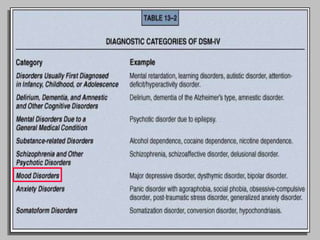
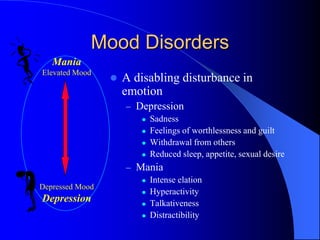
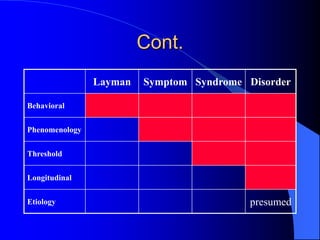
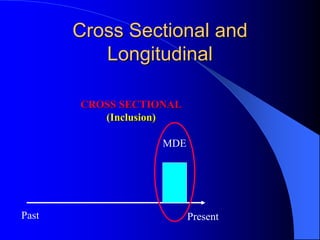
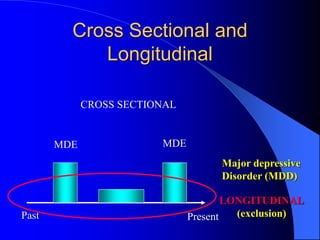
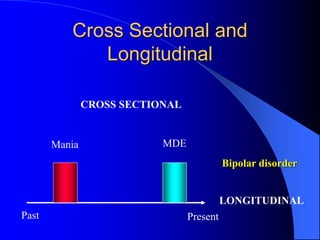
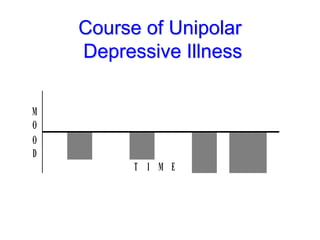
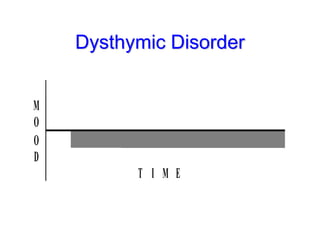
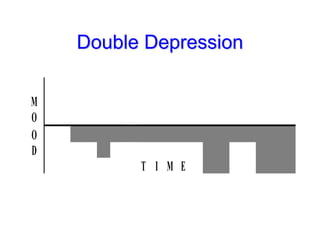
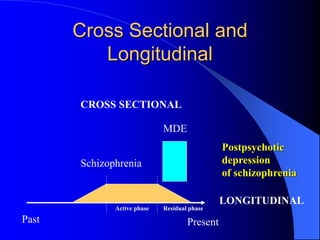
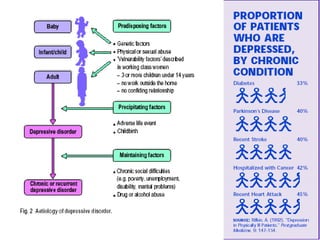
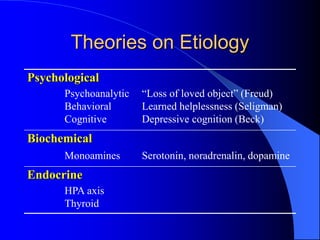
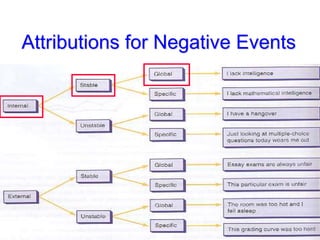
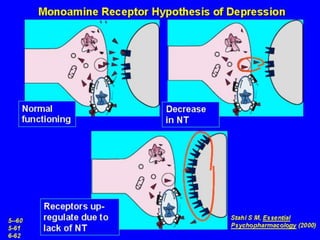
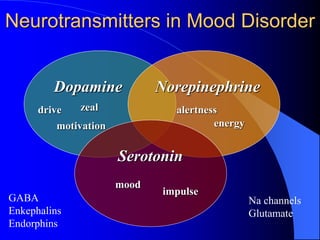
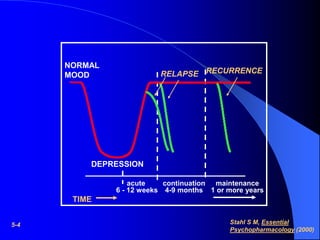
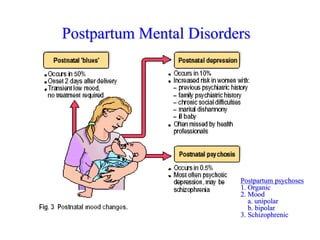
This document discusses depression, including its definition as a layman term, symptom, syndrome, or disorder. It describes the core symptoms of depression and different types including melancholic depression. The continuum of depression is presented, distinguishing depression from normal sadness. Major depressive disorder and dysthymic disorder are explained according to DSM-IV criteria. Theories on the etiology and risk factors for depression are mentioned. A case scenario of postpartum depression with psychotic features is provided and analyzed in terms of diagnosis, etiology, problems, and treatment approach.