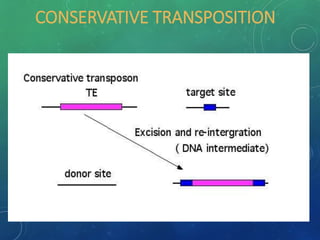
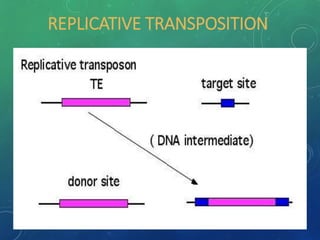
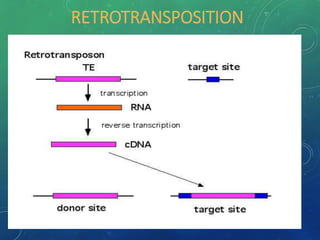
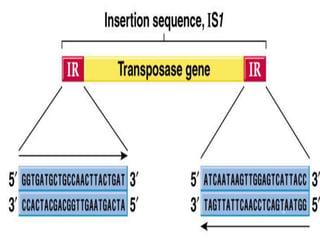
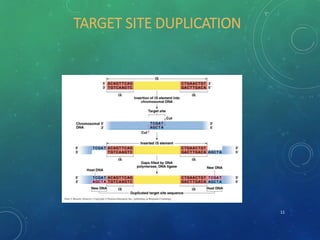
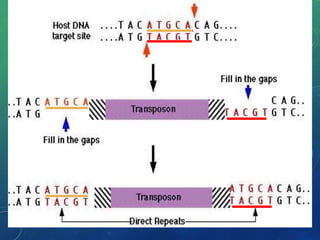
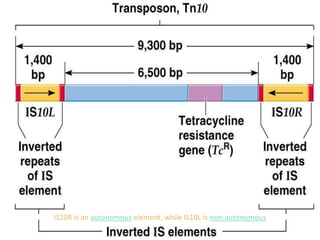
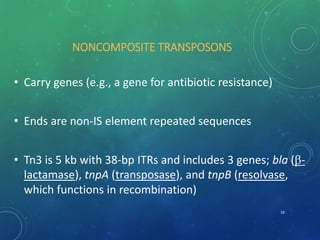
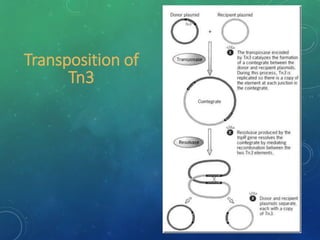
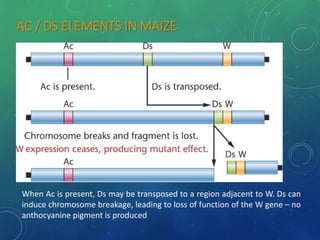
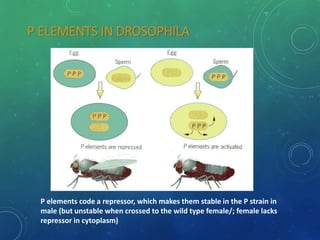
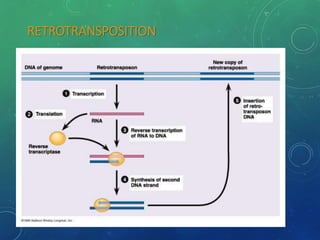
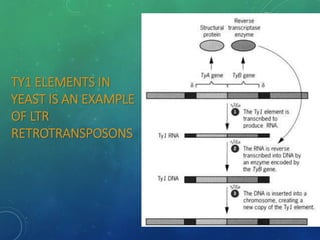
Mobile genetic elements called transposons can move within genomes. There are three mechanisms for transposition: conservative, replicative, and retrotransposition. Transposons are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In prokaryotes, common transposons include insertion sequences and Tn transposons, which can be composite or non-composite. Transposons can cause chromosomal rearrangements like deletions, inversions, and duplications through recombination.