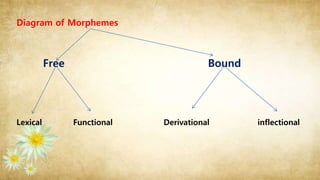
Morphology is the study of word structures and formation, focusing on morphemes. A morpheme is the smallest meaningful linguistic unit, such as prefixes, suffixes, and root words. There are two types of morphemes: free morphemes, which can stand alone as words, like nouns and verbs, and bound morphemes, or affixes, which must be attached to other morphemes. Bound morphemes include inflectional morphemes, which indicate grammatical functions without changing word class, and derivational morphemes, which sometimes change the word's part of speech. Morphology examines the rules of word formation in a given language.