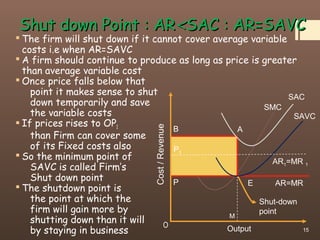
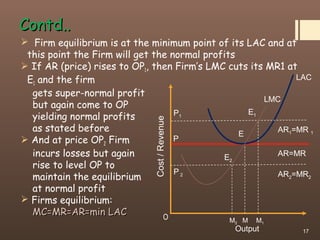
1) The document discusses the concept of perfect competition and firm equilibrium under conditions of perfect competition.
2) A key aspect of perfect competition is that there are many small producers and consumers in the market buying and selling homogeneous products, and all participants have perfect information. The market price is determined by supply and demand forces outside the control of individual firms.
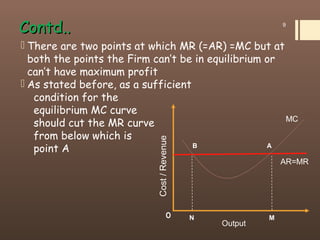
3) For a firm to be in equilibrium under perfect competition, its marginal cost must equal its marginal revenue (which is equal to the market price). At this equilibrium point, the firm maximizes its profits.
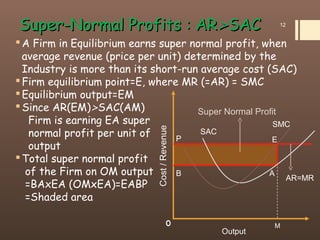
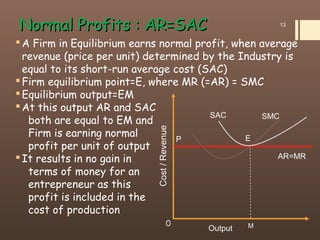
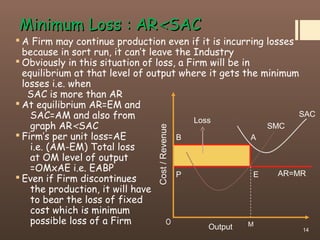
4) The document contrasts the short run and long run equilibriums for firms under perfect competition and how super normal profits, normal profits