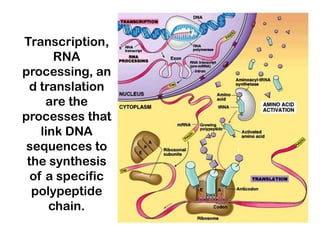
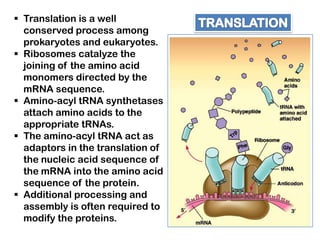
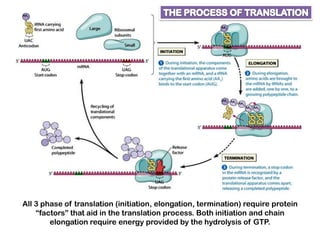
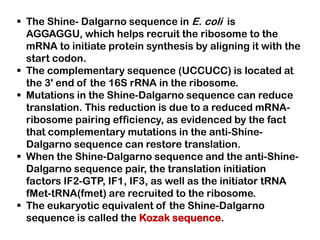
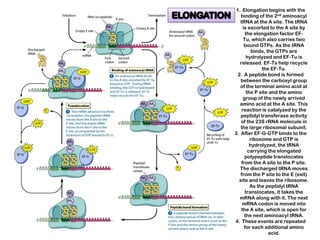
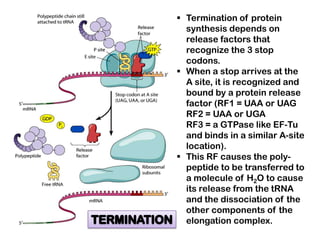
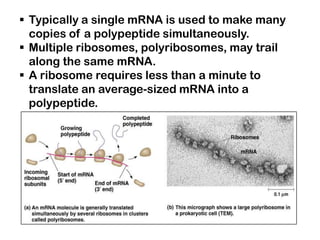
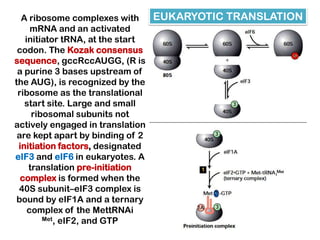
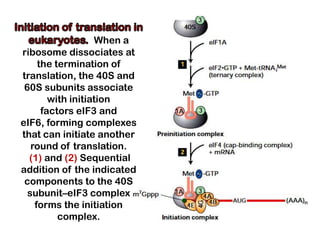
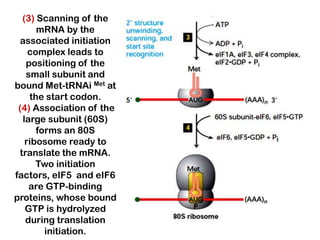
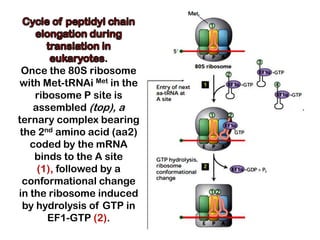
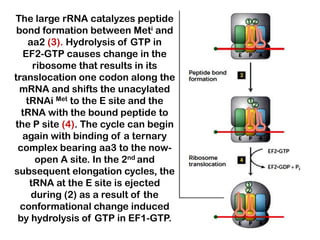
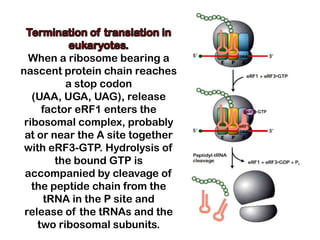
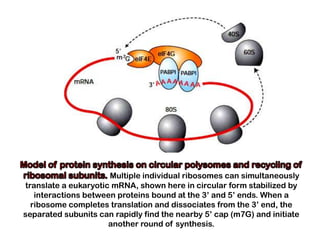
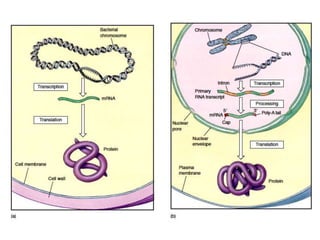
1. Translation is the process by which the genetic code in mRNA is used to synthesize polypeptide chains through the catalysis of ribosomes.
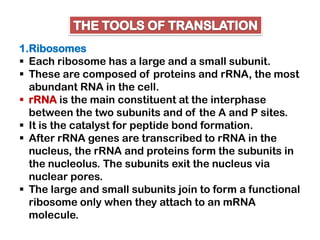
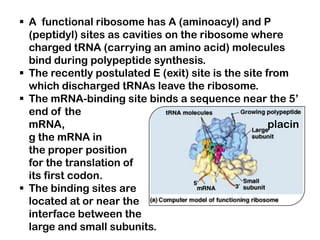
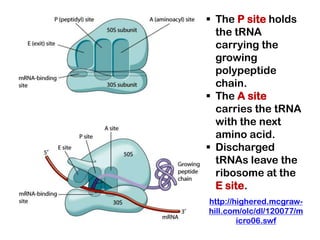
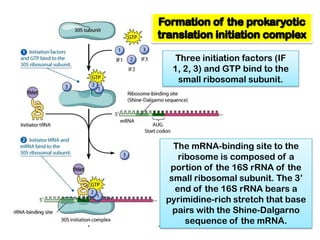
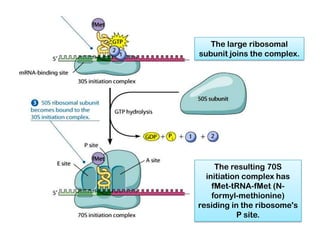
2. Ribosomes contain rRNA and proteins and have three binding sites (A, P, E sites) that facilitate the joining of amino acids specified by the mRNA sequence.
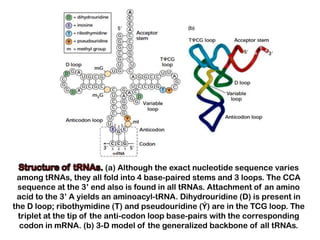
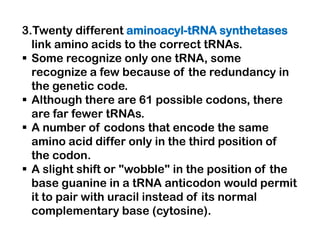
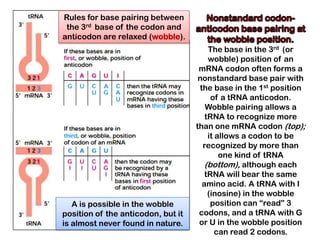
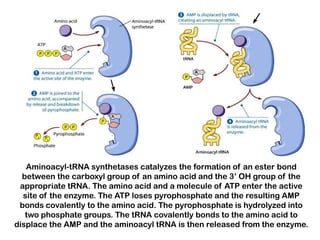
3. tRNAs act as adaptors by pairing their anticodons with mRNA codons and carrying the correct amino acid to the ribosome. Wobble base pairing allows some tRNAs to bind multiple codons.