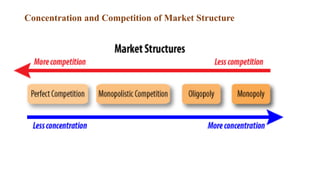
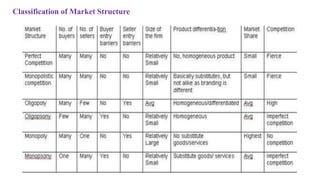
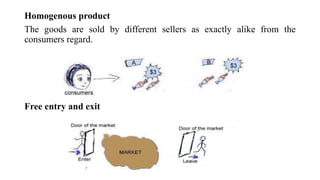
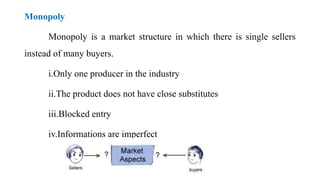
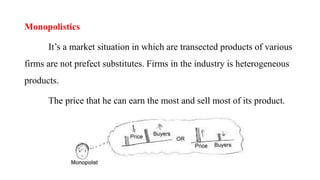
This document discusses market structure and its components. It defines market structure as the characteristics of a market that influence how buyers and sellers interact and behave. The key components of market structure are the number of buyers and sellers, type of product, conditions of entry and exit, and availability of information. The main types of market structure discussed are perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly, and monopolistic competition. Perfect competition has many buyers and sellers and a homogeneous product. A monopoly has a single seller. Oligopoly and monopolistic competition are forms of imperfect competition that deviate from perfect competition.