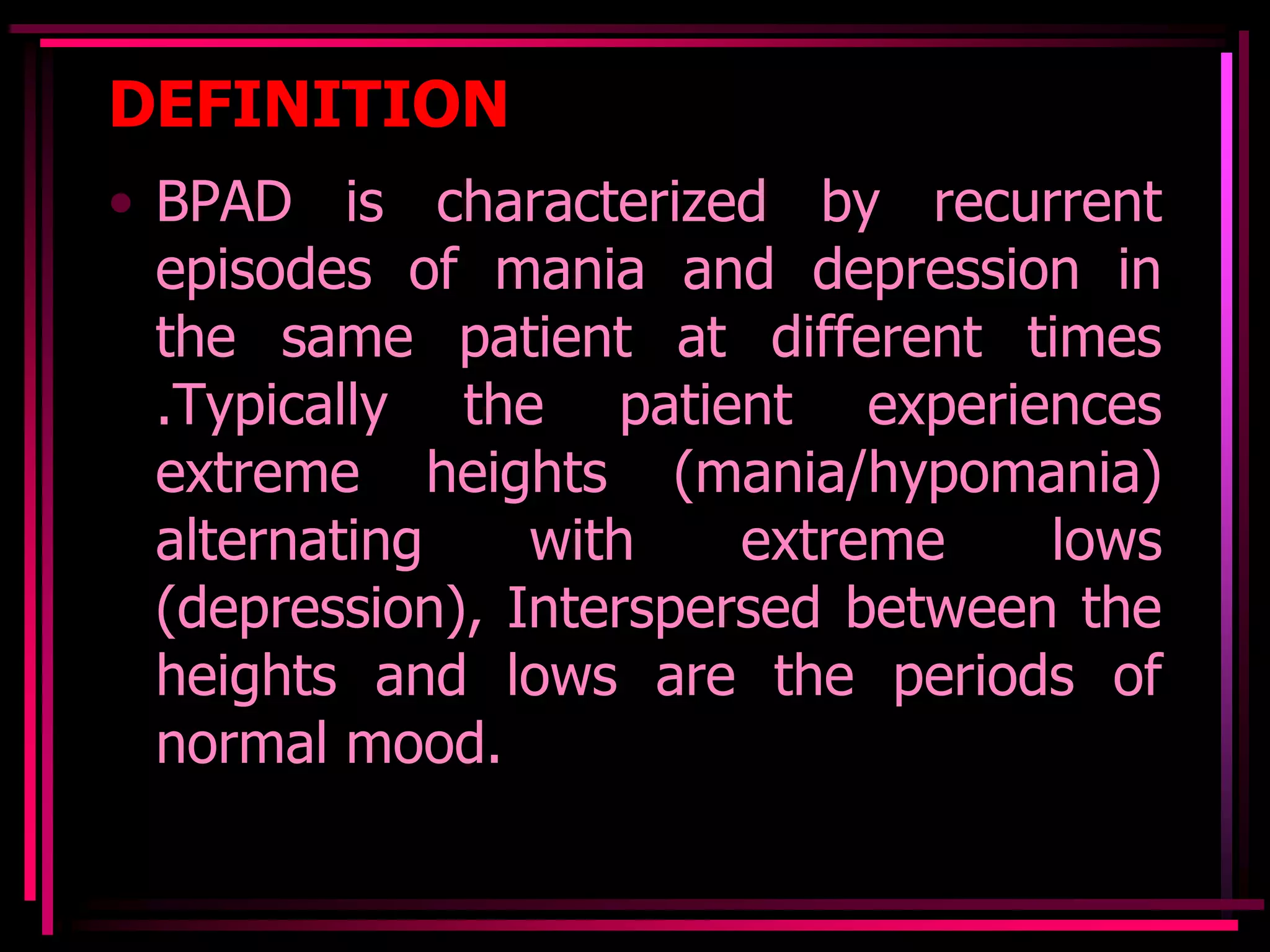
Bipolar disorder is characterized by mood swings between periods of profound depression and extreme euphoria or mania, with normal mood periods in between. It involves recurrent episodes of mania and depression in the same patient at different times, typically with extreme highs and lows. The disorder is classified based on current mood episode and presence of psychotic symptoms. Both biological and psychosocial factors are thought to play a role in its etiology. Treatment involves medication and nursing management focuses on safety, stabilization of mood, and prevention of relapse.