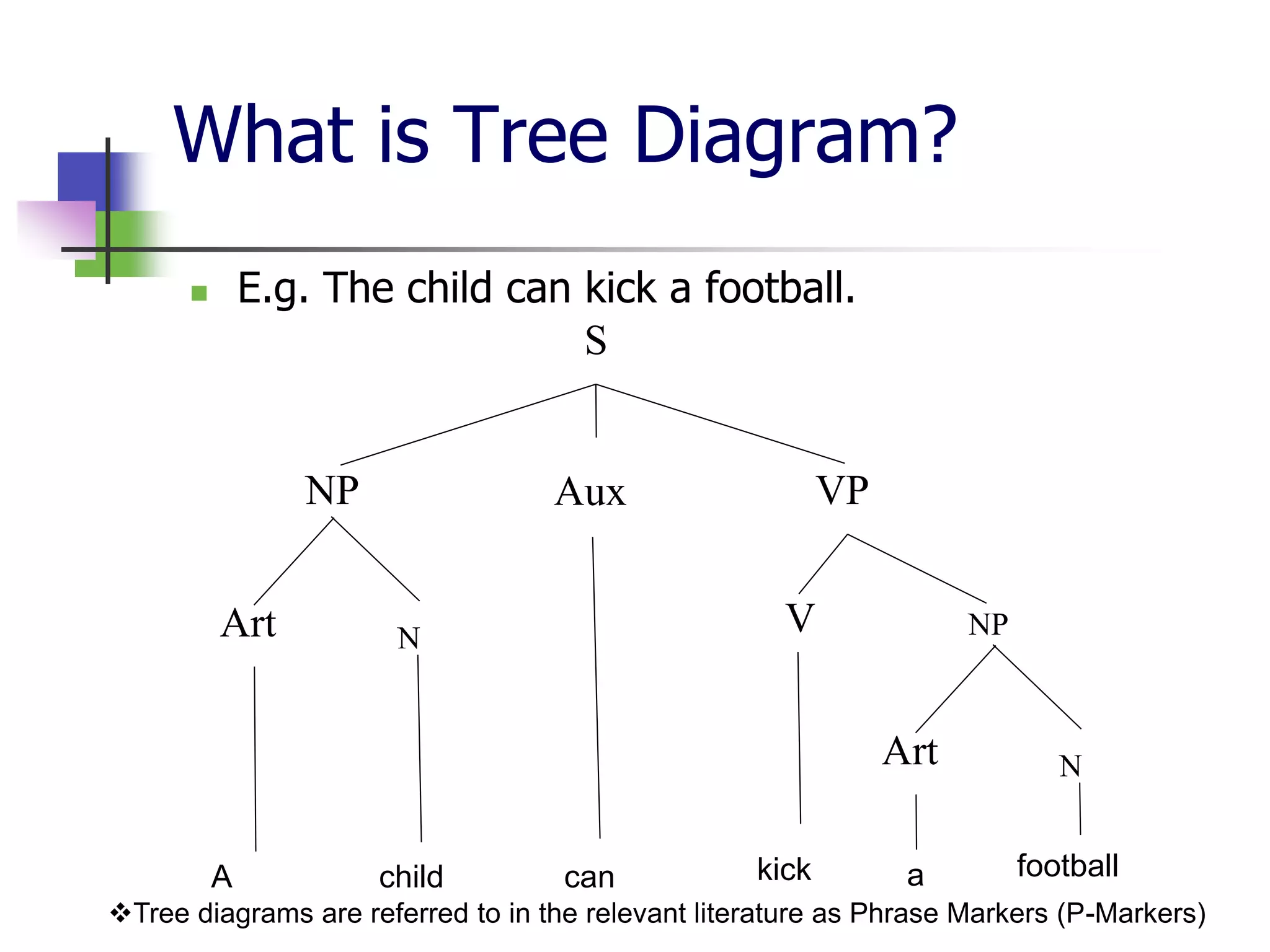
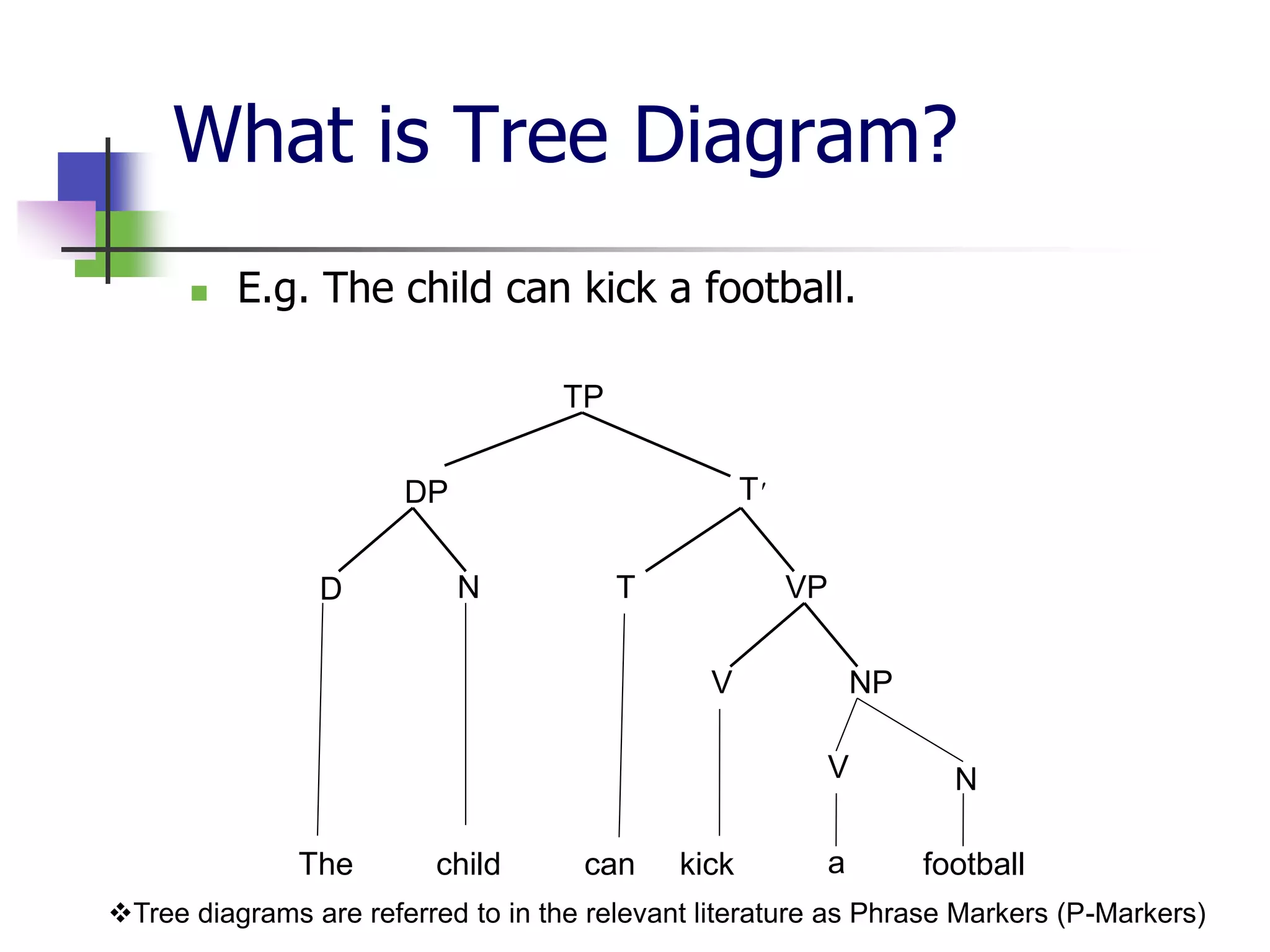
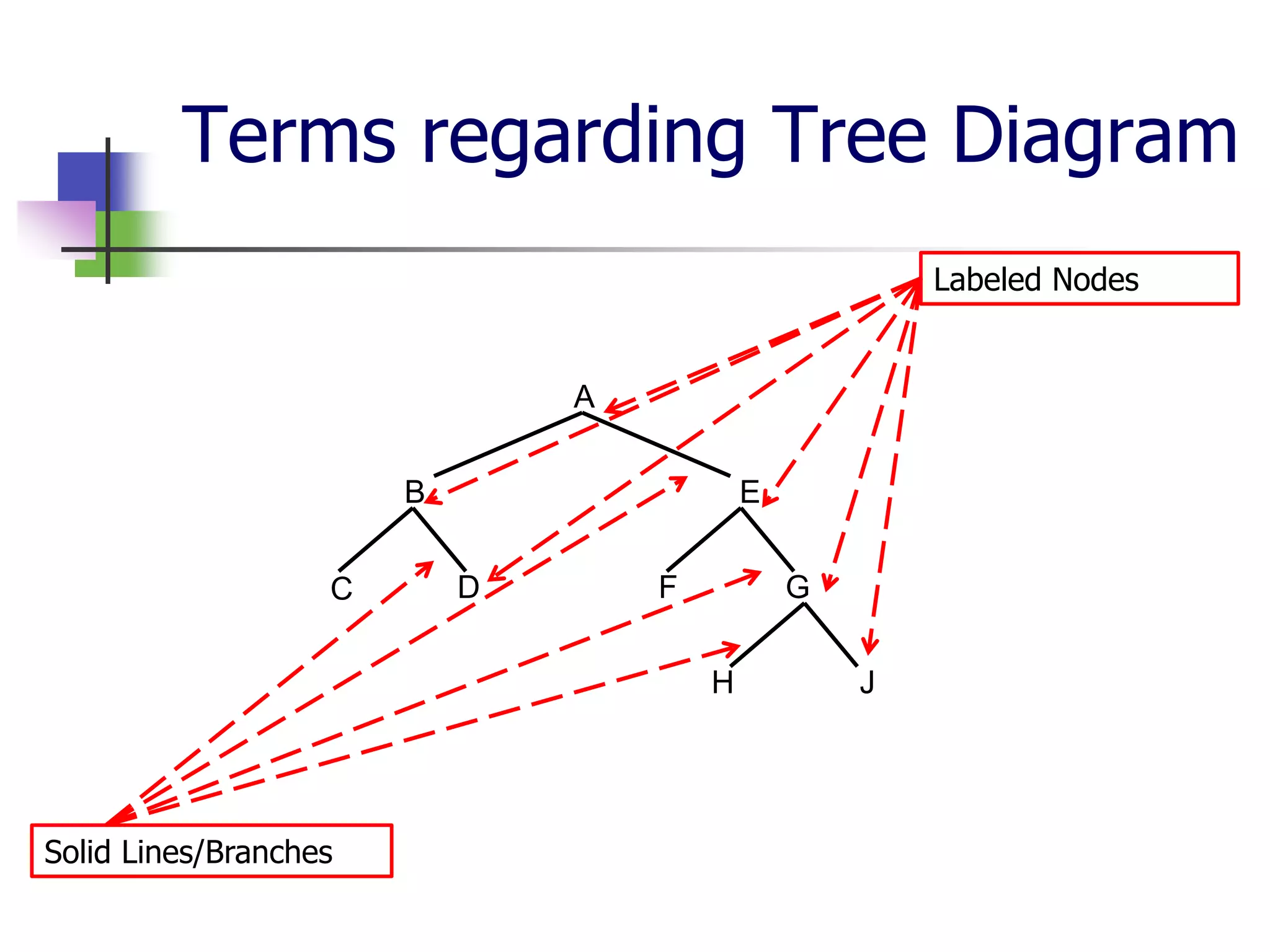
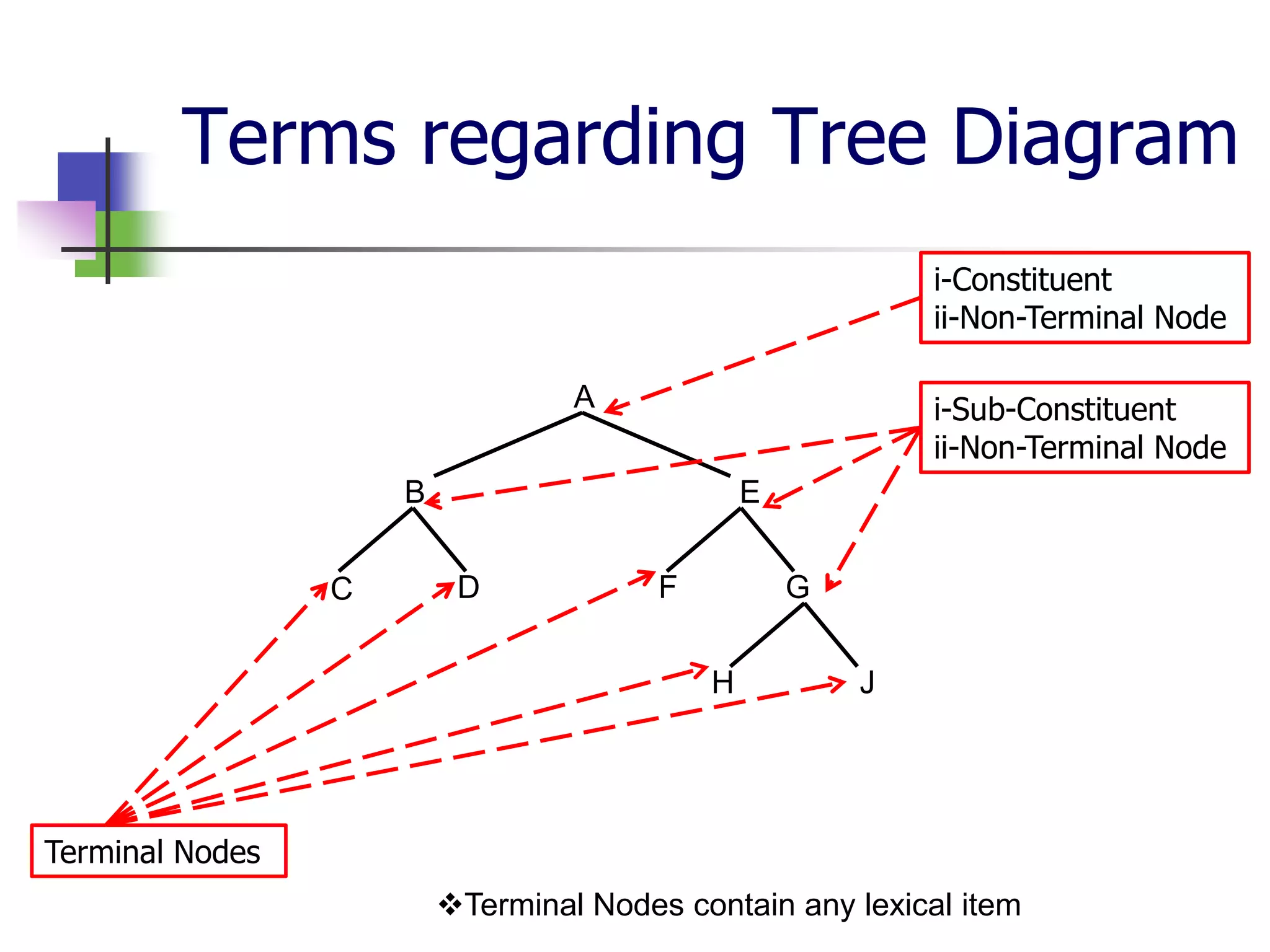
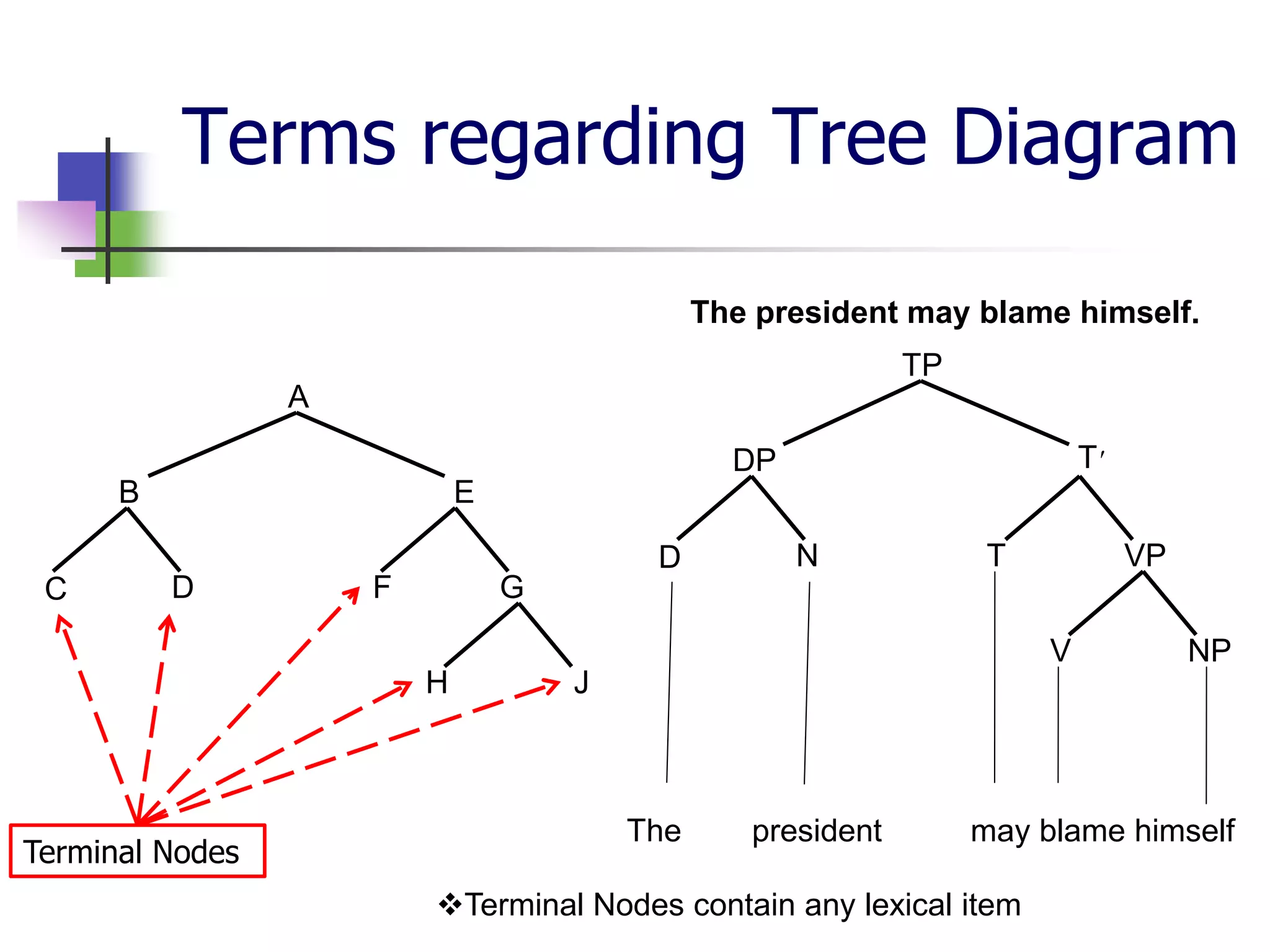
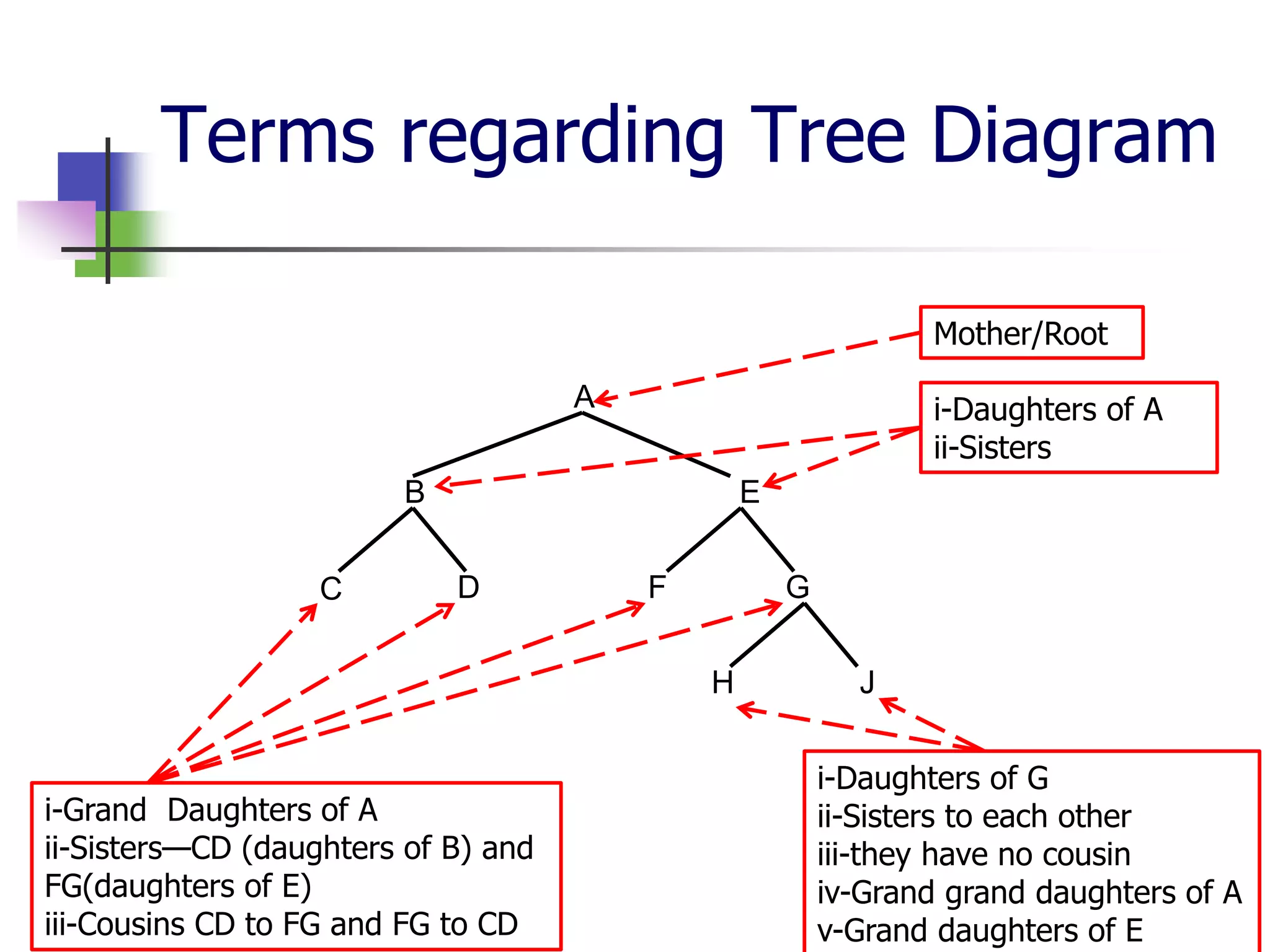
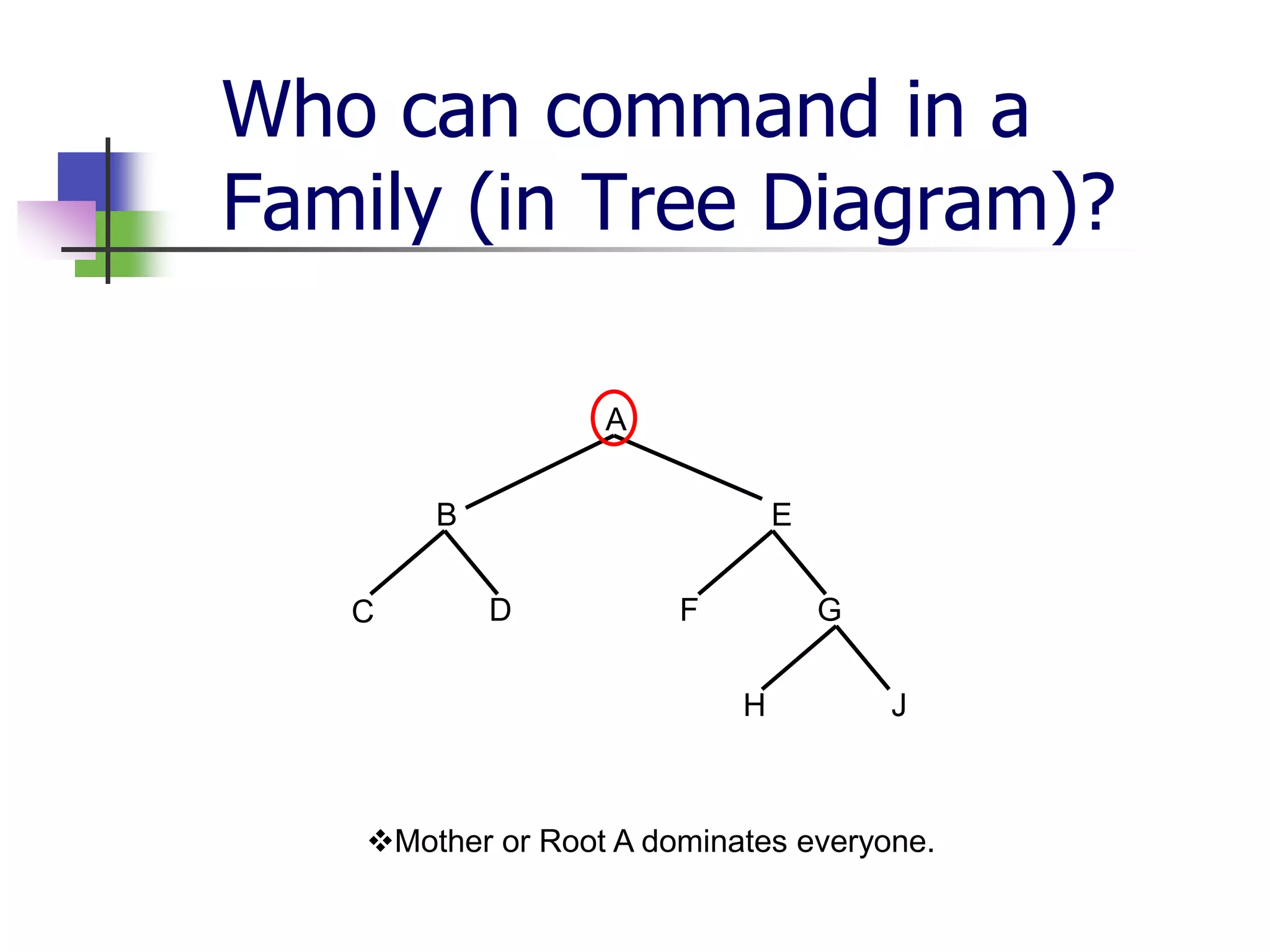
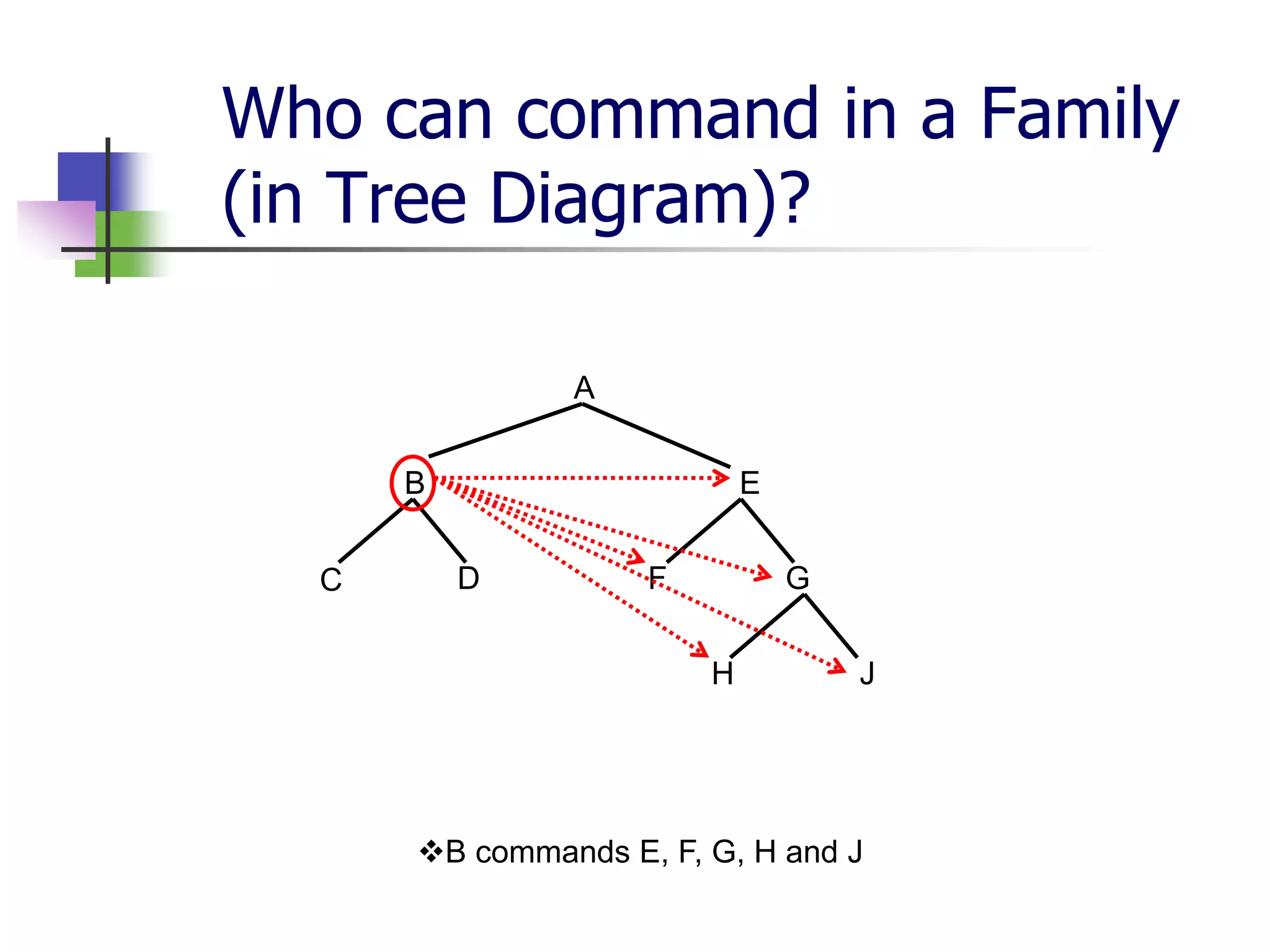
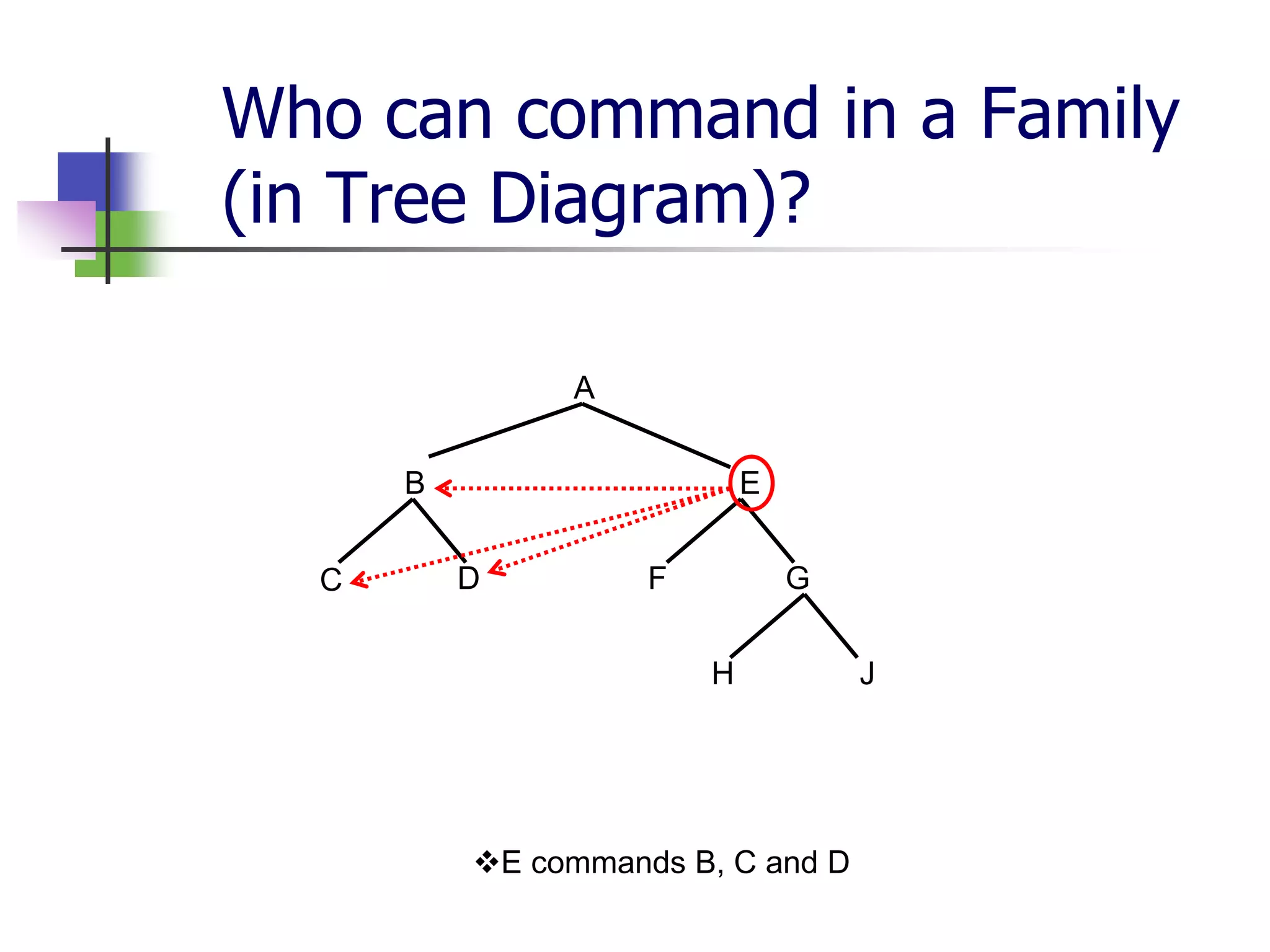
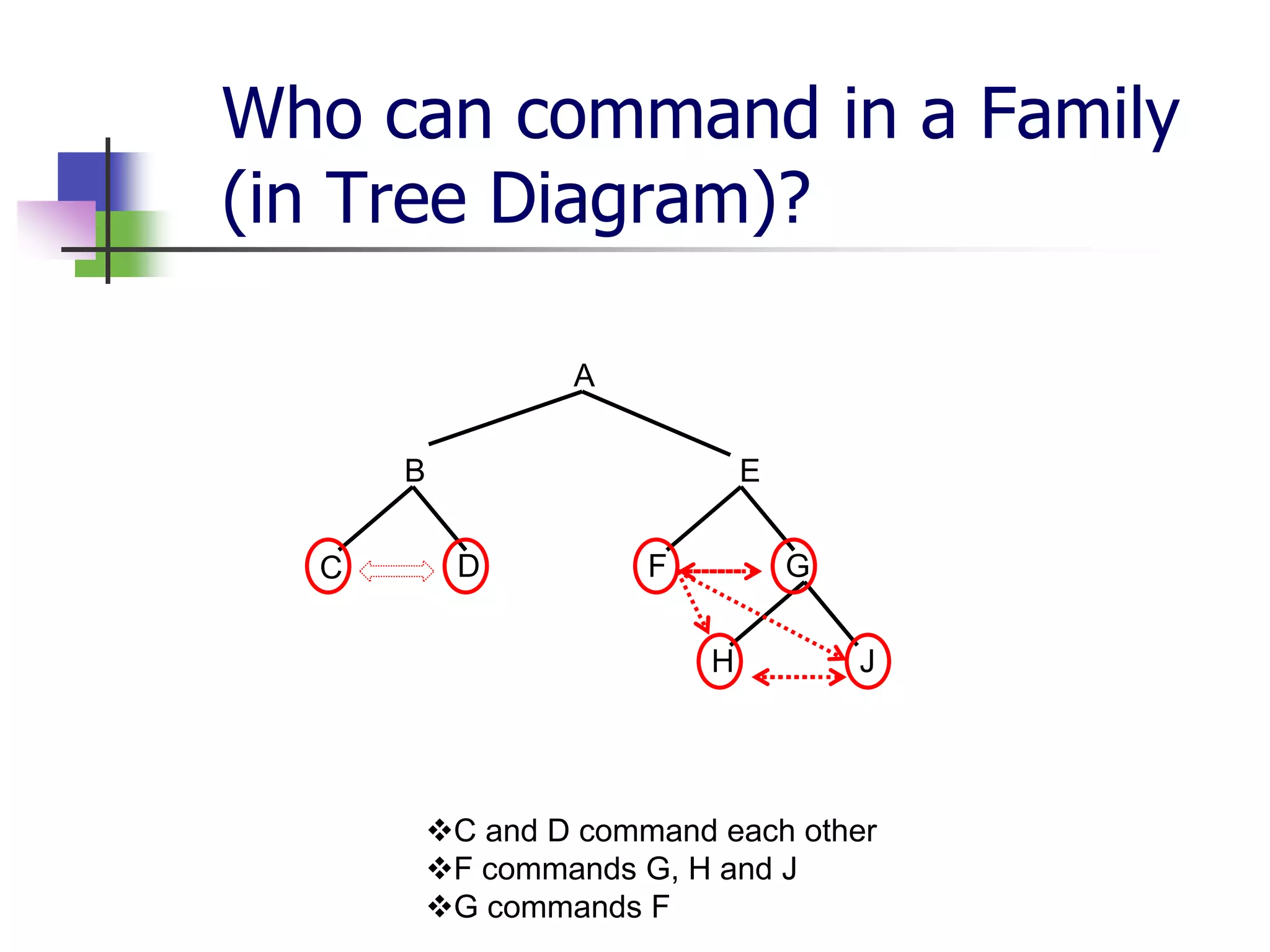
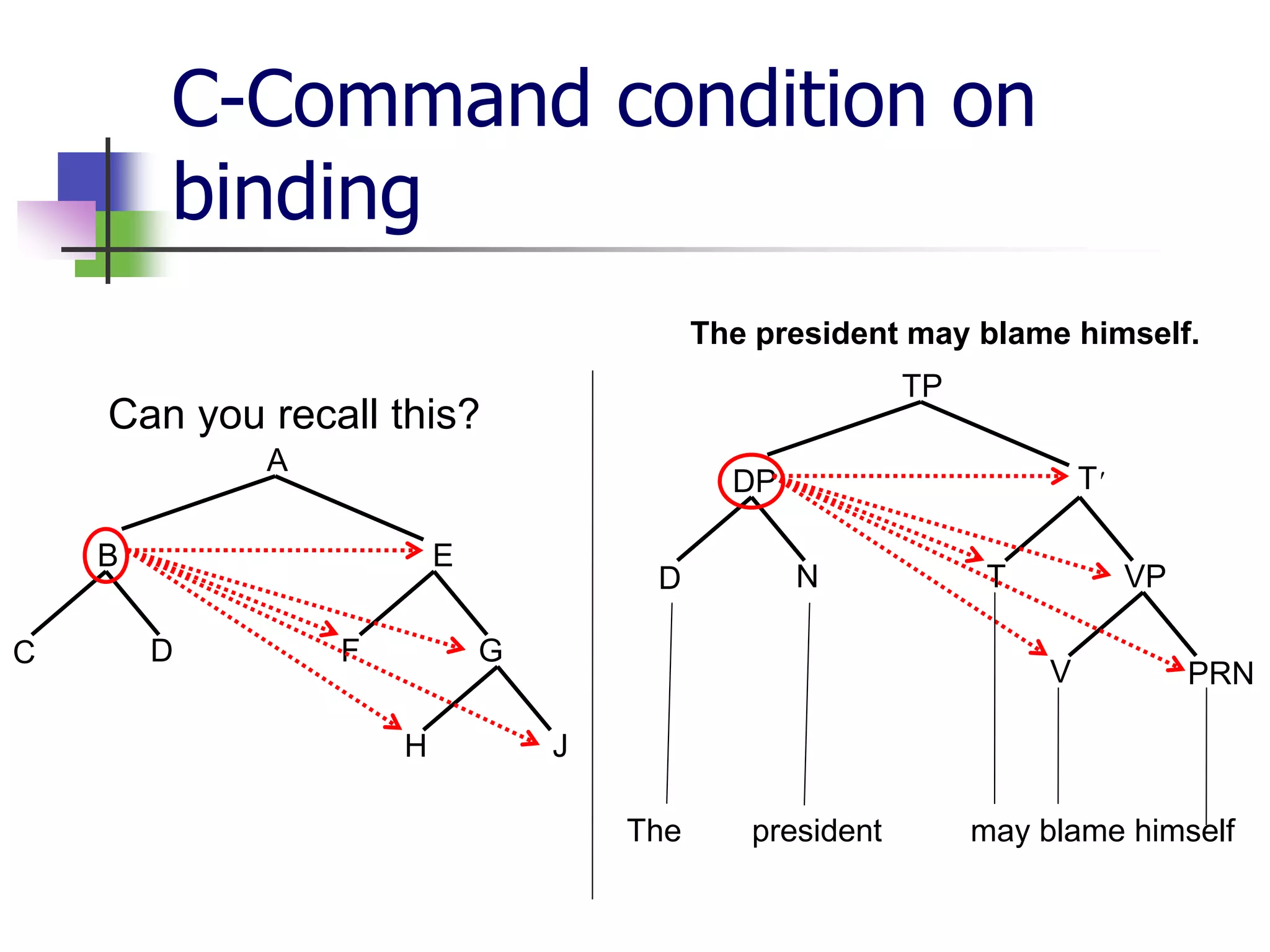
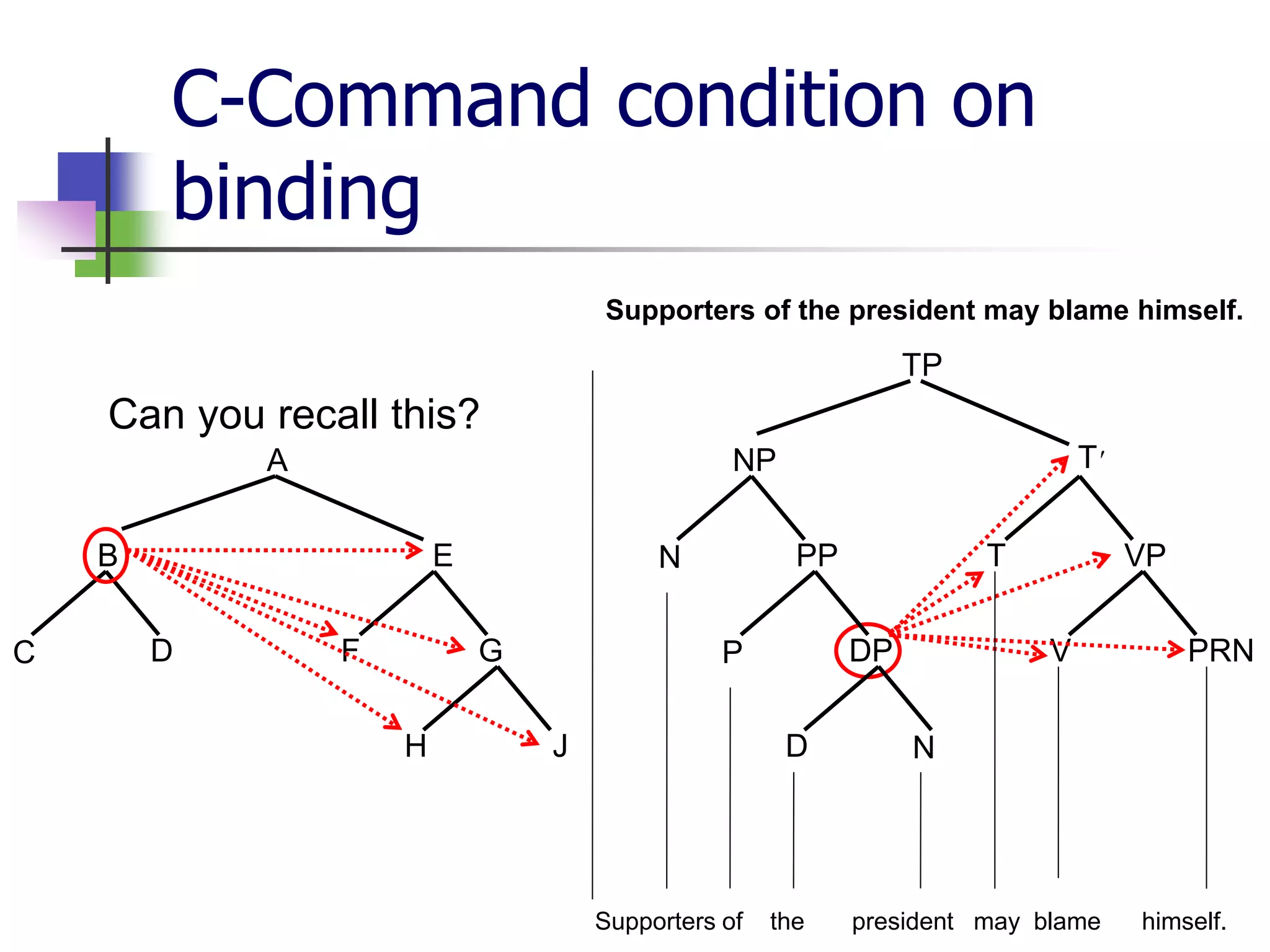
The document covers syntactic relations in linguistics, focusing on the functional relationships between constituents in phrases and sentences. It explains tree diagrams as graphical representations of these relationships, detailing key terms related to tree structures. Additionally, it explores the concept of c-command and its significance in understanding anaphoric relationships in sentences.