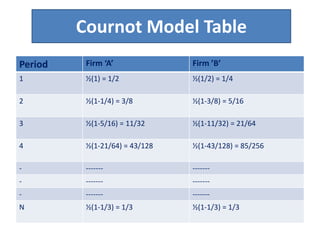
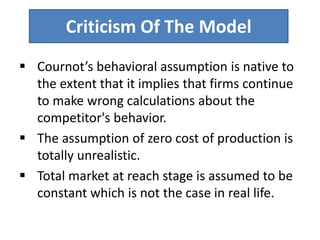
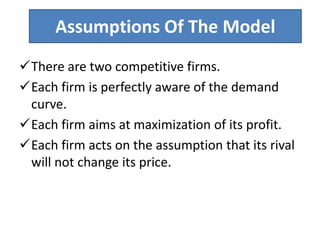
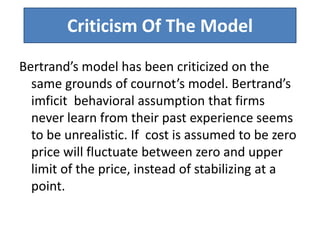
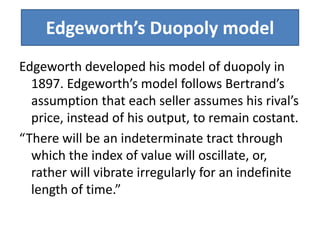
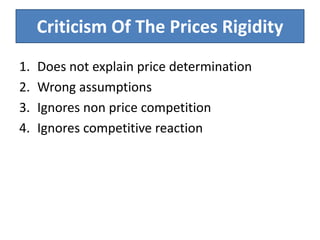
Price determination under oligopoly can occur through independent pricing, collusive pricing, or price leadership. There are several classical models of oligopoly including Cournot's model of duopoly, Bertrand's model of duopoly, and Edgeworth's duopoly model. Non-collusive oligopolies may lead to price wars if firms produce homogeneous goods. Under collusion, firms can jointly set prices or output to increase their bargaining power against consumers. Price leadership is a means for oligopolists to coordinate prices without explicit collusion, with the dominant firm initiating price changes that other firms follow.