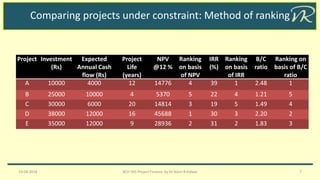
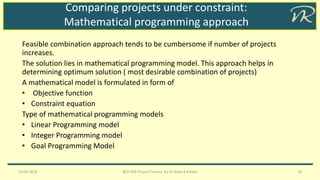
The document discusses the evaluation of investment projects under capital constraints, emphasizing the impact of project dependency and capital rationing on decision-making. It outlines different types of project relationships (independent, mutually exclusive, negatively dependent, and positively dependent) and presents methods for comparing projects, including ranking approaches and mathematical programming models. The analysis highlights how conflicts can arise in project ranking due to size, time, and life disparities, and suggests approaches to resolve these issues.