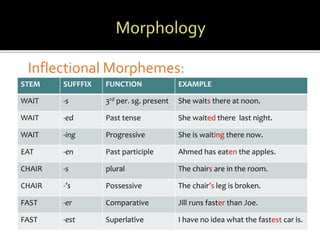
This document defines and provides examples of key concepts in morphology, the study of word structure. It discusses morphology as examining the categories of morphemes that make up words. A morpheme is the smallest unit of meaning or function. Free morphemes can stand alone as words, while bound morphemes must be attached to other elements. Lexical morphemes have meaning themselves, while functional morphemes specify relationships between lexical morphemes. Derivational morphemes change meaning or part of speech, and inflectional morphemes mark grammatical functions without creating new words. The document provides examples to illustrate these morphological concepts.