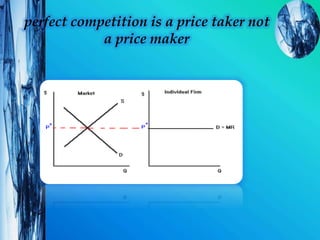
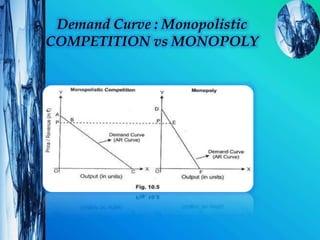
The document discusses different market structures: perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and duopoly. Perfect competition is characterized by many small firms, homogeneous products, perfect information, and price-taking behavior. Monopoly involves a single seller controlling the market. Monopolistic competition and oligopoly involve a small number of firms with some product differentiation. Oligopoly features mutual interdependence between firms. Duopoly is a special case of oligopoly with two firms.