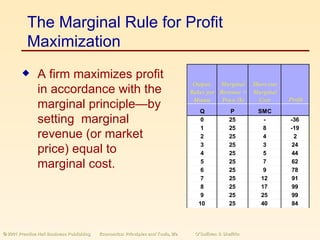
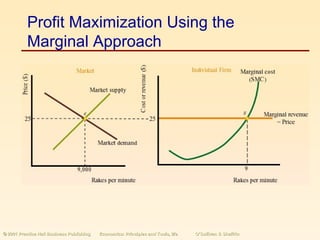
This document summarizes the concepts of perfect competition in the short run and long run. It discusses how a perfectly competitive firm determines profit-maximizing output by producing at the quantity where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. In the short run, firms can increase or decrease output but cannot exit the industry. In long run equilibrium, firms earn zero economic profit and the industry supply curve is determined by the minimum average cost of production as the number of firms adjusts.