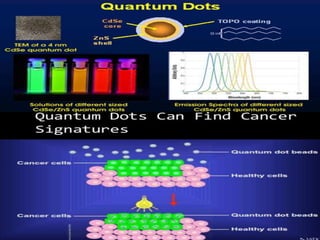
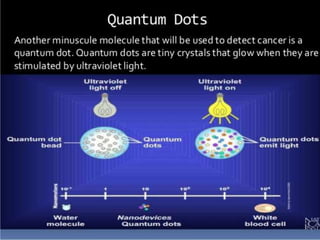
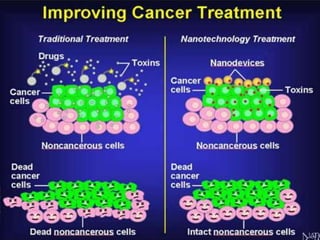
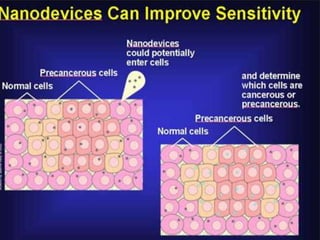
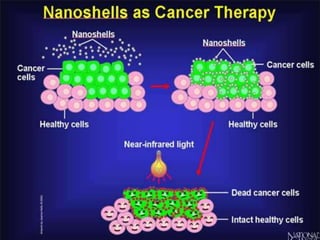
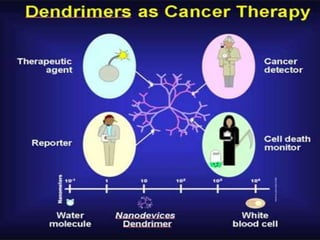
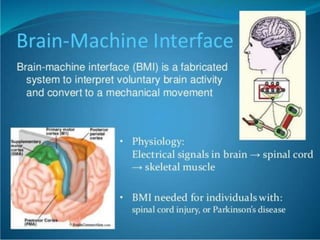
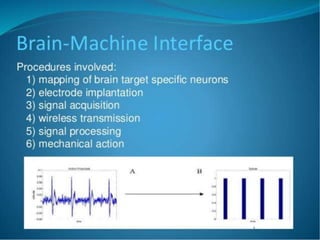
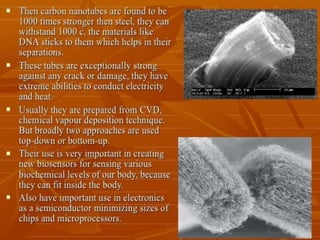
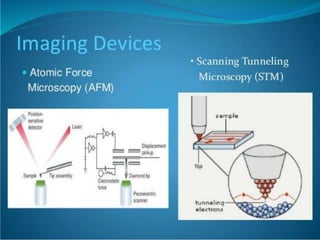
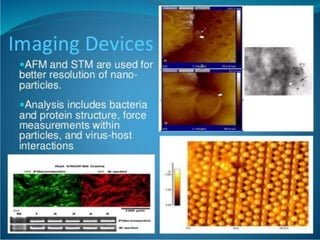
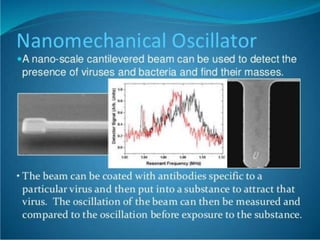
Bionanotechnology is an area that applies nanotechnology to biology and medicine. It uses biological materials to create nanoscale devices less than 100 nanometers in size to better understand life processes. Some examples include using nanoparticles like liposomes, dendrimers, carbon nanotubes, quantum dots and gold nanoparticles for applications in drug delivery, imaging, biosensing and gene therapy by taking advantage of their small sizes and unique properties. Bionanotechnology is a rapidly developing field that offers opportunities for new medical technologies at the nanoscale level.