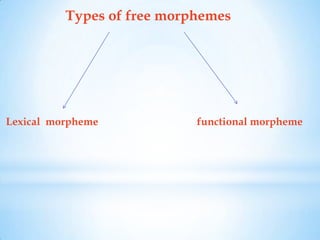
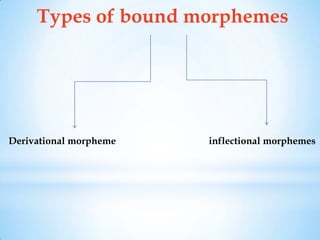
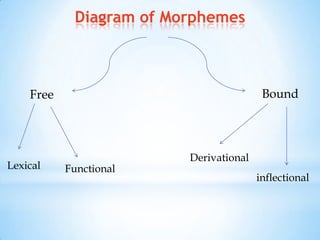
Morphology is the study of word structures and forms, specifically focusing on morphemes. It examines the ways that words are formed through processes like inflection, derivation, and compounding. A morpheme is the smallest meaningful linguistic unit that cannot be divided further. Morphemes can be free, able to stand alone as words, or bound, only occurring attached to other morphemes. Bound morphemes include derivational affixes, which can change a word's grammatical category, and inflectional affixes, which do not change category but indicate things like number, tense, or comparison. The analysis of morphology seeks to identify and describe the morphemes within words and their functions.