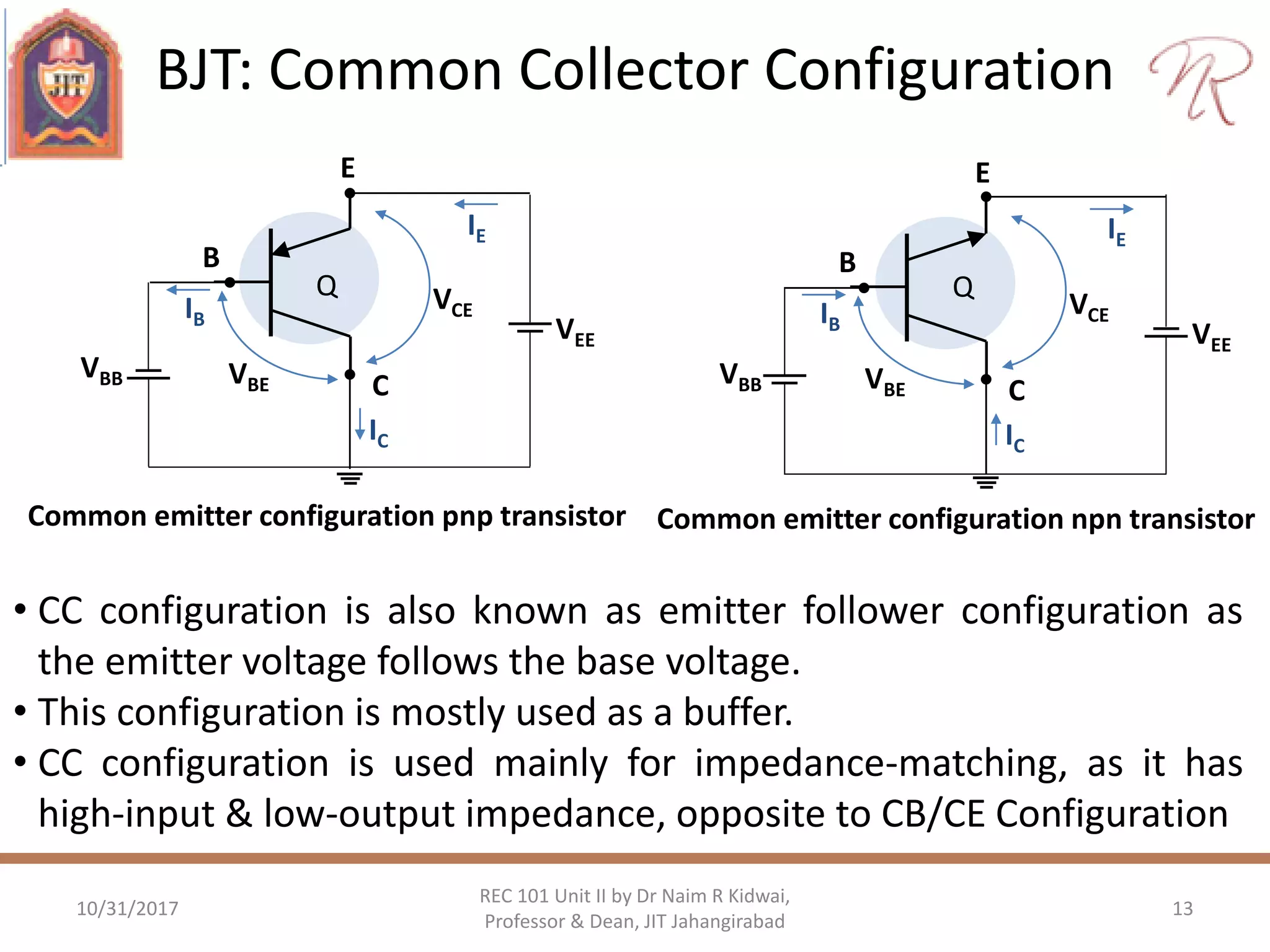
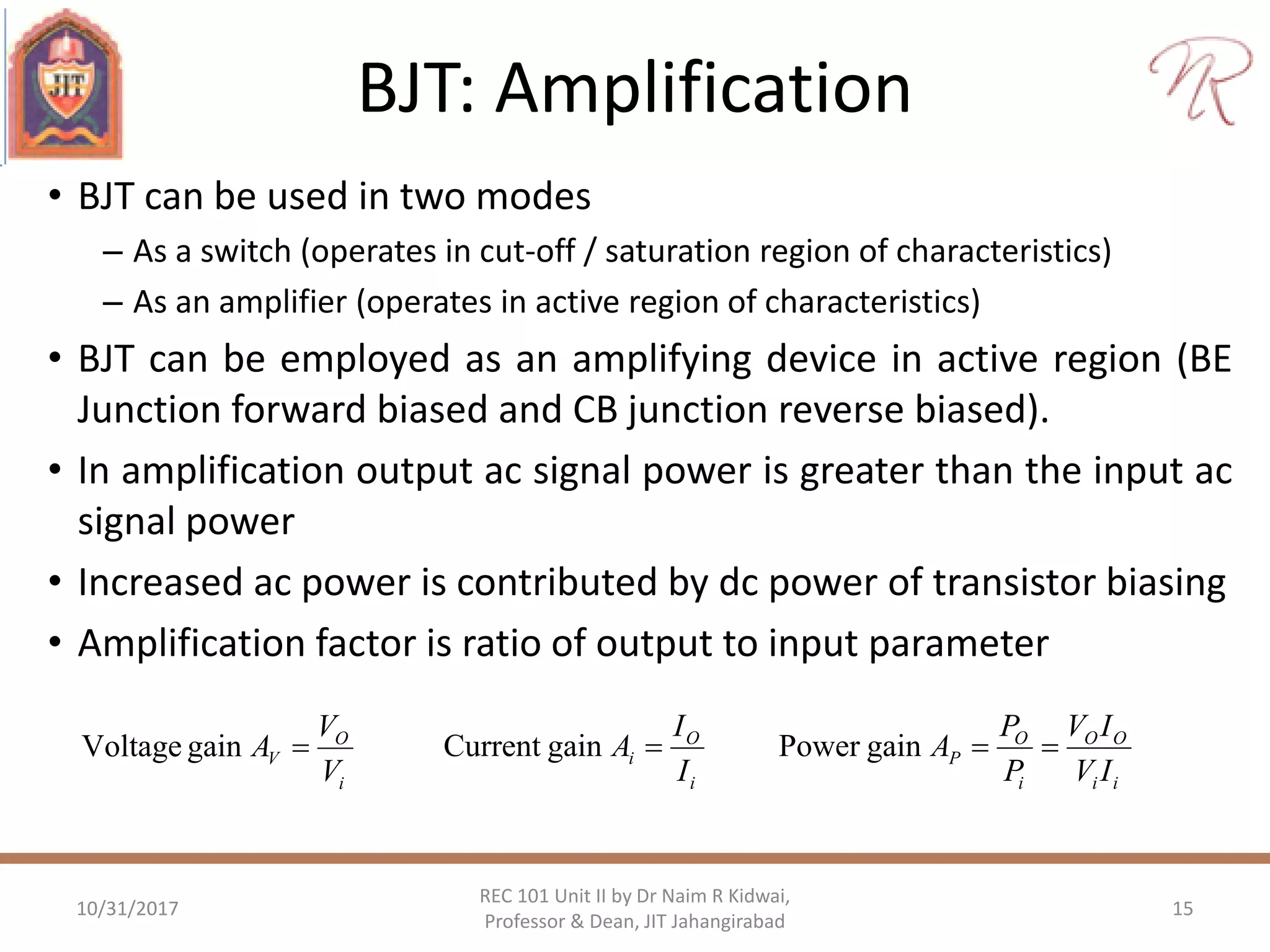
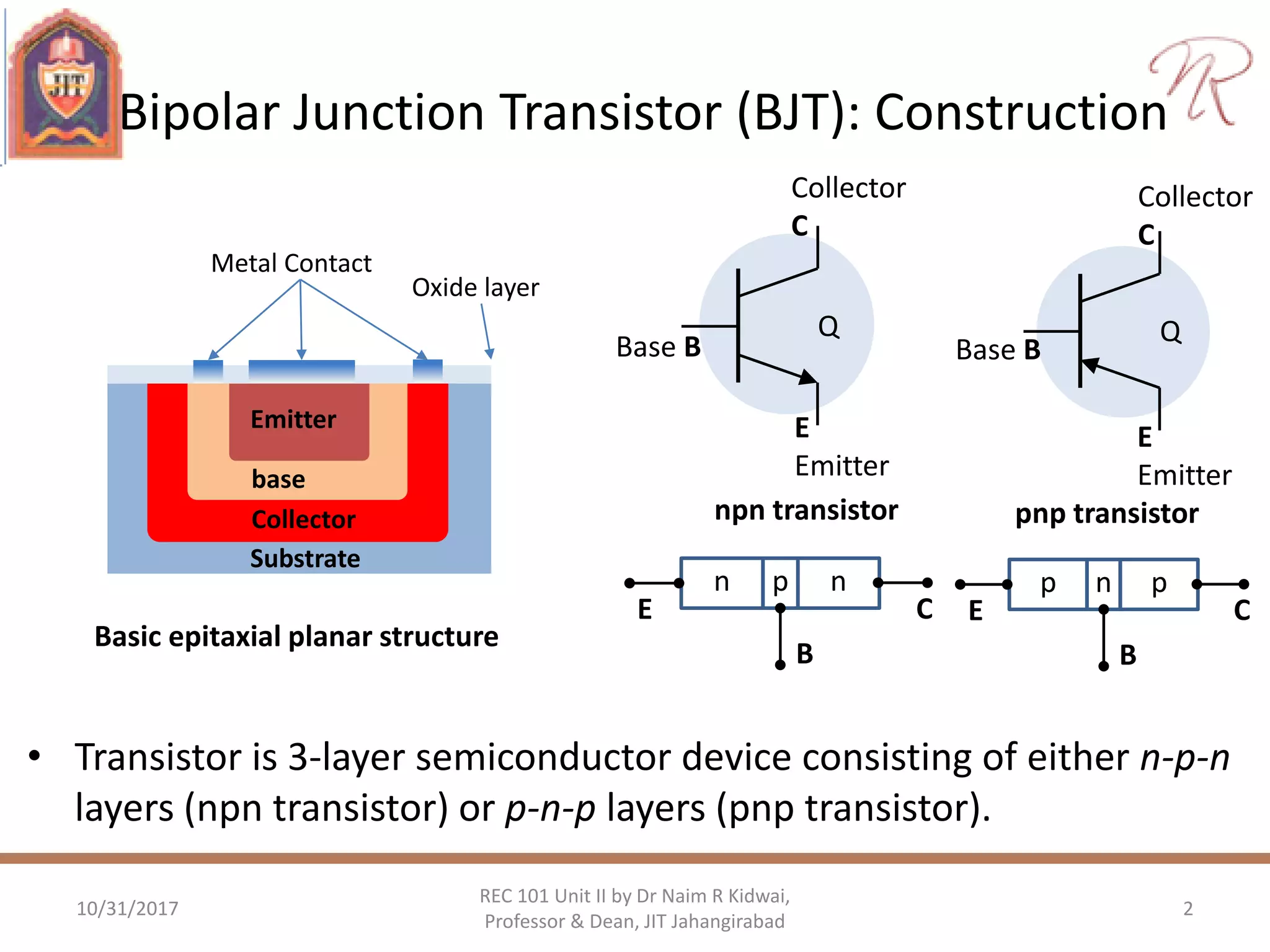
The document provides a comprehensive overview of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), including their construction, operation, and different configurations (common base, common emitter, common collector). It explains DC biasing methods, the role of input and output characteristics, and the operation of BJTs in both amplification and switching modes. Additionally, it covers the characteristics of field effect transistors (FETs), such as JFETs and MOSFETs, within the context of amplifiers.







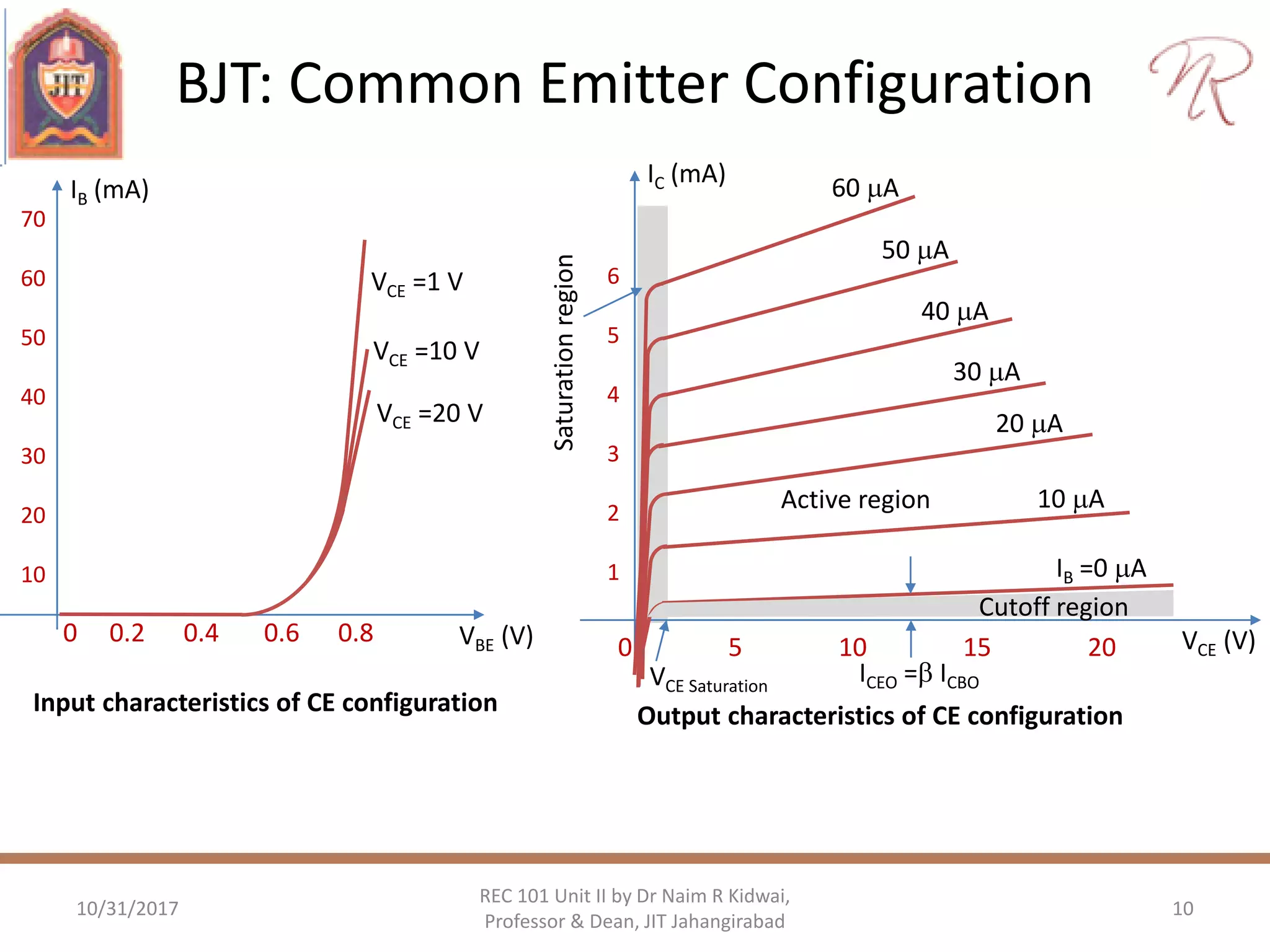

![BJT: Common Emitter Configuration
Beta ()
• Where IC and IB are the currents at the point of operation
• for practical devices Beta typically ranges in between 50 to 400
Relation between Alpha and Beta
10/31/2017 12
REC 101 Unit II by Dr Naim R Kidwai,
Professor & Dean, JIT Jahangirabad
B
C
I
I
gaincurrentemitterCommon
C
C
C
BCE
I
I
I
III
1
1
large]veryis[as)1(
1
CBOCBO
CBO
CEO II
I
I
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rec101unitiipart1bjtcharacteristics-171031095410/75/Rec101-unit-ii-part-1-bjt-characteristics-12-2048.jpg)