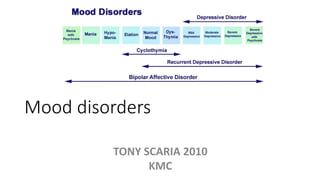
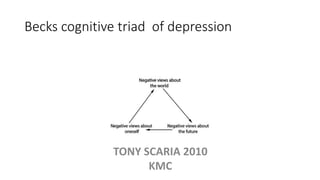
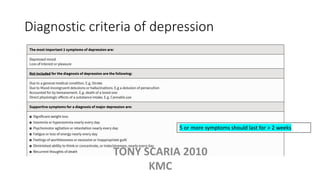
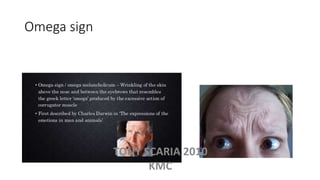
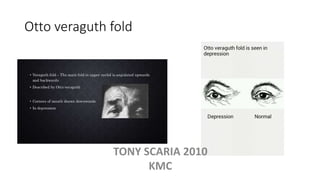
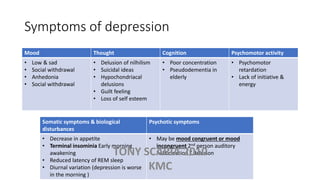
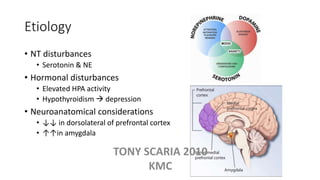
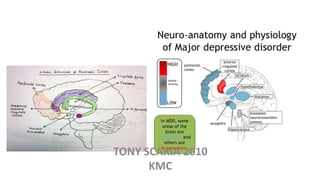
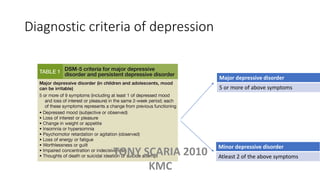
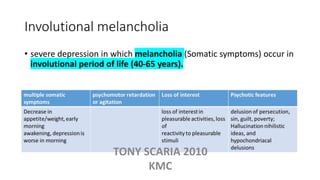
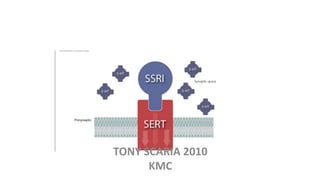
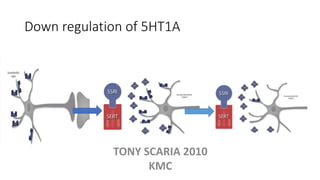
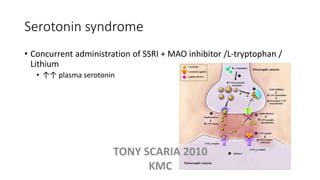
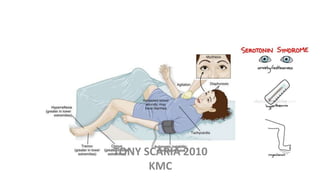
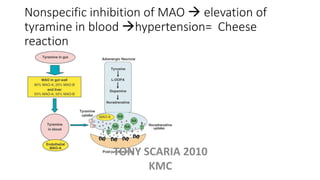
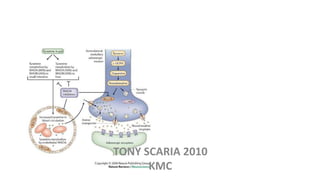
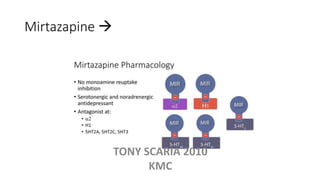
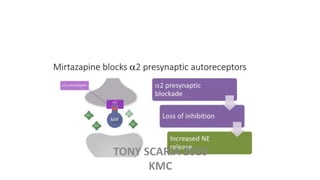
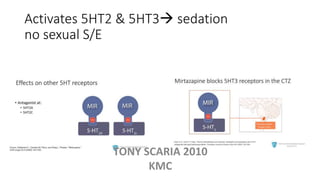
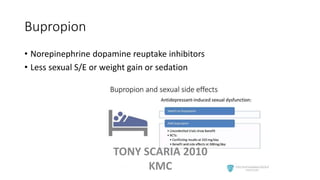
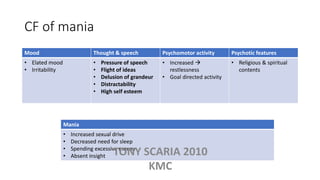
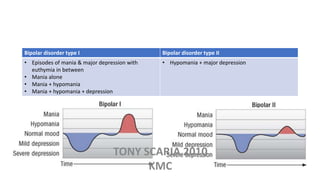
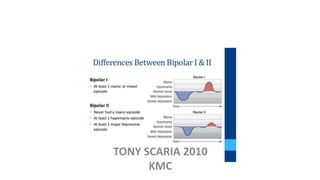
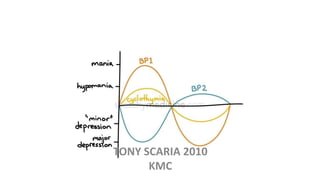
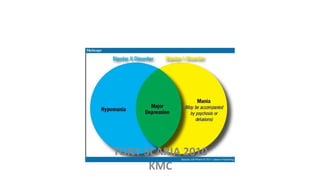
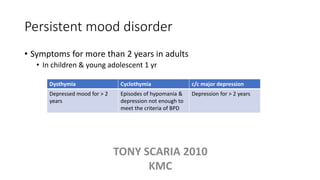
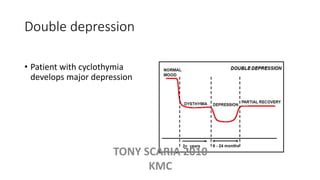
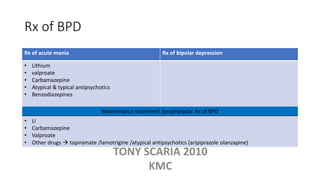
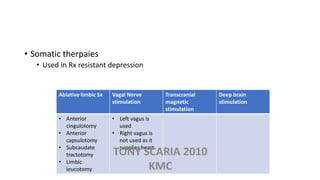
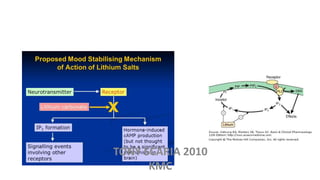
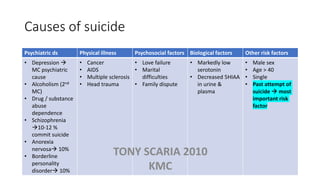
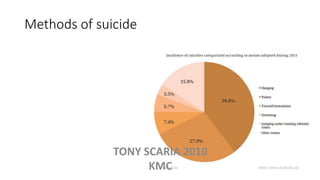
The document provides an overview of mood disorders, focusing on major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder, including their symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and treatment options. It details types of depression, including atypical and agitated depression, as well as pharmacotherapy approaches such as SSRIs, SNRIs, and mood stabilizers like lithium. The content also addresses suicide risk factors associated with mood disorders, emphasizing the significance of early diagnosis and treatment.