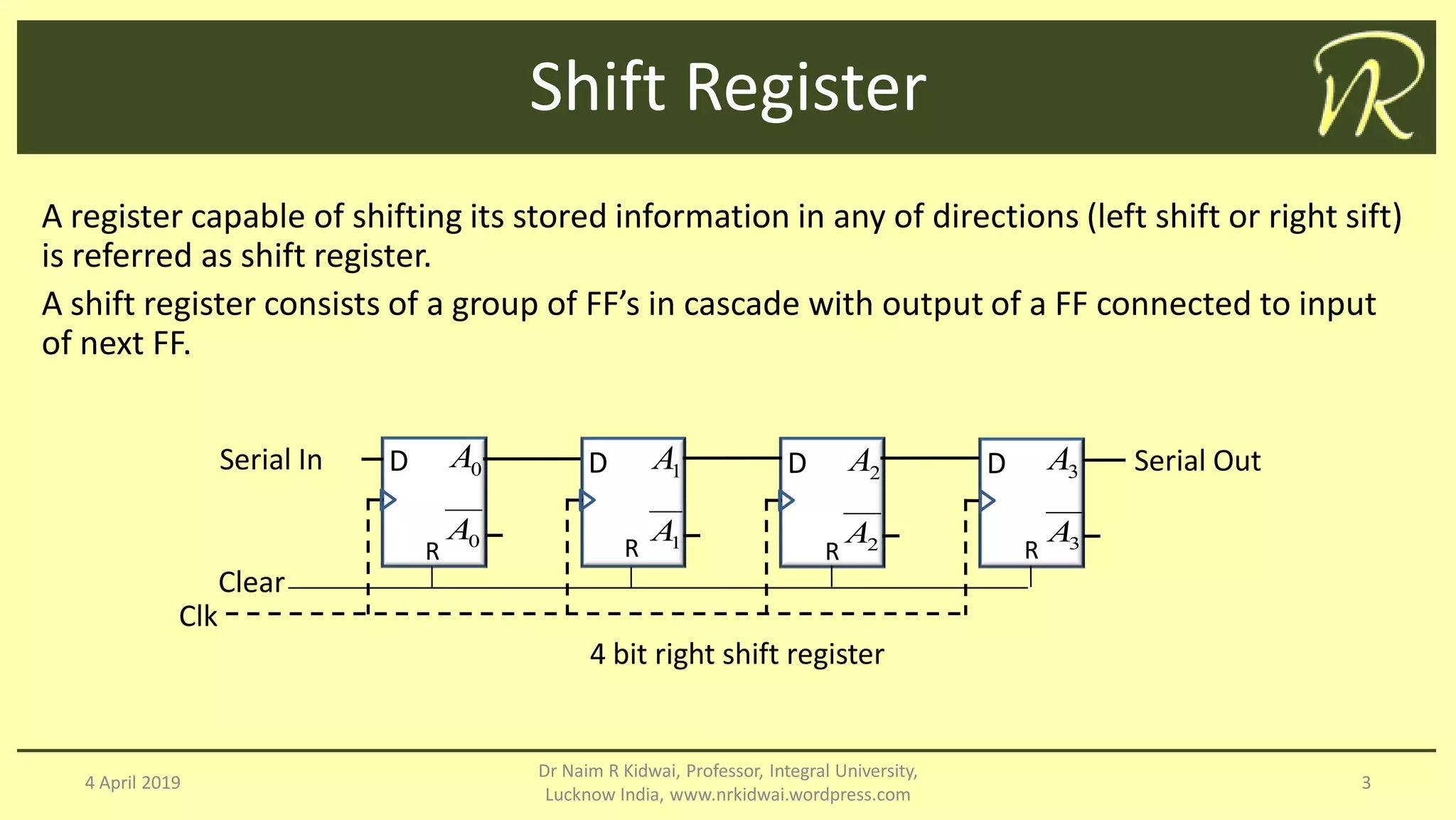
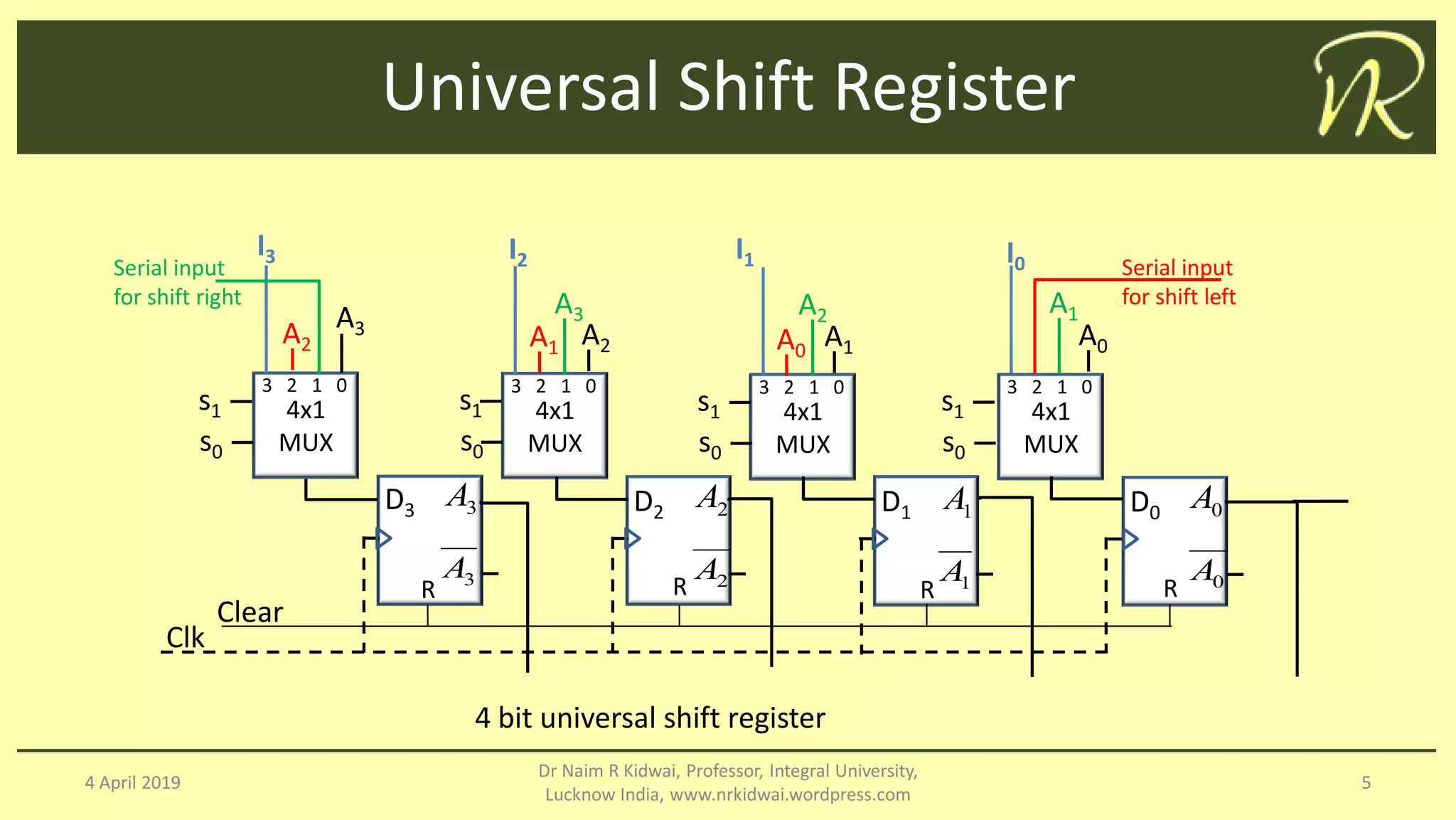
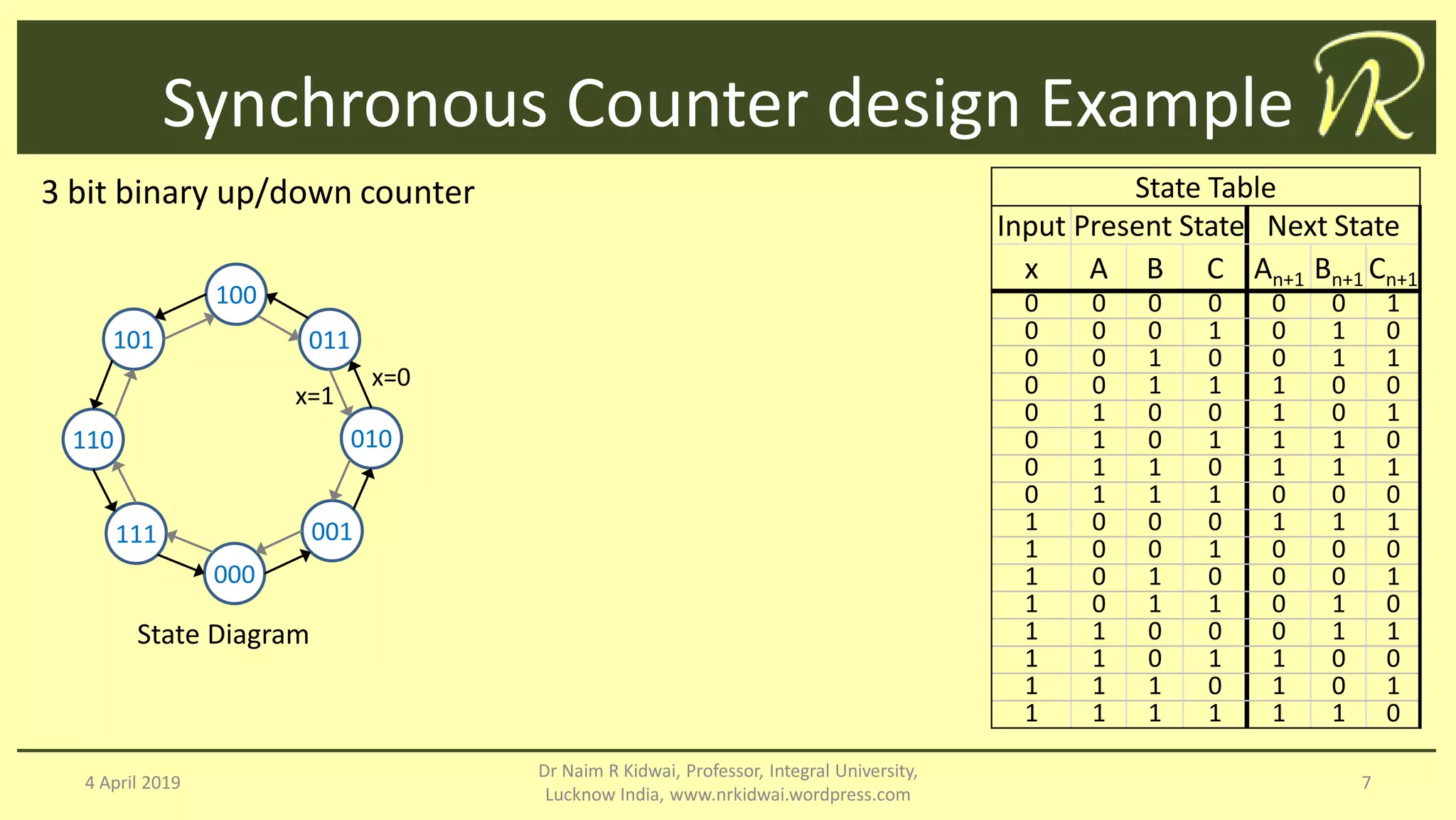
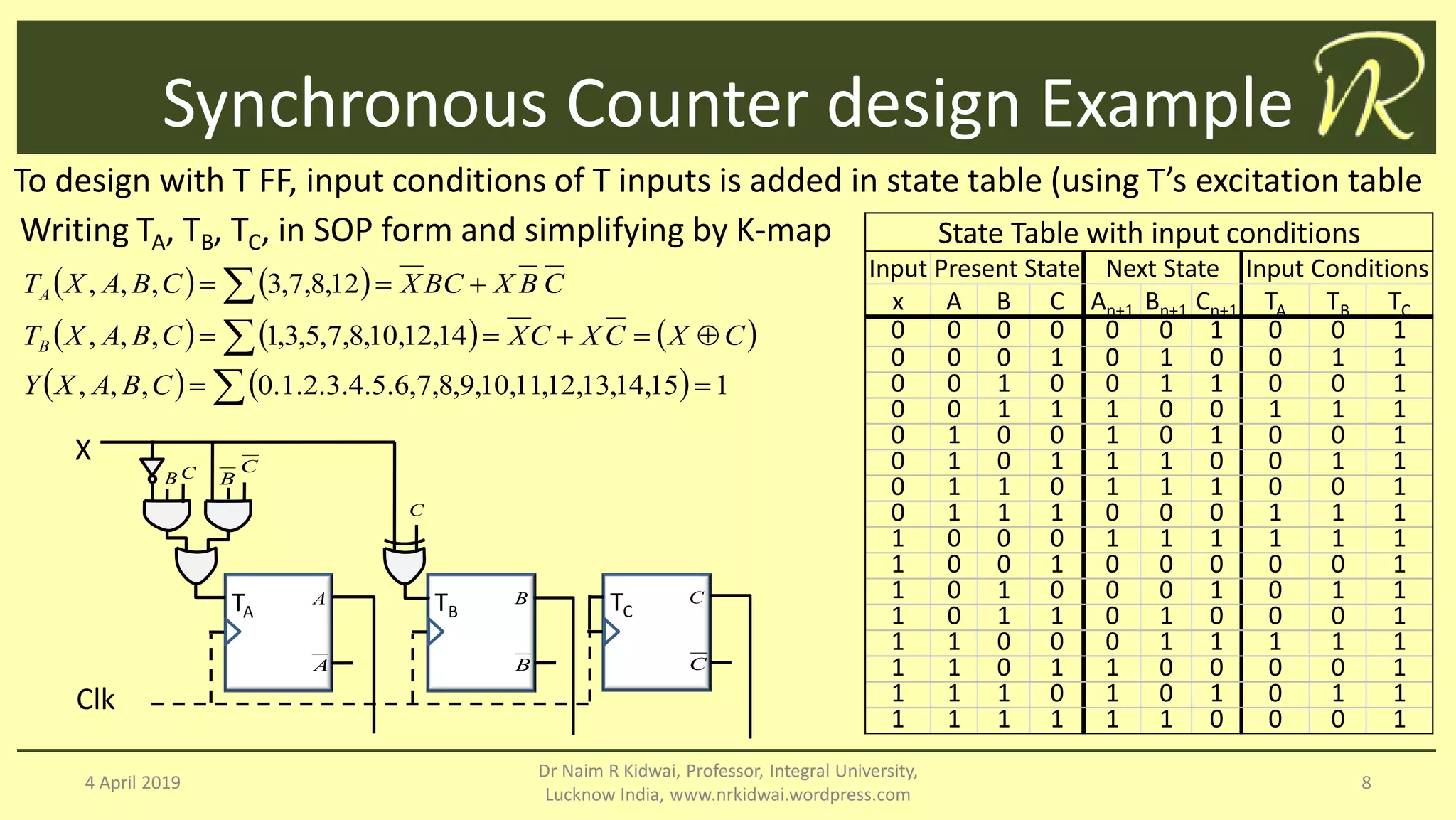
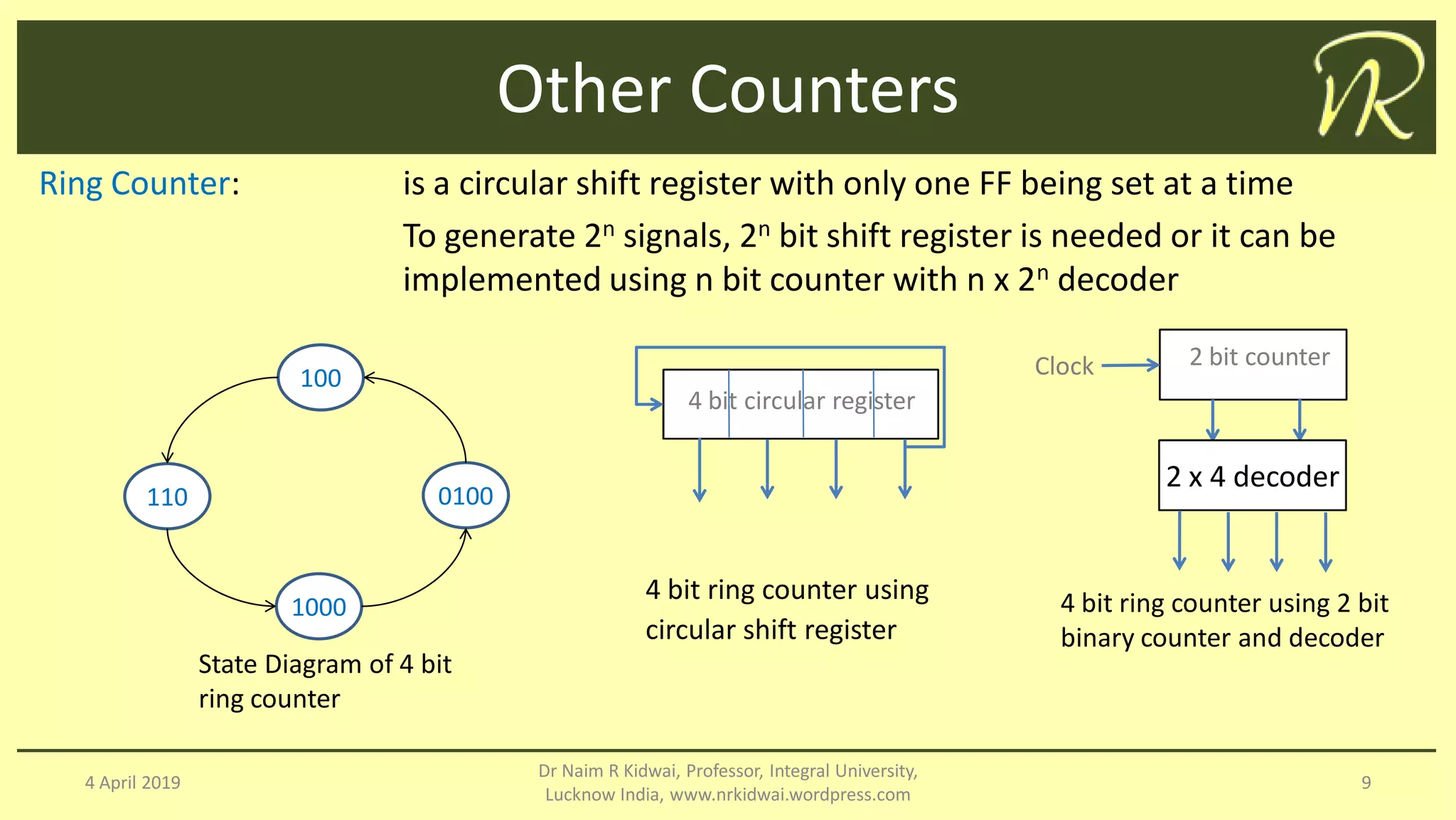
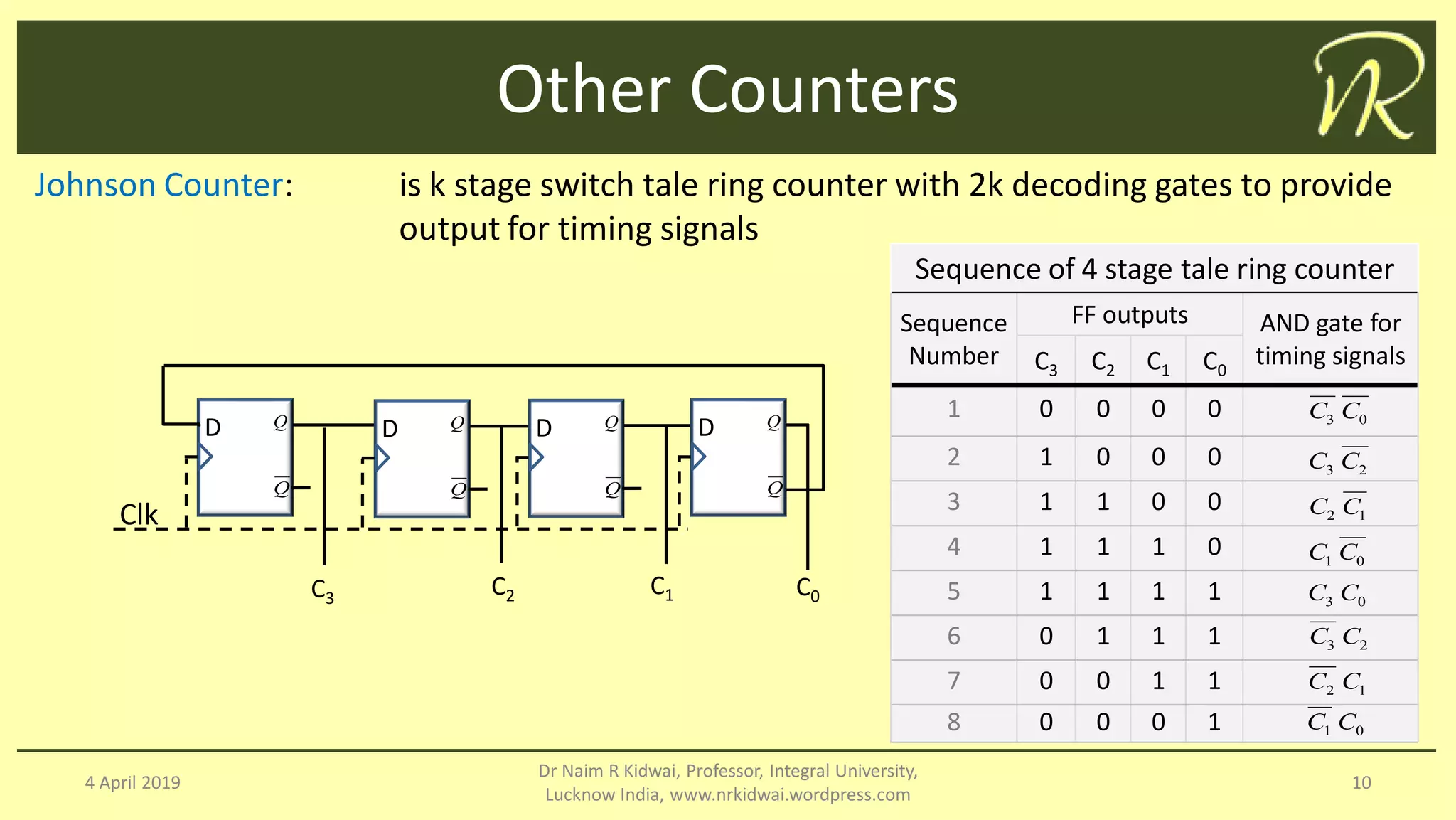
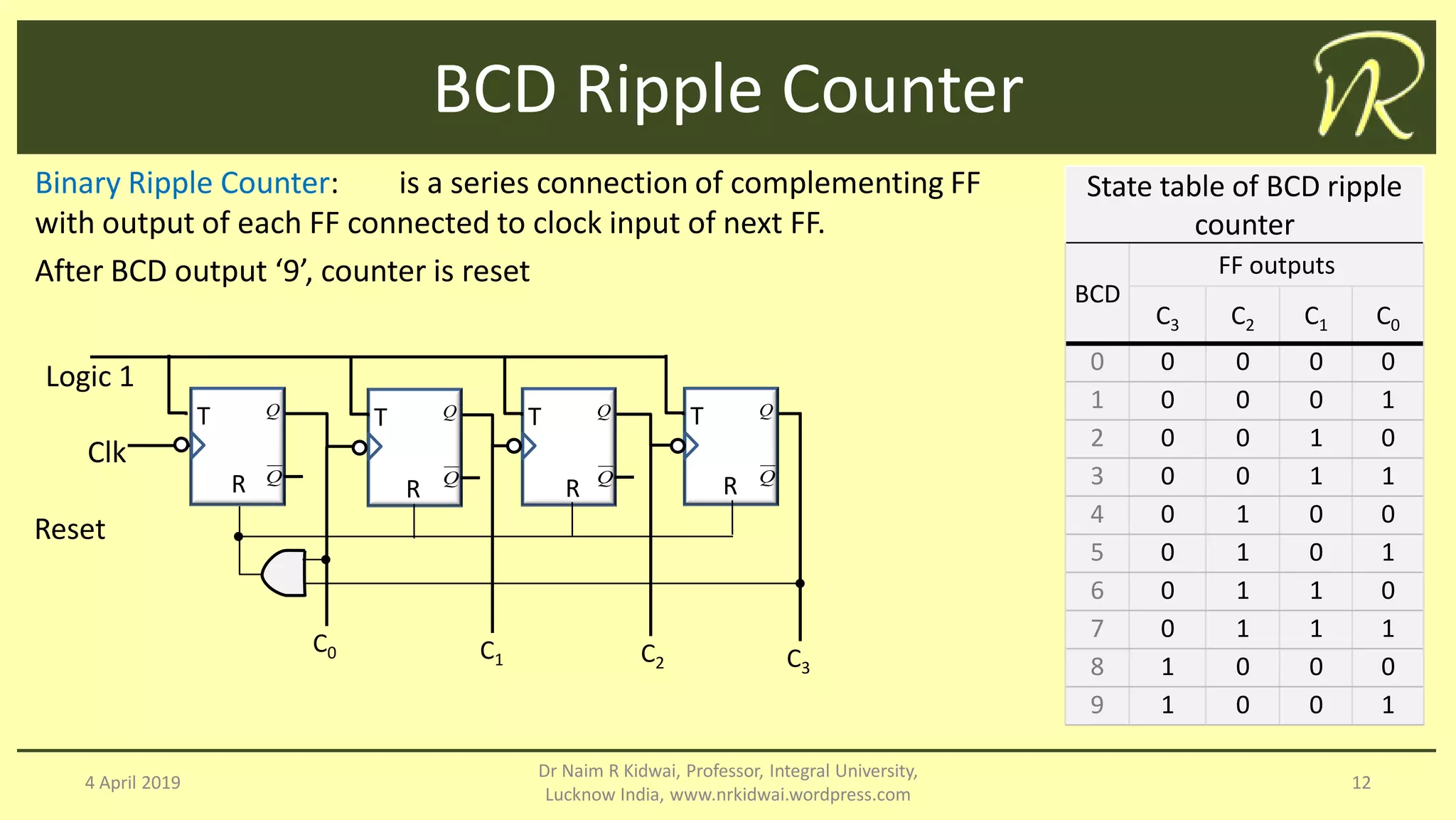
The document discusses clocked sequential circuits, specifically focusing on registers and counters, including types of registers such as shift registers and universal shift registers. It outlines the operation and design of different counters, including ripple counters, synchronous counters, ring counters, and Johnson counters, providing diagrams and state tables for clarity. The learning objectives of this document include understanding the design and analysis of these sequential circuits.