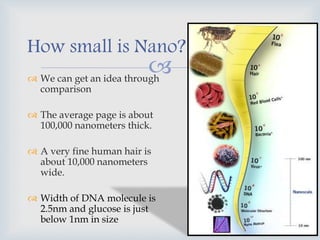
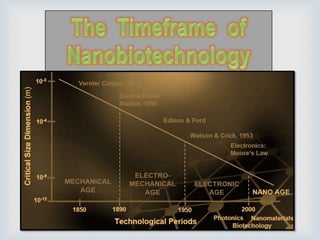
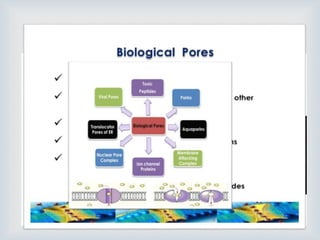
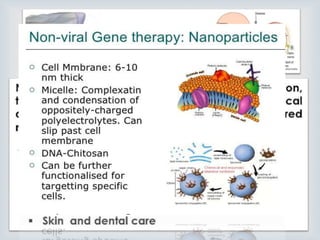
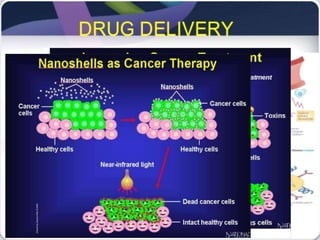
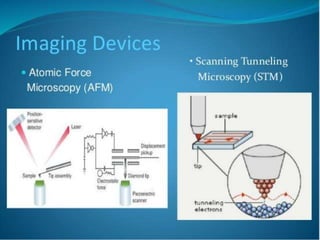
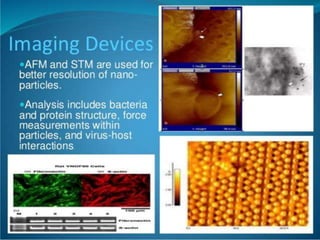
This document provides an overview of nanobiotechnology. It discusses how nanobiotechnology uses biological materials at the nanoscale and has applications in fields like bioengineering and medicine. Some key areas discussed include nanopores that can characterize nanoscale cell structures and functions, nanoparticles and nanomaterials like liposomes and dendrimers that have uses in drug delivery and imaging, and the benefits of nanotechnology for applications in areas such as biomedical imaging, drug delivery, and biosensing. However, the document also notes that the safety of nanotechnology needs further study.