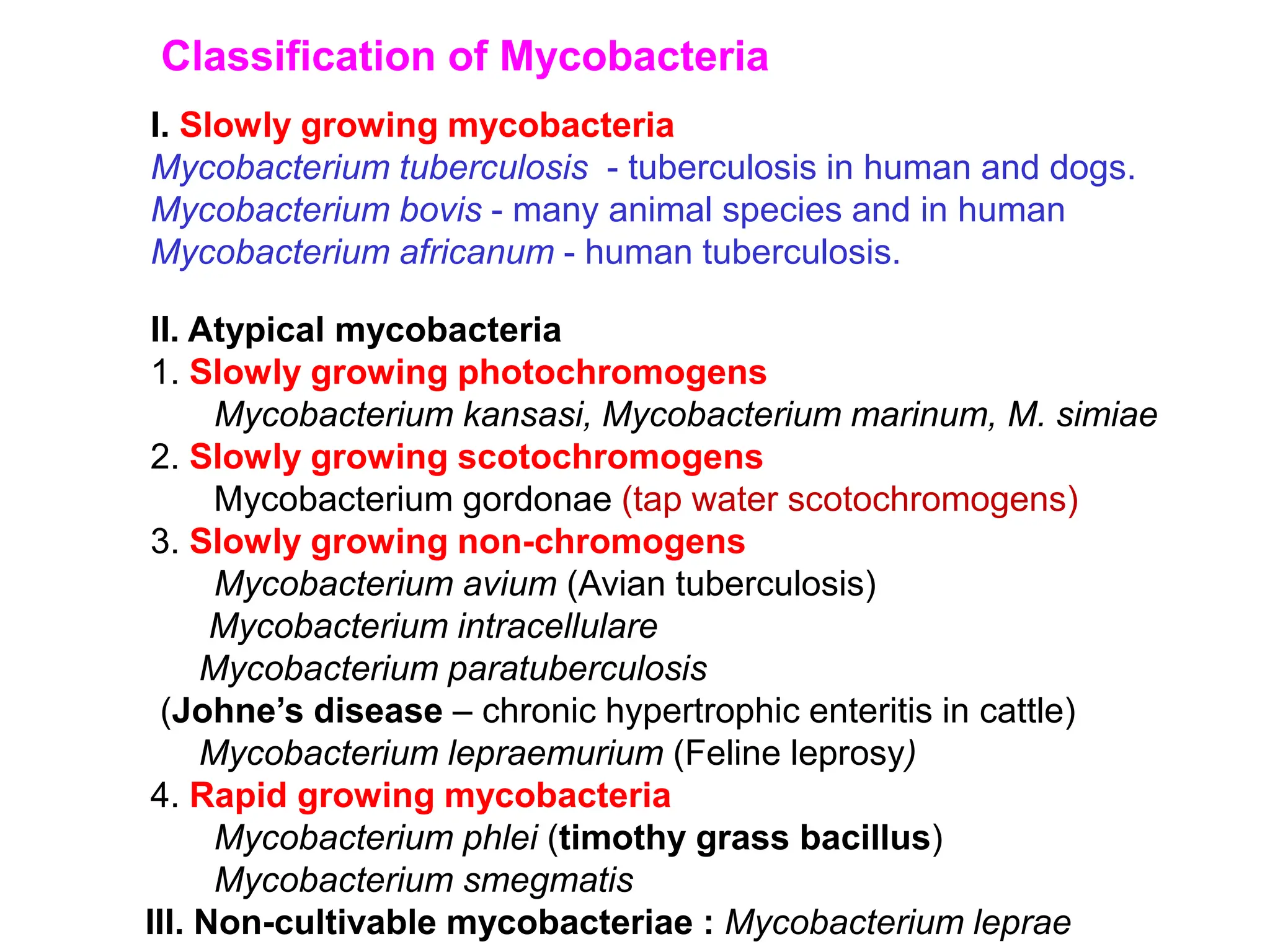
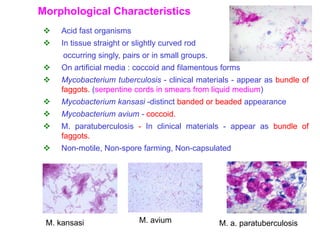
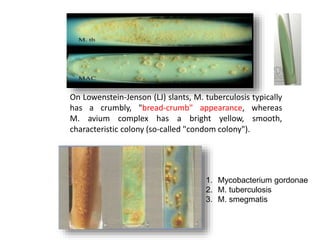
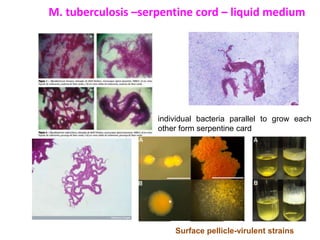
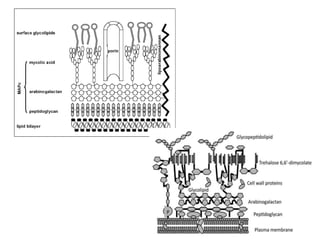
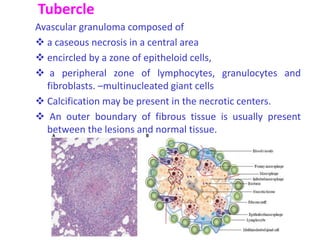
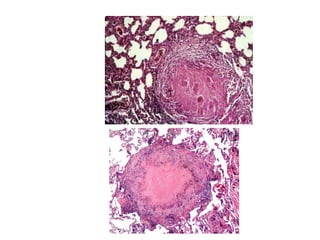
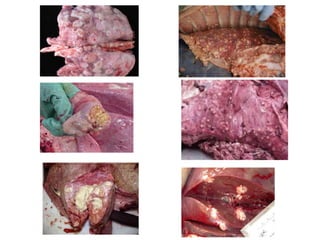
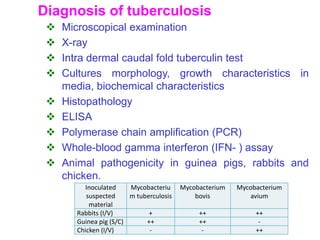
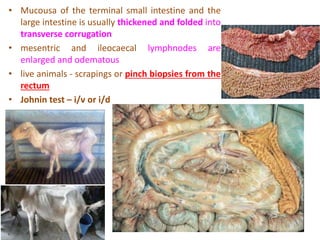
This document discusses mycobacteria, which are classified into slowly growing mycobacteria including M. tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. africanum, M. kansasi, M. marinum, M. simiae, M. gordonae, M. avium, M. intracellulare, M. paratuberculosis, M. lepraemurium, M. phlei, and M. smegmatis. It also discusses non-cultivable mycobacteria like M. leprae. Key characteristics include being acid-fast, having slow growth rates, and causing diseases like tuberculosis and leprosy in humans and animals.